Project function
- Analysis of complex headers of merged cells at any level
- Automatic conversion to target-level data structures
- Automatically generate antdv-based table column configuration data columns and dataSource for the data source. Reproduce the Excel effect on the page side.
Online example
- Step 0: If you need a quick test, you can click the sample button at the top to quickly fill in the test data and automatically download the corresponding Excel file. Click to upload the Excel file to reproduce the entire usage process
Step 1: Enter the mapping relationship between "Excel header structure string" and "target data structure key"
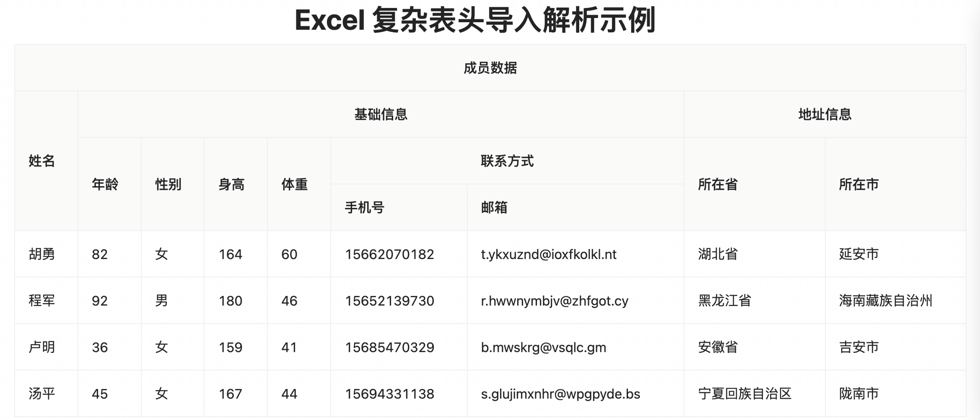
- "key" is the Excel header, the hierarchical relationship of each column. For example, "Basic Information. Age" corresponds to the relationship in the second column of the Excel table. The first level is "Basic Information" and the second level is "Age".
- "value" is the hierarchical relationship of the target data structure to be transformed. "baseInfo.age" means to convert the data in the second column of the Excel table into the property .baseInfo.age in the target object.
- [Special attention 1] The mapping relationship of "key":"value" has no order requirements, and there is no need to sort the data in each column of the Excel table.
- [Special attention 2] There are no mandatory constraints and requirements between the hierarchical mapping relationship of the Excel table and the hierarchical mapping relationship of the target object. For example, "mobile phone number" in Excel has only one layer of structure, but it can be completely transformed into the second-level structure of "contact.phone" in the target object. vice versa.
Step 2: Click on the right and upload the corresponding Excel file to complete the Excel analysis.
Introduction to the parsed page
The top is a reproduction of the antdv-based table component. Reproduce the effect of merging cells in an Excel table. The columns configuration used by the table component and the dataSource data are both returned by the parsing function. There is no need for secondary development and maintenance by developers.
At the bottom are the three data results returned by the parsing function after parsing. respectively
- The configuration item of the parsed antdv columns table column is directly passed to the columns property of the table component for use.
- The parsed antdv dataSource table data source is directly passed to the data-source attribute of the table component for use.
- An array of parsed target data structures. That is, according to the mapping table set in step 1, the data of each cell in Excel is converted into the target data structure. In general, this data structure is the data structure passed to the backend.
background, what problem to solve
- When directly using the XLSX.utils.sheet_to_json function of SheetJS for excel data conversion, it only supports Excel table data parsing with a row header (only the first row of the Excel content is recognized as the header), and cannot recognize Excel whose headers have merged cells data analysis
- The JSON data converted by sheet_to_json is an object whose key is Chinese, which does not conform to programming habits. Developers need to manually convert the Chinese and English keys of the data into the target data structure by themselves.
