This period
Recently, I changed my job and finally got some interesting bugs and problems. For example, I did in-depth research on ts, and some thoughts on international development. In short, the new job has just started and I have gained a lot. Students who are interested in the international business of "Byte Beat" can smash their resumes and challenge various interesting problems together in the future. (Of course I can also push inward for other positions besides internationalization! 🙋🏻)
Say in a low voice: I have been busy with a lot of things recently, and the series like 3D Earth can only be updated after a while...😭
1: URL encoding operation
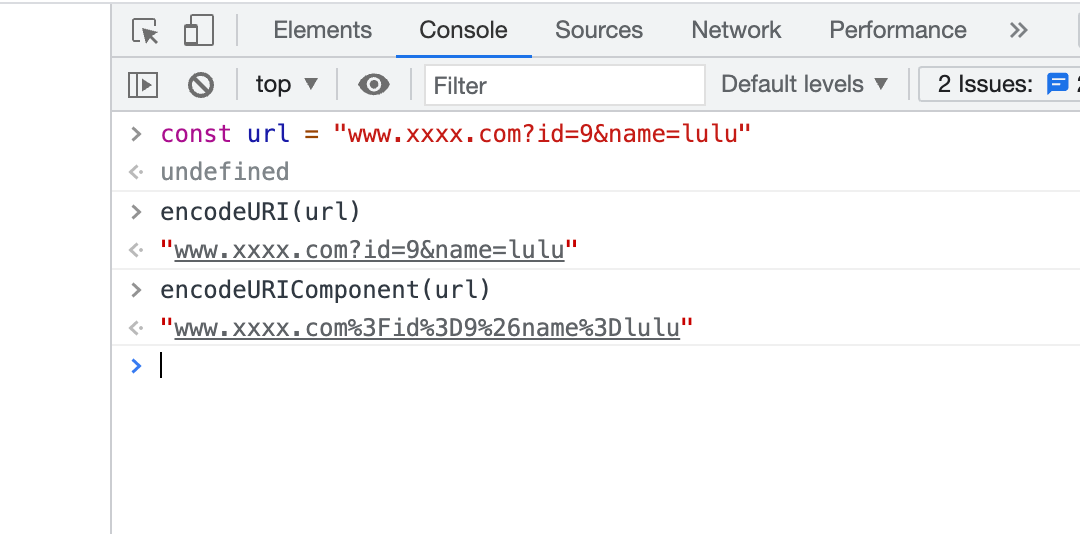
When we pass some information through the URL, some reading problems may occur. We often use encodeURI and encodeURIComponent for encoding before transmitting, but I found that encodeURIComponent . Why are these two types of information? What's the difference?
Because encodeURI not have ;/?:@&=+$,# as characters transferred, which will lead to some special cases uri resolve problems (backend language used different results in different analytical methods), encodeURIComponent will escape various parts of the URI punctuation For example, the commonly used connector & and ? , which means that it escapes more thoroughly and safer, so it is recommended to use encodeURIComponent as much as possible.
2: Flip left and right for international projects (front-end RTL adaptation)
Only when I came to the international front-end team, I learned that "LTR" is written from left to right, and "RTL" is written from right to left, such as'Hebrew','Arabic', etc. If your company To develop an app for use in multiple countries, it must be considered that the written text in some countries is from right to left, and many pictures should also be displayed from right to left, such as placing the return button on the upper right!
What we have to do is to flip the text writing, flip the input box, flip the icon itself and mirror the position, but some icons do not need to be inverted, such as "clock" or 30% does not need to be inverted to %03 Of course, these headaches are also There are mature solutions.
The first type: dir="rtl" attribute setting
Add the attribute dir="rtl" to the body element, and the browser can automatically flip it. If you haven't tried it, try it quickly, it's fun.
The disadvantages are also obvious, such as our css attribute margin: left; is still acting on the left.
The second type: rtlcss
rtlcss of official website , his idea is realized with rtl property use, on page left related properties are converted to right property, the core idea is to replace some of the properties globally.
