Hello everyone, I’m Lin Yiyi. This is an article on the principle of browser caching and local storage. I will continue to publish articles on the principle of browsers in the future.
1. Browser cache
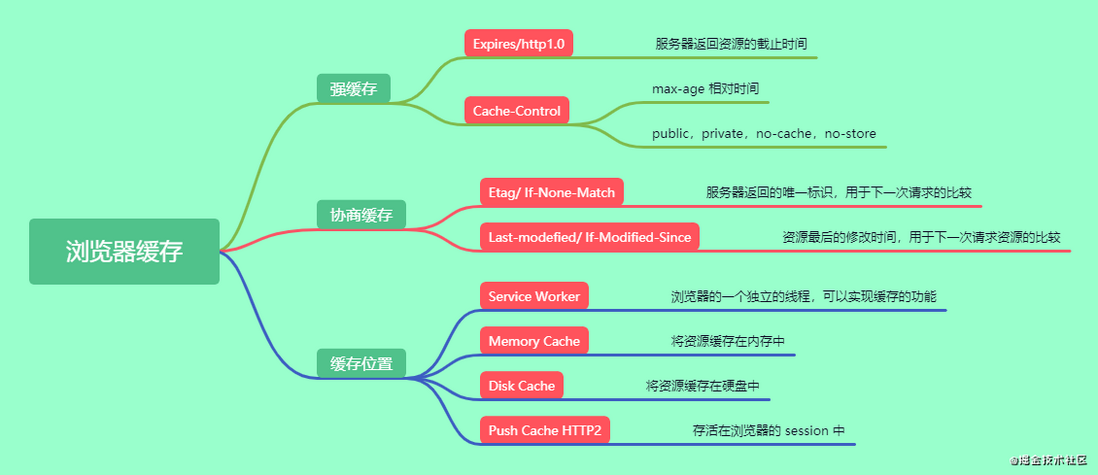
mind Mapping
The so-called browser cache isHTTPresources locally after requesting network resources through 060c86c227f543.back and forward buttons on the page is to use the browser's cache.
- The browser cache is divided into two types:
strong cache andnegotiation cache. - The location of browser cache resources is placed in four places
Service Worker, Memory Cache, Disk Cache, Push Cache.Service Workerhighest priority toPush Cache.
Browser request resource process
Local first, then server (strong cache first and then negotiate cache)
- When the browser requests a resource, it will first determine whether the
headerlocal cache resource has a strong cache hit. If it hits the strong cache, it will directly request the local resource without sending a request to the server. If the strong cache is not hit or the strong cache fails, it will send
HTTPrequest the server. This process uses thenegotiation cacheSimply put, browser cache requests are divided into two types
HTTP
Strong cache
The so-called strong cache is that we do not send a HTTP request, but directly obtain resources from the local cache. After success, the status code 200 is returned.Expires/http1.0andCache-Control/http1.1according to theheadersfield of the response header to perform the process of strong caching.If there is no or invalid strong cache, the browser will send request resources to the server.
Expires
The cache field of a page in http1.0 is a Green Time. This time is the time when the browser's strong cache resource expires
Expires: Wed, 22 Nov 2021 08:41:00 GMTThe above cached resource will
at 160c86c227f87b at 8:41 on November 22, 2021.- Disadvantages: the browser is to determine whether the resource expired according to local time, local time but can be modified, so
HTTP1.1whenExpireswas abandoned.
Cache-Control
The cache field of the page in HTTP1.1. If both Expires and Cache-Control exist, then Cache-Control a higher priority.Cache-Controlattribute value, many of them attributemax-agesaid opposing a cache timeCache-Control: max-age = 3600Indicates that the local cache can be used directly within one hour from the last request. No need to request again.
- The attribute
publicindicates that it can be cached by the browser or proxy server. - The attribute
privatemeans that it can only be cached by the browser. - The attribute
no-cacheneeds to send a request to the server to confirm whether it is cached, which needs to use the negotiation cache. - The attribute
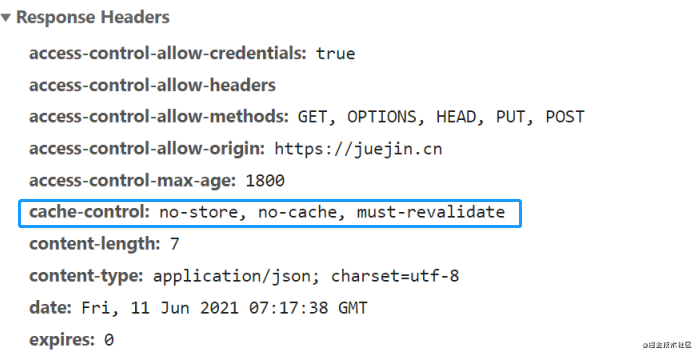
no-storeindicates that caching is forbidden, and the server needs to be requested every time.
Negotiation cache
The so-called negotiation cache means that the browser carries the cached identification tag to send a request to the server, and the server has the carried identifier to determine whether to use the cache. This process is the negotiation cache.- There are two types of results returned by the browser requesting the server. One type is
304, which means that the resources of the server have not been updated and the local cache of the browser can be used directly. The other returns200, indicating that the server resources are updated and the new resources are returned to the browser. - The cache identifier
tagdivided into two types:Last-Modified/If-Modified-SinceandETag/If-None-Match.Etag / If-None-Matchis higher than that ofLast-Modified.
Etag / If-None-Match
Etag is a unique identifier returned by the server when responding to a request. This identification can only be generated by the server.
