1 Introduction
Hello everyone, my name is . Recently organized source code reading activity , interested can add my WeChat ruochuan12 participate, has been for more than two months, we exchange and study together, and make progress together.
I wanted to learn the source code, strongly recommended before I wrote "learning Source overall architecture series" contains jQuery , underscore , lodash , vuex , sentry , axios , redux , koa , vue-devtools , vuex4 , koa-compose , vue-next-release , vue-this , create-vue more than ten Source code articles.
This article warehouse ni-analysis, ask for a star^_^
Recently organized source code reading activity , everyone learns the source code together. So search for all kinds of source code worth learning, and few lines of code.
I wrote two articles related Vue3
- Those practical basic tool functions in the Vue3 source code that beginners can understand
- Vue 3.2 is released, how did You Yuxi release Vue.js?
The articles are written using yarn . The friends who participated in the source code reading according to my article, but pulled the latest warehouse code, found that yarn install could not install the dependency, and reported an error to me. So I went to the github warehouse and found that You Yuxi changed the Vue3 warehouse from yarn to pnpm . is a sentence in the 1618b66fbc14c2 contribution document
We also recommend installing ni to help switching between repos using different package managers.
nialso provides the handynrcommand which running npm scripts easier.We also recommend installing ni to help switch between repos using different package managers.
nialso provides a convenientnrcommand, which makes it easier to run npm scripts.
Although the source code of this ni ts , it is also well understood by the friends who have never used ts , and the main file is actually less than 100 lines of , which is very suitable for us to learn.
After reading this article, you will learn:
1. 学会 ni 使用和理解其原理
2. 学会调试学习源码
3. 可以在日常工作中也使用 ni
4. 等等2. Principle
ni assuming you use lock files (and you should)
Before it runs, it will check your yarn.lock / pnpm-lock.yaml / package-lock.json to learn about the current package manager, and run the corresponding commands.
It may be a bit difficult to understand from this sentence alone, or I don’t know what it is. Let me explain.
使用 `ni` 在项目中安装依赖时:
假设你的项目中有锁文件 `yarn.lock`,那么它最终会执行 `yarn install` 命令。
假设你的项目中有锁文件 `pnpm-lock.yaml`,那么它最终会执行 `pnpm i` 命令。
假设你的项目中有锁文件 `package-lock.json`,那么它最终会执行 `npm i` 命令。
使用 `ni -g vue-cli` 安装全局依赖时
默认使用 `npm i -g vue-cli`
当然不只有 `ni` 安装依赖。
还有 `nr` - run
`nx` - execute
`nu` - upgrade
`nci` - clean install
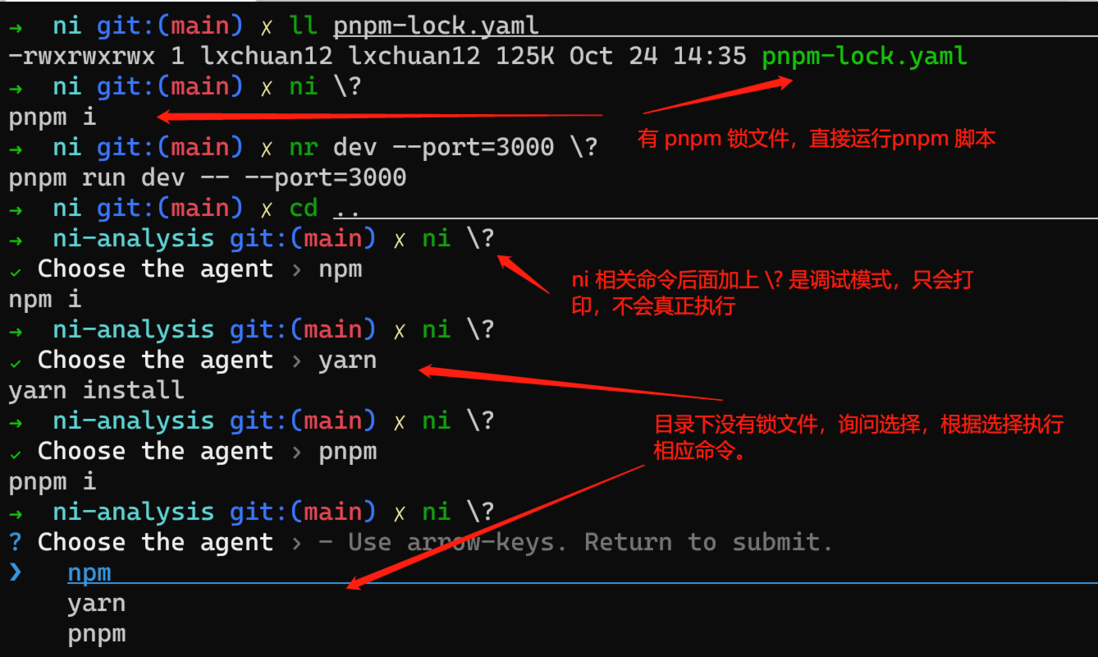
`nrm` - remove I looked at the source code and found that: ni related commands can be appended with \? at the end, which means that it only prints and does not actually execute .