3: Backend int64 type error
There is a library inside the company that can directly convert the back-end rpc interface specification to the ts specification for front-end use, but suddenly one day there is a type error. For example, the back-end specifies that the return parameter is code numeric type, msg is string type, then Generate the following files:
export type XxxxApi = {
code: number;
msg: string;
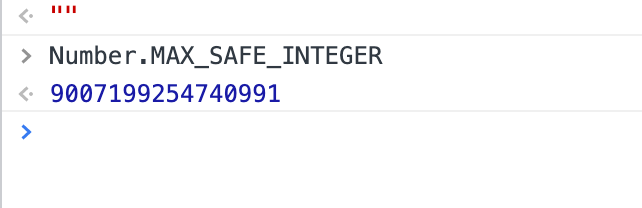
}code returned from the back end one night turned out to be string . My colleagues and I checked the code of the back-end classmates, and the defined int , but it was not int32 but int64 , which turned out to be because of the number js The limit is 2 to the power of 53:
Therefore, the string method is used to express int64 . If the back-end students change the type to int32 no problem. Of course, the back-end students change the type without notice and we will criticize it😁.
4: The style is good during development, and there is a problem after packaging
* bug scene
Obviously the development is good, but why there will be various errors after packaging, such as missing styles, here is one of the reasons:
A long time ago, I published the developed front-end project code on the server. The style was perfect when I visited it locally, but when I opened the project through the test environment URL, the table style was a little broken. The local one is different, but I didn't want to understand the cause of the bug, so I went to communicate with'Classmate a'why this phenomenon occurred.
'Classmate a'said it was caused by the user's browser being different from mine, but I am the user, and the development is on my browser and the test environment I visit with the browser, but it is the same browser, but' A classmate insisted that it is impossible for this situation to happen, so I showed him the whole process from development to release to the test environment. When he saw that the bug did appear again, he said it was a problem of my character... (Later it was resolved by changing some of the wording of css
I am still quite impressed with this matter, but one day this year, I suddenly discovered a problem when webpack postcss will have a setting when configuring, in the two modes of development and production What version is compatible with mainstream browsers, then here is actually the problem, because different translations are carried out for development and packaging, which will lead to unexpected errors, although the code is no longer in that company. I can't find it, but thinking about this, I still feel very strongly that there is a solution to the problem that I had no clue before!
5: Why does the PC call up WhatsApp & Email fail?
URL Schema
If you want to learn to evoke an app, you must first know what Schema is. Let me talk about it in a simple way, that is, every app you download to the system can actually register a url address that belongs to it. You can understand this address as Schema .
And we can use this "Schema address" by calling up an app.
Suppose the contact's phone number is 18200000000, and the area code for China is (86)
- window.open("https://wa.me/8618200000000") 会闪屏
- 或
- window.open("https://api.whatsapp.com/send/?phone=8618200000000")It is not recommended to use window.location.href to jump, it will cause a splash screen.
Why can't the PC terminal evoke WhatsApp with a given WhatsApp number?
- Because WhatsApp is an international software, it needs to be compatible to distinguish each country, so the country's area code must be added.
- Of course, this URL is sometimes unstable and it can't be loaded.
What is mailto
Mailto is a url protocol similar to http, but it is a local protocol (the local protocol is typically file), that is, a protocol that can be resolved without connecting to the network. The function of mailto is to evoke the default mailbox.