- Organization and reproduction of excel headers. When uploading an Excel table, it is usually necessary to display the content of the table on the front end, so that users need data reproduction and confirmation. This process requires developers to manually organize and complete.
- The principle of least knowledge, provides minimal demo examples, no scaffolding, and no need to install npm dependencies. Pure html + js files. Quickly test code feasibility. Change and test for secondary development.
How to use the specific function
- The example follows the principle of least knowledge. The core.js file in the project is the file where the conversion function is located. There are less than 200 lines of code in it. You can directly paste and copy it into the desired project.
- The example directly uses the way the script file is imported as a whole. Therefore, when migrating to an npm-based project, you need to change the usage of the 'XLSX.utils' global variable in core.js to the usage of
import { utils } from 'xlsx'.
- If this project really helps small partners, if they have needs, they can raise issues in github. If necessary, they will supplement the version based on npm and the version with ts type constraints.
The transformation function runs the logic
Get all cell data in Excel
- Borrow the 'encode_cell' method and 'format_cell' method of SheetJS to traverse to get the data of each cell in each sheet.
/**
* 获取所有单元格数据
* @param sheet sheet 对象
* @returns 该 sheet 所有单元格数据
*/
function getSheetCells(sheet) {
if (!sheet || !sheet['!ref']) {
return []
}
const range = XLSX.utils.decode_range(sheet['!ref'])
let allCells = []
for (let rowIndex = range.s.r; rowIndex <= range.e.r; ++rowIndex) {
let newRow = []
allCells.push(newRow)
for (let colIndex = range.s.c; colIndex <= range.e.c; ++colIndex) {
const cell = sheet[XLSX.utils.encode_cell({
c: colIndex,
r: rowIndex
})]
let cellContent = ''
if (cell && cell.t) {
cellContent = XLSX.utils.format_cell(cell)
}
newRow.push(cellContent)
}
}
return allCells
}According to the map mapping table, get the number of Excel header rows
- Traverse each Chinese key in the map, split the level according to the 'dot' keyword, and find the highest level of Excel. To get the number of rows in the Excel header. Distinguish which rows are headers and which rows are data.
// 获取菜单项在 Excel 中所占行数
function getHeaderRowNum(textKeyMap) {
let maxLevel = 1 // 最高层级
Object.keys(textKeyMap).forEach(textStr => {
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, textStr.split('.').length)
})
return maxLevel
}
const headerRowNum = getHeaderRowNum(textKeyMap)Through the container, recursively parse the Excel header configuration tree data structure
- Traverse through lastHeaderLevelColumns, keeping the latest container for each row in Excel.
- When the header traverses to a non-empty cell, add the configuration of this level to the container of the previous level.
- Thus recursively parsed to get the table header hierarchy array.
Use the index mapping table to link the Excel header object with the row index where Excel is located
- When recursively parsing the header hierarchy, record the current header data and column through columnIndexObjMap.
let headerColumns = [] // 收集 table 组件中,表头 columns 的对象数组结构
const lastHeaderLevelColumns = [] // 最近一个 columns,用于收集单元格子表头的内容
const textValueMaps = [] // 以中文字符串为 key 的对象数组,用于收集表格中的数据
const columnIndexObjMap = [] // 表的列索引,对应在对象中的位置,用于后续获取表格数据时,快速定位每一个单元格
for (let colIndex = 0; colIndex < headerRows[0].length; colIndex++) {
const headerCellList = headerRows.map(item => item[colIndex])
headerCellList.forEach((headerCell, headerCellIndex) => {
// 如果当前单元格没数据,这证明是合并后的单元格,跳过其处理
if (!headerCell) {
return
}
const tempColumn = { title: headerCell }
columnIndexObjMap[colIndex] = tempColumn // 通过 columnIndexObjMap 记录每一列数据,对应到那个对象中,实现一个映射表
// 如果表头数据第一轮就有值,这证明这是新起的一个表头项目,往 headerColumns 中,新加入一条数据
if (headerCellIndex === 0) {
headerColumns.push(tempColumn)
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex] = tempColumn // 记录当前层级,最新的一个表格容器,可能在下一列数据时合并单元格,下一个层级需要往该容器中添加数据
} else { // 不是第一列数据,这证明是子项目,需要加入到上一层表头的 children 项,作为其子项目
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children = lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children || []
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children.push(tempColumn)
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex] = tempColumn // 记录当前层级的容器索引,可能再下一层级中使用到
}
})
}Using this index table, traverse each row of the Excel data table, and quickly generate the data structure of each row of Excel
- Use columnIndexObjMap to traverse each row of the Excel data table, insert the value into the headerColumns configuration, and set it to a specific row, corresponding to the column data.