So ni globally, you can test as ni \? as you want, such as 0618b66fbc708e, nr dev --port=3000 \? , because of printing, it can be executed in various directories, which is helpful to understand the source code of ni I tested it as shown below:
Assuming that there is no lock file in the project directory, the user will be allowed to npm、yarn、pnpm default, and then execute the corresponding command.
But if ~/.nirc file, the default configuration will be used to execute the corresponding command.
Config
; ~/.nirc
; fallback when no lock found
defaultAgent=npm # default "prompt"
; for global installs
globalAgent=npmTherefore, we can know that this tool must do three things :
1. 根据锁文件猜测用哪个包管理器 npm/yarn/pnpm
2. 抹平不同的包管理器的命令差异
3. 最终运行相应的脚本Then continue to look at the README other commands 0618b66fbc71b4, it will be easy to understand.
3. Use
See ni github document .
npm i in a yarn project, again? F**k!ni - use the right package manager
Install globally.
npm i -g @antfu/niIf the global installation encounters a conflict, we can add the --force parameter to force the installation.
Give a few commonly used examples.
3.1 ni - install
ni
# npm install
# yarn install
# pnpm installni axios
# npm i axios
# yarn add axios
# pnpm i axios3.2 nr - run
nr dev --port=3000
# npm run dev -- --port=3000
# yarn run dev --port=3000
# pnpm run dev -- --port=3000nr
# 交互式选择命令去执行
# interactively select the script to run
# supports https://www.npmjs.com/package/npm-scripts-info conventionnr -
# 重新执行最后一次执行的命令
# rerun the last command3.3 nx - execute
nx jest
# npx jest
# yarn dlx jest
# pnpm dlx jest4. Preparation before reading the source code
4.1 Clone
# 推荐克隆我的仓库(我的保证对应文章版本)
git clone https://github.com/lxchuan12/ni-analysis.git
cd ni-analysis/ni
# npm i -g pnpm
# 安装依赖
pnpm i
# 当然也可以直接用 ni
# 或者克隆官方仓库
git clone https://github.com/antfu/ni.git
cd ni
# npm i -g pnpm
# 安装依赖
pnpm i
# 当然也可以直接用 niAs we all know, to look at an open source project, start with the package.json file.
4.2 package.json file
{
"name": "@antfu/ni",
"version": "0.10.0",
"description": "Use the right package manager",
// 暴露了六个命令
"bin": {
"ni": "bin/ni.js",
"nci": "bin/nci.js",
"nr": "bin/nr.js",
"nu": "bin/nu.js",
"nx": "bin/nx.js",
"nrm": "bin/nrm.js"
},
"scripts": {
// 省略了其他的命令 用 esno 执行 ts 文件
// 可以加上 ? 便于调试,也可以不加
// 或者是终端 npm run dev \?
"dev": "esno src/ni.ts ?"