Arouse Email
- Suppose the email number of the contact is xxx@qqqqq.com
指定收件人
- window.location.href="mailto: xxx@qqqqq.com"
如果为多个人发邮件则 ',' 分割
- window.location.href="mailto: xxx1@qqqqq.com, xxx2@qqqqq.com"
如果要添加主题, 增加subject参数
- window.location.href=`mailto: xxx@qqqqq.com?subject=${encodeURIComponent("我是主题xxx")}`
如果要添加主题, 增加body参数
- window.location.href=`mailto: xxx@qqqqq.com?subject=${encodeURIComponent("我是主题xxx")}&body=${encodeURIComponent('我是内容xxx')}`6: React.FC
React.Fc often appears. For example, if I don't use React.Fc to process the function of the component, if props.children will be reported. Let's enter the source code analysis together.
type FC<P = {}> = FunctionComponent<P>;
interface FunctionComponent<P = {}> {
// 第一句
(props: PropsWithChildren<P>, context?: any): ReactElement<any, any> | null;
propTypes?: WeakValidationMap<P> | undefined;
contextTypes?: ValidationMap<any> | undefined;
defaultProps?: Partial<P> | undefined;
displayName?: string | undefined;
}FCThistypereceives a parameterP, the default value is an empty object, and thisP.FunctionComponentis just an excessive name, you can think thatFCisFunctionComponent.- The meaning of the first sentence is that the first parameter is of
PropsWithChildren<P>, the second parameter can be optional, if there is any type, it returns React's dom or returnsnull. - The last four parameters are not required, we mainly study the first sentence.
Let's track down PropsWithChildren
type PropsWithChildren<P> = P & { children?: ReactNode | undefined };Just merge the type of the incoming P with { children?: ReactNode | undefined } Seeing this, we will understand. Its practical React.FC package can help ts deduce that props may have children attributes.
7: RematchRootState
rematch is Redux second package, and RematchRootState is rematch a ts derived derivation function, RematchRootState in the end what has been done so that the programmer hair loss operation ...
After using this RematchRootState project, it was found that some types were derived from the never type as shown in the figure:
Explore the meaning of the source code together
export type RematchRootState<M> = ExtractRematchStateFromModels<M>
export type ExtractRematchStateFromModels<M> = {
[modelKey in keyof M]: M[modelKey] extends ModelConfig ? M[modelKey]['state'] : never
}
When using
RematchRootState, we exported a ts type in the form of typeof. The use of typeof in ts is not the meaning of js:Xxx<typeof {name:'金毛', age:9}> // 此处就相当于: Xxx<typeof {name:string, age:number}>[modelKey in keyof M]loopsMobject, each time it loops, it is named modelKey.M[modelKey]is to take out the corresponding value, here specifically refers to the type value intsM[modelKey] extends ModelConfig ? M[modelKey]['state'] : never, that is, every time out 'value', and this 'value' in line withModelConfig type, then returnedM[modelKey]['state']type, otherwisenever, hereextendsyou can understandisused to determine if a value is not compliantextendsarticles will also cover other usages of 061348019679f4.
At this point we have to understand, the problem certainly lies in M[modelKey] type of non-compliance with ModelConfig type specification due to the return of never , that ModelConfig what is the specification that?
export interface ModelConfig<S = any, SS = S, K extends string = string> {
name?: string
state: S
baseReducer?: (state: SS, action: Action) => SS
reducers?: ModelReducers<S>
effects?:
| ModelEffects<any>
| (<M extends Models<K> | void = void>(dispatch: RematchDispatch<M>) => ModelEffects<any>)
}
- Since
ModelConfig, the default value is used. - When the
nameattribute we assign thenumberwill cause an error. statecorresponds to theStype, which is the defaultanyAny type can be used.baseReducerthe parameters of 06134801967ad5 do not meet the specifications, or the return value does not meet the specifications.
effects should be taken out separately
First: effects = ModelEffects<any>
type ModelEffects<S> = {
[key: string]: ( this: { [key: string]: (payload?: any, meta?: any) => Action<any, any> },payload: any,rootState: S) => void
}
export type Action<P = any, M = any> = {
type: string,
payload?: P,
meta?: M,
}
[key: string]means to take out all the items in it to loop.ModelEffectsEach item is a function, and there is no return value.ModelEffectsobject is an object, the values in this object are all functions, and the return value isAction<any, any>.- The second parameter of each function of the
ModelEffects - The third parameter of each function of the
ModelEffectsrootState: SS type, and S is passed in in the previous step, which isany.
the second:
effects = (<M extends Models<K> | void = void>(dispatch: RematchDispatch<M>)
=> ModelEffects<any>)Mis a newly defined generic type, which conforms toModels<K>, if it does not, it is typevoid- This
Kis the default abovestring(I write to you I feel good trouble 😭).