- Generate a copy of the object from headerColumns via Object.create.
// 将以数组形式记录的对象信息,转化为正常的对象结构
function transformListToObj(listObjs) {
const resultObj = {}
listObjs.forEach(item => {
if (item.value) {
resultObj[item.title] = item.value
return
}
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
resultObj[item.title] = transformListToObj(item.children)
}
})
return resultObj
}
// 以 headerColumns 为对象结构模板,遍历 excel 表数据中的所有数据,并利用 columnIndexObjMap 的映射,快速填充每一项数据
dataRows.forEach(dataRow => {
dataRow.forEach((value, index) => {
columnIndexObjMap[index].value = value
})
const titleObj = Object.create(headerColumns) // columnIndexObjMap 的指针索引,仅指向 headerColumns,以 headerColumns 为数据模板,复制一份数据,获得数据填充后的效果对象
textValueMaps.push(transformListToObj(titleObj)) // 将 listObj 对象转化化普通的对象
})- Parse the JSON data structure with key map mapping to generate the target data structure
/**
* 将以点拼接的扁平字符串对象,解析为具有深度的对象
* @param dotStrObj 点拼接的扁平化字符串对象
* @returns 具有深度的对象
*/
function parseDotStrObjToObj(dotStrObj) {
const resultObj = {}
Object.keys(dotStrObj).forEach(key => {
let keys = key.split('.')
keys.reduce((resultObj, curValue, currentIndex) => {
resultObj[curValue] = currentIndex === keys.length - 1 ? dotStrObj[key] : resultObj[curValue] || {}
return resultObj[curValue]
}, resultObj)
})
return resultObj
}
/**
* 将具有深度的对象扁平化,变成以点拼接的扁平字符串对象
* @param targetObj 具有深度的对象
* @returns 扁平化后,由点操作符拼接的对象
*/
function transformObjToDotStrObj(targetObj) {
const resultObj = {}
function transform(currentObj, preKeys) {
Object.keys(currentObj).forEach(key => {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(currentObj[key]) !== '[object Object]') {
resultObj[[...preKeys, key].join('.')] = currentObj[key]
} else {
transform(currentObj[key], [...preKeys, key])
}
})
}
transform(targetObj, [])
return resultObj
}
// 将以中文为 key 的对象,通过 textKeyMap 映射,找到对应的 key,转化为以 key 对键的对象,转化为后端对应的 json 对象
function transformTextToKey(textDataList, textKeyMap) {
const textDotStrDataList = textDataList.map(obj => transformObjToDotStrObj(obj))
let textDotStrDataListStr = JSON.stringify(textDotStrDataList)
Object.keys(textKeyMap).forEach(text => {
const key = textKeyMap[text]
textDotStrDataListStr = textDotStrDataListStr.replaceAll(`"${text}"`, `"${key}"`) // 在这里,通过字符串的替换,实现表头数据层级结构,与实际对象将数据结构的转换
})
const keyDotStrDataList = JSON.parse(textDotStrDataListStr)
const keyDataList = keyDotStrDataList.map(keyDotStrData => parseDotStrObjToObj(keyDotStrData))
return keyDataList
}- Return to antdv the columns configuration used to reproduce the table, dataSource table data, and dataList backend JSON data
- The above source code is really not easy to understand and describe, if this project can really help the small partners, and the small partners are also interested in the source code. You can raise issues, and I will fill in the detailed explanation and diagram of the running logic later.