},
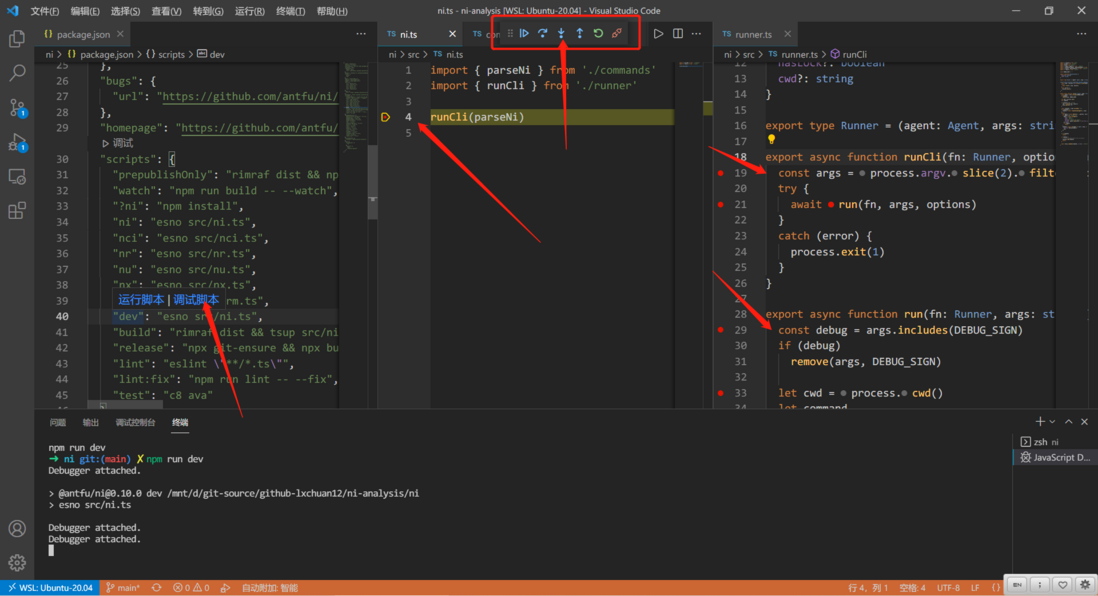
}According to the dev command, we find the main entry file src/ni.ts .
4.3 Start debugging from the main entrance of the source code
// ni/src/ni.ts
import { parseNi } from './commands'
import { runCli } from './runner'
// 我们可以在这里断点
runCli(parseNi)Find ni/package.json of scripts , move the mouse to the dev command, there will be running script and debugging script commands. As shown in the figure below, select the debug script.
5. Main process runner-runCli function
This function is to do a parsing of the command line parameters passed in by the terminal. In the end, the run function is executed.
For process do not understand the reader can see Ruan Yifeng teacher writing process objects
// ni/src/runner.ts
export async function runCli(fn: Runner, options: DetectOptions = {}) {
// process.argv:返回一个数组,成员是当前进程的所有命令行参数。
// 其中 process.argv 的第一和第二个元素是Node可执行文件和被执行JavaScript文件的完全限定的文件系统路径,无论你是否这样输入他们。
const args = process.argv.slice(2).filter(Boolean)
try {
await run(fn, args, options)
}
catch (error) {
// process.exit方法用来退出当前进程。它可以接受一个数值参数,如果参数大于0,表示执行失败;如果等于0表示执行成功。
process.exit(1)
}
}Let's then look at the run function.
