Foreword: Some time ago, I started to land applications based on vue3, so I paid attention to some open source projects around vue3 in the community. I accidentally saw the open sourceFes.jssolution of theWeBankFinTechIn the design idea of this scheme, the characteristics of quick start, easy to use, and high expansibility caused me to further explore the project.
1. Early stage of new project
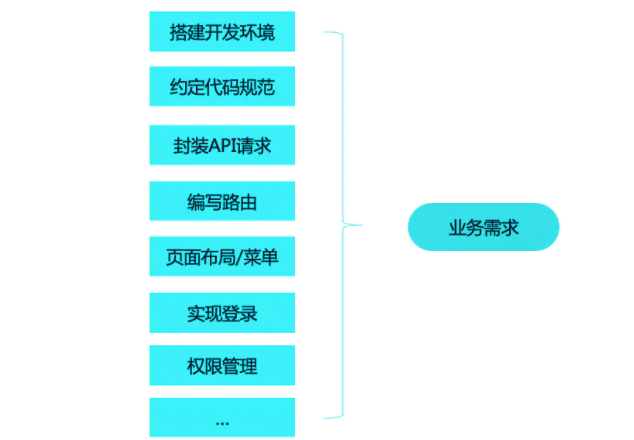
When we start the preparation of a new project (here specifically referring to mid- and back-end applications), project initialization often we may consider the following issues
- How to do authority management in a unified way?
- How to uniformly encapsulate the request library, such as based on Axios (unified handling of cancellation of repeated requests, request throttling, error exception handling, etc.)
- How to be embedded into the micro front-end system as a sub-application (assuming to be based on qiankun)
- How to share responsive data?
- How to manage configuration information?
1.1 You might do this
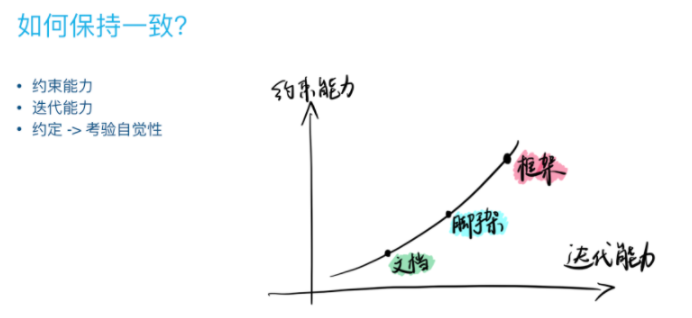
If every time we create a new project, we have to deal with the above problems manually, then it will be a repetitive operation, but also to ensure that the team is consistent, then we have to consider the constraint ability
Before seeing the Fes.js , my solution to the above problem is- Encapsulate by maintaining a public tool library, such as the secondary packaging of axios
- Develop a simple scaffold, integrate these things into a template, and then pull it through the command line
Generate templates directly through
vue-cliand then customize configuration modifications, etc., simply use documents, tools, scaffolding to empowerBut is there a better solution?
The picture is quoted from the article "Ant Front-end R&D Best Practices"
1.2 Other solutions-framework (plug-in)
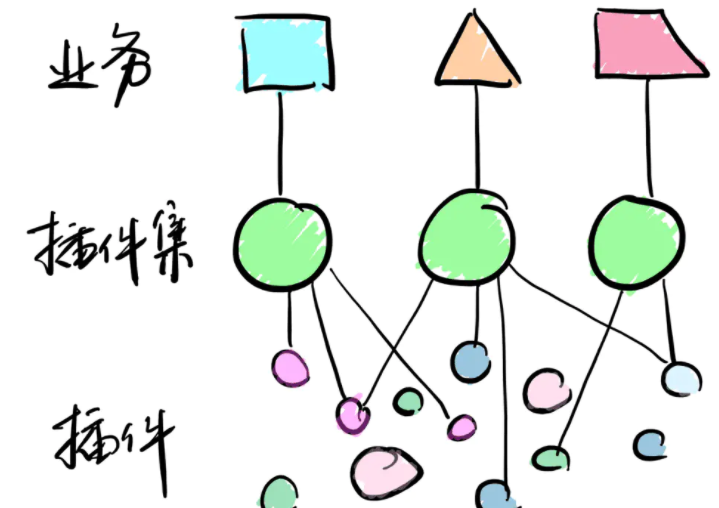
Children who learn react know that there is a plug-in front-end application framework UmiJS in the react community, which does not exist in the world of vue, and the Fes.js and we will share next are UmiJS in vue, Fes.js and many functions It is based on UmiJS. UmiJS has built-in routing, construction, deployment, testing, etc. It also supports plug-ins and plug-in sets to meet the hierarchical needs of functions and vertical domains.