All core source code
/**
* 将以点拼接的扁平字符串对象,解析为具有深度的对象
* @param dotStrObj 点拼接的扁平化字符串对象
* @returns 具有深度的对象
*/
function parseDotStrObjToObj(dotStrObj) {
const resultObj = {}
Object.keys(dotStrObj).forEach(key => {
let keys = key.split('.')
keys.reduce((resultObj, curValue, currentIndex) => {
resultObj[curValue] = currentIndex === keys.length - 1 ? dotStrObj[key] : resultObj[curValue] || {}
return resultObj[curValue]
}, resultObj)
})
return resultObj
}
/**
* 将具有深度的对象扁平化,变成以点拼接的扁平字符串对象
* @param targetObj 具有深度的对象
* @returns 扁平化后,由点操作符拼接的对象
*/
function transformObjToDotStrObj(targetObj) {
const resultObj = {}
function transform(currentObj, preKeys) {
Object.keys(currentObj).forEach(key => {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(currentObj[key]) !== '[object Object]') {
resultObj[[...preKeys, key].join('.')] = currentObj[key]
} else {
transform(currentObj[key], [...preKeys, key])
}
})
}
transform(targetObj, [])
return resultObj
}
/**
* 获取所有单元格数据
* @param sheet sheet 对象
* @returns 该 sheet 所有单元格数据
*/
function getSheetCells(sheet) {
if (!sheet || !sheet['!ref']) {
return []
}
const range = XLSX.utils.decode_range(sheet['!ref'])
let allCells = []
for (let rowIndex = range.s.r; rowIndex <= range.e.r; ++rowIndex) {
let newRow = []
allCells.push(newRow)
for (let colIndex = range.s.c; colIndex <= range.e.c; ++colIndex) {
const cell = sheet[XLSX.utils.encode_cell({
c: colIndex,
r: rowIndex
})]
let cellContent = ''
if (cell && cell.t) {
cellContent = XLSX.utils.format_cell(cell)
}
newRow.push(cellContent)
}
}
return allCells
}
/**
* 获取表头任意层级单元格合并后的表格内容解析
* @param sheet 一个 sheet 中所有单元格内容
* @param textKeyMap 表头中文与对应英文 key 之间的映射表
* @returns antdv 中的表格 column,dataSource,以及转化后的,直接传输给后端的 json 对象数组
*/
function getSheetHeaderAndData(sheet, textKeyMap) {
// 获取菜单项在 Excel 中所占行数
function getHeaderRowNum(textKeyMap) {
let maxLevel = 1 // 最高层级
Object.keys(textKeyMap).forEach(textStr => {
maxLevel = Math.max(maxLevel, textStr.split('.').length)
})
return maxLevel
}
const headerRowNum = getHeaderRowNum(textKeyMap)
const headerRows = sheet.slice(0, headerRowNum)
const dataRows = sheet.slice(headerRowNum)
let headerColumns = [] // 收集 table 组件中,表头 columns 的对象数组结构
const lastHeaderLevelColumns = [] // 最近一个 columns,用于收集单元格子表头的内容
const textValueMaps = [] // 以中文字符串为 key 的对象数组,用于收集表格中的数据
const columnIndexObjMap = [] // 表的列索引,对应在对象中的位置,用于后续获取表格数据时,快速定位每一个单元格
for (let colIndex = 0; colIndex < headerRows[0].length; colIndex++) {
const headerCellList = headerRows.map(item => item[colIndex])
// eslint-disable-next-line no-loop-func
headerCellList.forEach((headerCell, headerCellIndex) => {
// 如果当前单元格没数据,这证明是合并后的单元格,跳过其处理
if (!headerCell) {
return
}
const tempColumn = { title: headerCell }
columnIndexObjMap[colIndex] = tempColumn // 通过 columnIndexObjMap 记录每一列数据,对应到那个对象中,实现一个映射表
// 如果表头数据第一轮就有值,这证明这是新起的一个表头项目,往 headerColumns 中,新加入一条数据