6. Main process runner-run main function
This function mainly does three things :
1. 根据锁文件猜测用哪个包管理器 npm/yarn/pnpm - detect 函数
2. 抹平不同的包管理器的命令差异 - parseNi 函数
3. 最终运行相应的脚本 - execa 工具// ni/src/runner.ts
// 源码有删减
import execa from 'execa'
const DEBUG_SIGN = '?'
export async function run(fn: Runner, args: string[], options: DetectOptions = {}) {
// 命令参数包含 问号? 则是调试模式,不执行脚本
const debug = args.includes(DEBUG_SIGN)
if (debug)
// 调试模式下,删除这个问号
remove(args, DEBUG_SIGN)
// cwd 方法返回进程的当前目录(绝对路径)
let cwd = process.cwd()
let command
// 支持指定 文件目录
// ni -C packages/foo vite
// nr -C playground dev
if (args[0] === '-C') {
cwd = resolve(cwd, args[1])
// 删掉这两个参数 -C packages/foo
args.splice(0, 2)
}
// 如果是全局安装,那么实用全局的包管理器
const isGlobal = args.includes('-g')
if (isGlobal) {
command = await fn(getGlobalAgent(), args)
}
else {
let agent = await detect({ ...options, cwd }) || getDefaultAgent()
// 猜测使用哪个包管理器,如果没有发现锁文件,会返回 null,则调用 getDefaultAgent 函数,默认返回是让用户选择 prompt
if (agent === 'prompt') {
agent = (await prompts({
name: 'agent',
type: 'select',
message: 'Choose the agent',
choices: agents.map(value => ({ title: value, value })),
})).agent
if (!agent)
return
}
// 这里的 fn 是 传入解析代码的函数
command = await fn(agent as Agent, args, {
hasLock: Boolean(agent),
cwd,
})
}
// 如果没有命令,直接返回,上一个 runCli 函数报错,退出进程
if (!command)
return
// 如果是调试模式,那么直接打印出命令。调试非常有用。
if (debug) {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-console
console.log(command)
return
}
// 最终用 execa 执行命令,比如 npm i
// https://github.com/sindresorhus/execa
// 介绍:Process execution for humans
await execa.command(command, { stdio: 'inherit', encoding: 'utf-8', cwd })
}After learning the main process, we will then look at two important functions: detect function and parseNi function.
According to the entrance, we can know.
runCli(parseNi)
run(fn)
这里 fn 则是 parseNi6.1 Guess which package manager to use based on the lock file (npm/yarn/pnpm)-detect function
The code is relatively small, so I put it all out.
主要就做了三件事情
1. 找到项目根路径下的锁文件。返回对应的包管理器 `npm/yarn/pnpm`。
2. 如果没找到,那就返回 `null`。
3. 如果找到了,但是用户电脑没有这个命令,则询问用户是否自动安装。// ni/src/agents.ts
export const LOCKS: Record<string, Agent> = {
'pnpm-lock.yaml': 'pnpm',
'yarn.lock': 'yarn',
'package-lock.json': 'npm',
}// ni/src/detect.ts
export async function detect({ autoInstall, cwd }: DetectOptions) {
const result = await findUp(Object.keys(LOCKS), { cwd })
const agent = (result ? LOCKS[path.basename(result)] : null)
if (agent && !cmdExists(agent)) {
if (!autoInstall) {
console.warn(`Detected ${agent} but it doesn't seem to be installed.\n`)
if (process.env.CI)
process.exit(1)
const link = terminalLink(agent, INSTALL_PAGE[agent])
const { tryInstall } = await prompts({
name: 'tryInstall',
type: 'confirm',
message: `Would you like to globally install ${link}?`,
})
if (!tryInstall)
process.exit(1)
}
await execa.command(`npm i -g ${agent}`, { stdio: 'inherit', cwd })
}
return agent
}Then we look at the parseNi function.