In essence, it is for more convenient and faster development of middle and back-end applications. The core of the framework is the plug-in management. The built-in plug-ins provided encapsulate a large number of construction-related logic and have a rich plug-in ecology. The that needs to be processed in the business is solved by plug-ins, and users only need simple configuration or can be used according to the specification
You can even aggregate plug-ins into plug-in sets, similar to plugin and preset of babel, or rule and config of eslint. Meet the business of different occasions through plug-ins and plug-in sets
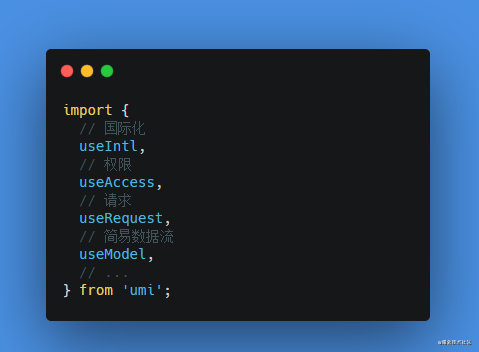
import from UmiJS the capabilities of 060d5b03eac5a2 through plug-ins, such as the picture below, is it very vue 3 the 060d5b03eac5a6 design Composition API
Further reading:
Some preliminary understanding of
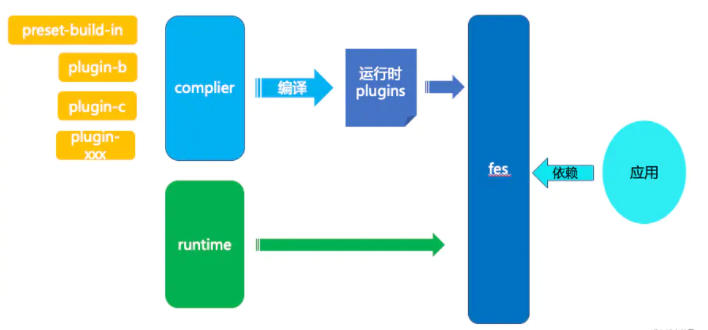
2. Fes.js
Official introduction: Fes.js is an easy-to-use front-end application solution. Fes.js 2.0 is based on Vue 3.0 and routing, and supports configuration routing and contract routing at the same time, and expands its functions. It matches a complete plug-in system covering the compile-time and runtime life cycle, and supports various function extensions and business requirements.
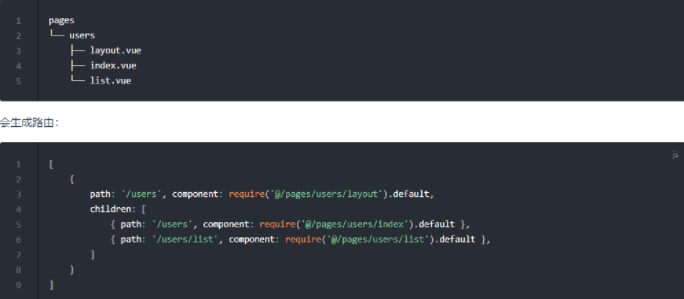
2.1 Support Conventional Routing
What is conventional routing? Conventional routing is also called file routing. It does not require handwriting configuration. The file system is routing. Now more and more frameworks support conventional routing, including UmiJS mentioned above, and SSR's nuxt etc., saving us manually Time to configure routing. For more routing configuration of fes, see routing document 2.2 Plug-in support
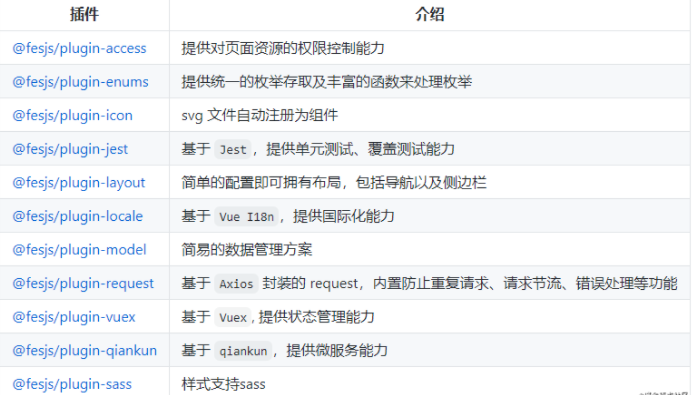
In essence, a plug-in is a npm package, which extends the functions of Fes.js through plug-ins. At present, Fes.js has many plug-ins open source. And the plugin can manage the compile time and runtime of the plugin document
Plug-in source code address link . fesjs also supports developer custom plug-ins, see plug-in development document
Student Binbin: So what does it mean to support compile time and runtime?