if (headerCellIndex === 0) {
headerColumns.push(tempColumn)
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex] = tempColumn // 记录当前层级,最新的一个表格容器,可能在下一列数据时合并单元格,下一个层级需要往该容器中添加数据
} else { // 不是第一列数据,这证明是子项目,需要加入到上一层表头的 children 项,作为其子项目
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children = lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children || []
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex - 1].children.push(tempColumn)
lastHeaderLevelColumns[headerCellIndex] = tempColumn // 记录当前层级的容器索引,可能再下一层级中使用到
}
})
}
// 运行以上代码,得到 headerColumns,以及 headerColumns 中,每个对象对应在表格中的哪一行索引
// 将以数组形式记录的对象信息,转化为正常的对象结构
function transformListToObj(listObjs) {
const resultObj = {}
listObjs.forEach(item => {
if (item.value) {
resultObj[item.title] = item.value
return
}
if (item.children && item.children.length > 0) {
resultObj[item.title] = transformListToObj(item.children)
}
})
return resultObj
}
// 以 headerColumns 为对象结构模板,遍历 excel 表数据中的所有数据,并利用 columnIndexObjMap 的映射,快速填充每一项数据
dataRows.forEach(dataRow => {
dataRow.forEach((value, index) => {
columnIndexObjMap[index].value = value
})
const titleObj = Object.create(headerColumns) // columnIndexObjMap 的指针索引,仅指向 headerColumns,以 headerColumns 为数据模板,复制一份数据,获得数据填充后的效果对象
textValueMaps.push(transformListToObj(titleObj)) // 将 listObj 对象转化化普通的对象
})
// 根据表头的 title 值,从 textKeyMap 中寻找映射关系,设置 headerColumn 对应的 dataIndex
function setHeaderColumnDataIndex(headerColumns, preTitle) {
headerColumns.forEach(headerObj => {
if (headerObj.children) {
headerObj.children = setHeaderColumnDataIndex(headerObj.children, [...preTitle, headerObj.title])
} else {
const titleStr = [...preTitle, headerObj.title].join('.')
headerObj.dataIndex = textKeyMap[titleStr]
}
})
return headerColumns
}
// 将以中文为 key 的对象,通过 textKeyMap 映射,找到对应的 key,转化为以 key 对键的对象,转化为后端对应的 json 对象
function transformTextToKey(textDataList, textKeyMap) {
const textDotStrDataList = textDataList.map(obj => transformObjToDotStrObj(obj))
let textDotStrDataListStr = JSON.stringify(textDotStrDataList)
Object.keys(textKeyMap).forEach(text => {
const key = textKeyMap[text]
textDotStrDataListStr = textDotStrDataListStr.replaceAll(`"${text}"`, `"${key}"`) // 在这里,通过字符串的替换,实现表头数据层级结构,与实际对象将数据结构的转换
})
const keyDotStrDataList = JSON.parse(textDotStrDataListStr)
const keyDataList = keyDotStrDataList.map(keyDotStrData => parseDotStrObjToObj(keyDotStrData))
return keyDataList
}
headerColumns = setHeaderColumnDataIndex(headerColumns, [])
const dataList = transformTextToKey(textValueMaps, textKeyMap)
const dataSource = dataList.map(row => transformObjToDotStrObj(row)) // 将 JSON 对象转化为 “点.” 拼接的扁平对象,使得数据与 headerColumn 中的 dataIndex 相对应。实现 table 的数据填充
return {
headerColumns,
dataList,
dataSourceList: dataSource,
}
}






















**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。