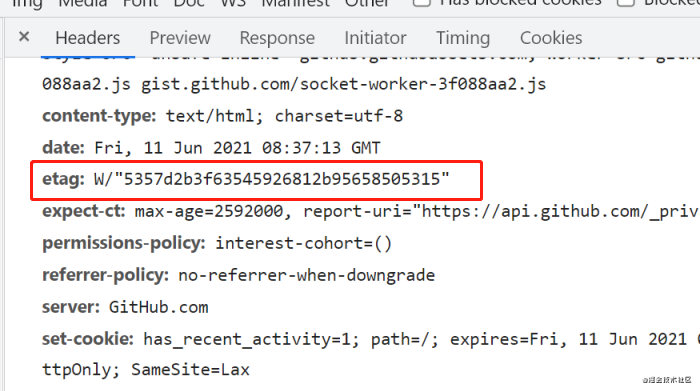
etag: W/"5357d2b3f63545926812b95658505315"- If-None-Match, when the browser requests the server again, it will carry the
Etagidentification value and send it to the server. The server will compare this value with theEtagin the server. If the two values are equal, it will return304. If they are not equal, it will return200New resources are returned.
Last-Modified/If-Modified-Since
Last-Modified refers to the time when the requested resource file was last modified on the server.
Last-Modified: Wed, 23 Nov 2021 08:41:00 GMT- If-Modified-Since, when the browser requests the resource again, it will
Last-Modifiedreturned last time to the server. The server compares the last modified time with the current last modified time. If it is greater thanIf-Modified-Since, the server will return the new resource 200, otherwise it will return304.
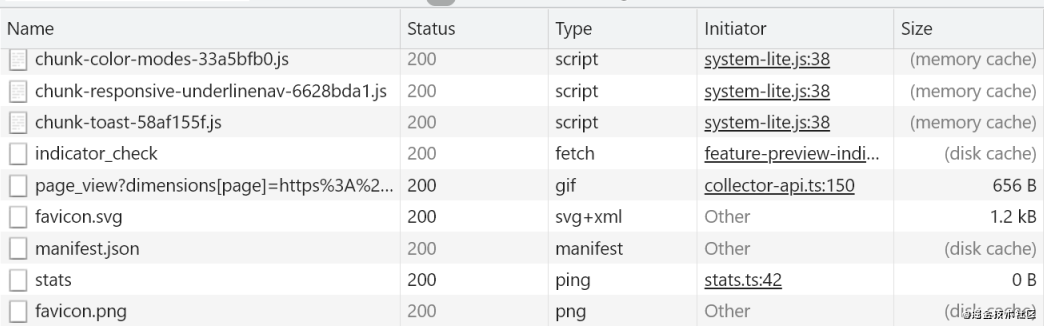
Cache location
The cache locationService Worker, Memory Cache, Disk Cache, Push Cachementioned above.Service Workerhighest priority toPush Cache
- Service Worker running in the browser's independent thread can realize the browser's caching function, and the transmission protocol needs to use
HTTPS. - Memory Cache is to cache resources in memory.
- Disk Cache is to cache resources in the disk
- Push Cache (Push Cache) is in HTTP/2, which survives in the session
session, and the survival time is very short.
Second, the browser's local cache
The browser's local cache is mainly divided into 5 types, localStorage, sessionStorage, cookie, WebSql, indexedDB .cookie
The cookie is generated by the server and saved to a local file in the browser. The front end canSet-Cookie, and the front end can set multipleSet-Cookie.
The cookie can be set to expire time or not, and it will become invalid after the browser is closed.
Set-Cookie: BDSVRTM=7; path=/ Set-Cookie: H_PS_PSSID=34130_34099_33969_31253_33848_33607_26350; path=/; domain=.baidu.com- cookie reason : It is used for
state storage, because http is stateless and cannot record data state, cookie can record data state. Such as user id, password, browsed pages, etc. - The advantages of cookie : 1. Remember the status of data, passwords, etc. 2. Make up for the statelessness of HTTP.
- The shortcomings of : 1. Capacity defect, can only store the
4kb; 2. Security issue, cookie is a text form that transmits information before the browser and server, and it is likely to be modified. 3. The requested cookie file is easily deleted. 4. High performance consumption, the cookie is closely following the domain name, any address under the domain name is modified to carry the cookie to the server. Cause performance waste.
localStorage
localStoragevalue in a similar way to cookies. They are all stored under the same domain name. LocalStorage can be stored for a long time without time limit. The value can be accessed throughlocalStorage.setItem()/getItem()
- localStorage Advantages : 1. Expanded the storage size of cookies, can store 5M size, different browsers; 2. Only stored in the browser will not communicate with the server, which solves the security issues and performance consumption issues of cookies.
- localStorage Disadvantages : 1. Need to manually delete the saved data; 2. Only support string type, JSON type needs to be converted
JSON.stringify() - localStorage usage scenario : Use localStorage to store some stable resources and base64 pictures, etc.
sessionStorage
sessionStorage is the same as localStorage, the only big difference is that sessionStorage is session-level storage
- The session-level
sessionStoragemeans that this storage disappears after the browser page is closed. - sessionStorage scenario : sessionStorage can be used to save some temporary data to prevent the data from disappearing after the page disappears, such as form filling and user browser records.
indexedDB
The non-relational database provided by the browser, indexedDB provides a large number of interfaces to provide query functions, and can also create queries.
- Store values in the form of key-value pairs, including js objects
- indexedDB is asynchronous, and storing data will not cause page freezes.
- indexedDB supports transactions. A transaction is a series of operations where an error occurs, and the database will fall back to the state before the transaction.
- Same-origin restrictions, databases from different sources cannot be accessed.
- There is no limit to storage space.
webSQL
Obsolete, aiming to use js statement to manipulate sql statement to complete the reading and writing of data.
reference
"Illustrated HTTP"

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。