Here is the type Models
export type Models<K extends string = string> = {
[key in K]: ModelConfig
}
Each item is ModelConfig , and ModelConfig we have already mentioned above.
dispatchreceived by this function must conform to the typeRematchDispatch<M>, which is no longer extended here, and there is a special depth further down:
export type RematchDispatch<M = void> =
ExtractRematchDispatchersFromModels<M> &
(RematchDispatcher | RematchDispatcherAsync) &
(Redux.Dispatch<any>)
It can be seen that the type of this parameter is Redux.Dispatch<any> to define it.
- The return value must be:
ModelEffects<any>which we have just talked about.
The correct usage can be as follows:
effects: (dispatch: Redux.Dispatch) => ({
async FnXxx(_: any, state: RootState) {
console.log(state.xxx.xxxList)
},
}),
To sum up the sentence is "I'm so tired to read this code"!
8: ts modify function parameters
Implementation: Add a parameter to the function
Suppose I currently have such a type :
type Obj = {
getX: (a: string, c: boolean) => void;
getN: (a: number) => void;
};And I hope to process this type into the following:
type Obj = {
getX: (s: string[], a: string, c: boolean) => void;
getN: (s: string[], a: number) => void;
};The key point here is to get the type of the function return value and the type collection of the function parameters. The implementation code is as follows:
type Obj2<T> = {
[Key in keyof T]: T[Key] extends (...arg: any) => any
?(s: string[], ...arg: Parameters<T[Key]>) => ReturnType<T[Key]>
: T[Key];
};- Loop
Tall the values in the generic 06134801967deb. - If
T[Key]does not meet(...arg: any) => any, it will not be processed, becauseT[Key]may not be a function type. - On the contrary,
T[Key]is a function type, and the first parameter iss: string[]. ...argis the subsequent parameter type,Parameters<>is the self-contained method, which can deduce the type of the array composed of all the parameters of the function.ReturnType<>is a built-in method, which can deduce the type of the return value of the function.
The method of use is:
type NewObj = Obj2<Obj1>
Implementation: remove the first parameter of the function
Suppose I currently have such a type :
type Obj = {
getX: (a: string, c: boolean) => void;
getN: (a: number) => void;
};And I hope to process this type into the following:
type Obj = {
getX: (c: boolean) => void;
getN: () => void;
};The key point here is how to remove the first element of the array in ts, and use the remaining elements to form the array and return it:
type Obj2<T> = {
[Key in keyof T]: T[Key] extends (s: any, ...arg: infer Arg) => any
? (...arg: Arg) => ReturnType<T[Key]>
: T[Key];
};
- The overall logic here is unchanged, with the above principle.
(s: any, ...arg: infer Arg) => any, here is the core, the parameters other than the first parameter of the function processing are separately named asArg, and thenArgused to define the parameters of the function.inferis a built-in keyword of ts, a bit similar tovarjs, it can define a variable.
The method of use is:
type NewObj = Obj2<Obj1>
9: gzip What can be used instead of fbd compression
I have always thought that gzip compression is currently the best front-end compression scheme, but its compression scheme is not unique and has many categories. The compression method is "stateless compression" and "stateful compression".
Stateless means that any large chunks of data it sees will be compressed without relying on previous input. It is faster but usually less compressed; stateful compression looks at the previous data to decide how to compress the current data, but it is slower but compresses much better.
For example, zstd compression is a stateful compression. A dictionary is generated based on the repeated code blocks encountered during the compression process, and then the same code is encountered with the corresponding key in the dictionary to identify it.
end
This is the case this time, I hope to make progress with you.



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。