It can be understood like this: If it is the configuration at compile time, that is, when packaging, the corresponding code construction is completed according to the configuration, and the configuration at runtime is that when the code is executed in the browser, it will do the corresponding according to the read configuration Processing, if you are interested, you can understand the fesjs plug-in source code in depth, and learn how to process it according to compile time and runtime fes-plugin-access source link
2.3 How to use Fes.js
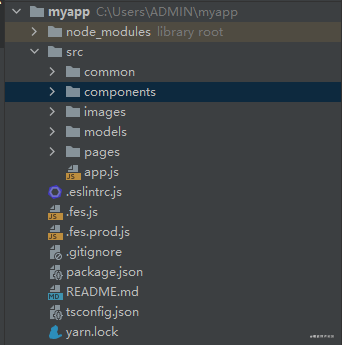
Fes.js provides a command line tool create-fes-app , which is used to create a project template directly after the global installation. The project structure is shown belowThen run npm run dev to open your path to fes, as shown in the figure below
2.4 Why choose Fes.js
Like vue-cli can only solve the basic problems of development, construction, and packaging in our projects, while Fes.js can directly solve most of the business scenarios of conventional middle and back-end applications, including the following
- Configurable layout: solve configuration problems such as layout, menu, navigation, etc., similar to low-code mechanism
- Authority control: realize complex authority management of the site through the built-in access plug-in
- Request library package: through the built-in request plug-in, built-in request anti-weight, request throttling, error handling and other functions
- Micro-front-end integration: Quickly integrate into the micro-front-end system through the built-in qiankun plug-in
Looking forward to more plug-ins that can empower mid- and back-end application business scenarios
3. Review vue 3
3.1 New features
Compared with vue2.0, the major changes of vue3.0 include the following
performance improvement: With the support of mainstream browsers fores6es modulebecomes a solution that can be truly implemented, and further optimizes the performance of vuesupports typescript: through ts itstype checking mechanism, we can avoid introducing unexpected errors in the reconstruction processsize of the 160d5b03eaca53 framework becomes smaller: After the framework size is optimized, on the one hand, it is becauseComposition APItree-shakingtree shake is supported at the same time. Module APIs are introduced on demand. Useless modules will eventually be shaken off, making the final packaged bundle more volume smallbetter program to achieve virtual Dom: add a markflag, how much the entire template Vue2 of Virtual DOM regardless of changes in re-alignment, and vue3 dynamic dom node taggedPatchFlag, only need to track the nodes with PatchFlag. And when there are many nesting levels of nodes, the dynamic nodes are directly bounddiff algorithm reaches the root dom node, it will directly locate the dynamically changing node. Will go to traverse static dom nodes to improve efficiency
introduces the Proxy feature: It replaces the 060d5b03eacb35 ofObject.definePropertyto achieve two-way binding. Because of its own limitations, it can only hijack the properties of the object. If the object property value is an object, it needs to be traversed in depth to achieve hijacking. In the true sense, the entire object is hijacked completely, and the proxy can hijack the entire object completely
3.2 About Composition API
vue3 replaces the original vue2 throughOptions APIto build component design (forcing us to layer the code), and adopts a design similar to React Hooks, which allows us to build components through a composable, low-invasive, and functional API More flexible. Official definition:A set of additional APIs based on functions, which can flexibly combine component logic
Through the comparison of the above figure, we can see Composition API and Options API . It is obvious that building based on Composition API will be clearer. We will find several differences in vue3:
- Vue3 provides two
data responsive monitoring APIsrefandreactive. The difference between the two is that reactive is mainly used to define complex data types such as objects, while ref is used to define basic types such as strings. - Vue3 provides the
setup(props, context)method, which is the prerequisite entry for using the Composition API. It is equivalent tovue2.xexecuted before created after the life cycle beforeCreate. Theprops parameter in the method is used to obtain the props defined in the component. Note that props It is responsive, and es6 deconstruction cannot be used (it will eliminate the responsiveness of prop). If you need to monitor the response, you need to usewacth. Thecontext parameter is used to get the attribute, get the slot, or send the event, such ascontext.emit, because there is nothiscontext in the setup, you can only use the context to get the mountain below
More practices about vue3 will continue to be updated later, this issue is mainly a brief review
Hello, I am 🌲 tree sauce, please have a drink🍵 Remember Sanlian~
1. After reading, remember to like it, there is 👍 motivated
2. Follow those interesting things on the front end of the official account, and chat with you about the interesting things on the front end
3. The article is included in Github frontendThings, thanks to Star✨



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。