6.2 Smoothing out the command differences of different package managers-parseNi function
// ni/src/commands.ts
export const parseNi = <Runner>((agent, args, ctx) => {
// ni -v 输出版本号
if (args.length === 1 && args[0] === '-v') {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-console
console.log(`@antfu/ni v${version}`)
process.exit(0)
}
if (args.length === 0)
return getCommand(agent, 'install')
// 省略一些代码
})Get the command through getCommand
// ni/src/agents.ts
// 有删减
// 一份配置,写个这三种包管理器中的命令。
export const AGENTS = {
npm: {
'install': 'npm i'
},
yarn: {
'install': 'yarn install'
},
pnpm: {
'install': 'pnpm i'
},
}// ni/src/commands.ts
export function getCommand(
agent: Agent,
command: Command,
args: string[] = [],
) {
// 包管理器不在 AGENTS 中则报错
// 比如 npm 不在
if (!(agent in AGENTS))
throw new Error(`Unsupported agent "${agent}"`)
// 获取命令 安装则对应 npm install
const c = AGENTS[agent][command]
// 如果是函数,则执行函数。
if (typeof c === 'function')
return c(args)
// 命令 没找到,则报错
if (!c)
throw new Error(`Command "${command}" is not support by agent "${agent}"`)
// 最终拼接成命令字符串
return c.replace('{0}', args.join(' ')).trim()
}6.3 Finally run the corresponding script
Get the corresponding command, such as npm i , and finally use this tool execa execute the corresponding script finally obtained.
await execa.command(command, { stdio: 'inherit', encoding: 'utf-8', cwd })7. Summary
reading the source code, we can know that this artifact ni mainly does three things :
1. 根据锁文件猜测用哪个包管理器 npm/yarn/pnpm - detect 函数
2. 抹平不同的包管理器的命令差异 - parseNi 函数
3. 最终运行相应的脚本 - execa 工具In our daily development, it may be easy to npm , yarn , and pnpm . With ni , it can be used for daily development. Vue core member Anthony Fu found the problem, and finally developed a tool ni solve the problem. And this ability to discover and solve problems is exactly what our front-end development engineers need.
In addition, I found that Vue ecology have basically switched to pnpm .
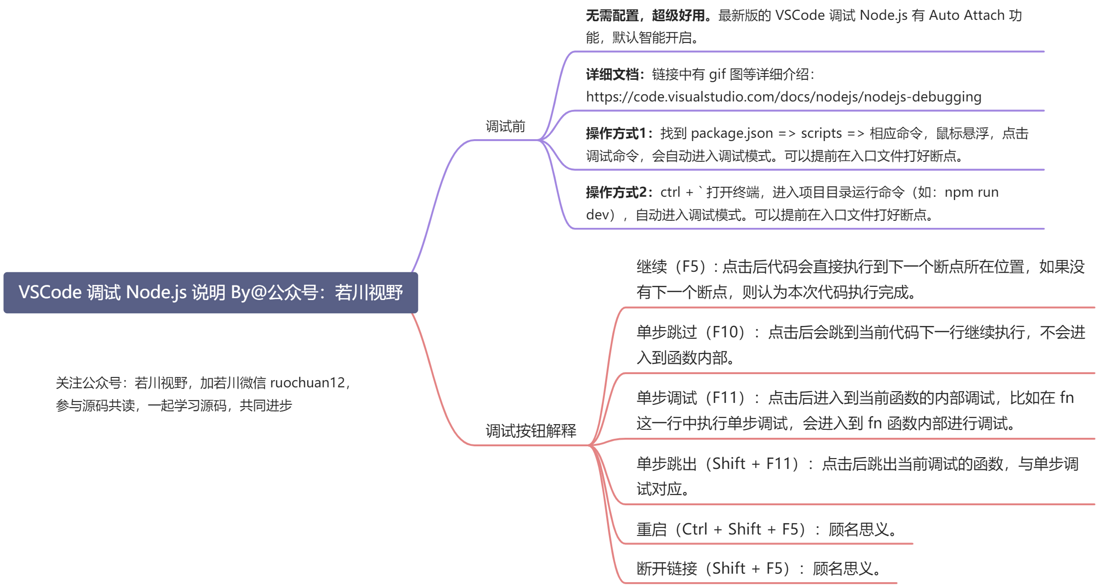
Because the article should not be too long, it did not fully explain all the details of the source code. It is highly recommended that readers use VSCode debug the ni source code according to the method in the article. learning to debug the source code, the source code is not as difficult as .
Finally, you can continue to follow me @若川. Welcome to add me on WeChat ruochuan12 , participate in the source code reading activity, everyone learn the source code and make progress together.
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。