How does Eureka-Server determine that a service is unavailable?
Eureka checks the health status of various service providers by means of heartbeat renewal.
In fact, the part of judging that the service is unavailable will be divided into two pieces of logic.
- Eureka-Server needs to regularly check the health status of the service provider.
- Eureka-Client needs to update its registration information regularly during its operation.
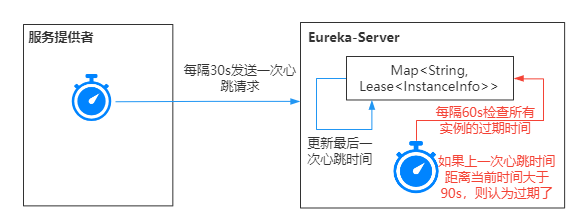
Eureka's heartbeat renewal mechanism is shown in the figure below.
- When the client is started, it will start a heartbeat task and send a heartbeat request to the service ticket every 30s.
- The server maintains the last heartbeat time of each instance. After the client sends a heartbeat packet, it will update this heartbeat time.
- When the server starts, a timing task is started. The task is executed every 60s to check whether the last heartbeat time of each instance exceeds 90s. If it exceeds, it is considered expired and needs to be eliminated.
Regarding the time involved in the above process, you can change it through the following configuration.
#Server 至上一次收到 Client 的心跳之后,等待下一次心跳的超时时间,在这个时间内若没收到下一次心跳,则将移除该 Instance。
eureka.instance.lease-expiration-duration-in-seconds=90
# Server 清理无效节点的时间间隔,默认60000毫秒,即60秒。
eureka.server.eviction-interval-timer-in-ms=60Client heartbeat initiation process
The heartbeat renewal is initiated by the client and executed every 30s.
DiscoveryClient.initScheduledTasks
Continue back to the DiscoveryClient.initScheduledTasks method,
private void initScheduledTasks() {
//省略....
heartbeatTask = new TimedSupervisorTask(
"heartbeat",
scheduler,
heartbeatExecutor,
renewalIntervalInSecs,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
expBackOffBound,
new HeartbeatThread()
);
scheduler.schedule(
heartbeatTask,
renewalIntervalInSecs, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
//省略....
}renewalIntervalInSecs=30s, it will be executed every 30s by default.
HeartbeatThread
The implementation of this thread is very simple. Call renew() renew the contract. If the renewal is successful, the last heartbeat renewal time is updated.
private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable {
public void run() {
if (renew()) {
lastSuccessfulHeartbeatTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
}In the renew() method, call "apps/" + appName + '/' + id; to renew the contract.
boolean renew() {
EurekaHttpResponse<InstanceInfo> httpResponse;
try {
httpResponse = eurekaTransport.registrationClient.sendHeartBeat(instanceInfo.getAppName(), instanceInfo.getId(), instanceInfo, null);
logger.debug(PREFIX + "{} - Heartbeat status: {}", appPathIdentifier, httpResponse.getStatusCode());
if (httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()) {
REREGISTER_COUNTER.increment();
logger.info(PREFIX + "{} - Re-registering apps/{}", appPathIdentifier, instanceInfo.getAppName());
long timestamp = instanceInfo.setIsDirtyWithTime();
boolean success = register();
if (success) {
instanceInfo.unsetIsDirty(timestamp);
}
return success;
}
return httpResponse.getStatusCode() == Status.OK.getStatusCode();
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error(PREFIX + "{} - was unable to send heartbeat!", appPathIdentifier, e);
return false;
}
}The server receives the heartbeat processing
The server specifically calls the renewLease method of the InstanceResource class under the [com.netflix.eureka.resources] package to renew the contract. The code is as follows
@PUT
public Response renewLease(
@HeaderParam(PeerEurekaNode.HEADER_REPLICATION) String isReplication,
@QueryParam("overriddenstatus") String overriddenStatus,
@QueryParam("status") String status,
@QueryParam("lastDirtyTimestamp") String lastDirtyTimestamp) {
boolean isFromReplicaNode = "true".equals(isReplication);
//调用renew进行续约
boolean isSuccess = registry.renew(app.getName(), id, isFromReplicaNode);
// Not found in the registry, immediately ask for a register
if (!isSuccess) { //如果续约失败,返回异常
logger.warn("Not Found (Renew): {} - {}", app.getName(), id);
return Response.status(Status.NOT_FOUND).build();
}
// Check if we need to sync based on dirty time stamp, the client
// instance might have changed some value
Response response;
//校验客户端与服务端的时间差异,如果存在问题则需要重新发起注册
if (lastDirtyTimestamp != null && serverConfig.shouldSyncWhenTimestampDiffers()) {
response = this.validateDirtyTimestamp(Long.valueOf(lastDirtyTimestamp), isFromReplicaNode);
// Store the overridden status since the validation found out the node that replicates wins
if (response.getStatus() == Response.Status.NOT_FOUND.getStatusCode()
&& (overriddenStatus != null)
&& !(InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN.name().equals(overriddenStatus))
&& isFromReplicaNode) {
registry.storeOverriddenStatusIfRequired(app.getAppName(), id, InstanceStatus.valueOf(overriddenStatus));
}
} else {
response = Response.ok().build(); // 续约成功,返回200
}
logger.debug("Found (Renew): {} - {}; reply status={}", app.getName(), id, response.getStatus());
return response;
}InstanceRegistry.renew
The implementation method of renew is as follows, there are two main processes
- Find an instance that matches the current request from the service registration list
- Post EurekaInstanceRenewedEvent event
@Override
public boolean renew(final String appName, final String serverId,
boolean isReplication) {
log("renew " + appName + " serverId " + serverId + ", isReplication {}"
+ isReplication);
//获取所有服务注册信息
List<Application> applications = getSortedApplications();
for (Application input : applications) { //逐一遍历
if (input.getName().equals(appName)) { //如果当前续约的客户端和某个服务注册信息节点相同
InstanceInfo instance = null;
for (InstanceInfo info : input.getInstances()) { //遍历这个服务集群下的所有节点,找到某个匹配的实例instance返回。
if (info.getId().equals(serverId)) {
instance = info; //
break;
}
}
//发布EurekaInstanceRenewedEvent事件,这个事件在EurekaServer中并没有处理,我们可以监听这个事件来做一些事情,比如做监控。
publishEvent(new EurekaInstanceRenewedEvent(this, appName, serverId,
instance, isReplication));
break;
}
}
return super.renew(appName, serverId, isReplication);
}super.renew
public boolean renew(final String appName, final String id, final boolean isReplication) {
if (super.renew(appName, id, isReplication)) { //调用父类的续约方法,如果续约成功
replicateToPeers(Action.Heartbeat, appName, id, null, null, isReplication); //同步给集群中的所有节点
return true;
}
return false;
}AbstractInstanceRegistry.renew
In this method, you will get the list of instances corresponding to the application, and then call Lease.renew() to renew the contract.
public boolean renew(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
RENEW.increment(isReplication);
Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>> gMap = registry.get(appName); //根据服务名字获取实例信息
Lease<InstanceInfo> leaseToRenew = null;
if (gMap != null) {
leaseToRenew = gMap.get(id); //获取需要续约的服务实例,
}
if (leaseToRenew == null) { //如果为空,说明这个服务实例不存在,直接返回续约失败
RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
logger.warn("DS: Registry: lease doesn't exist, registering resource: {} - {}", appName, id);
return false;
} else { //表示实例存在
InstanceInfo instanceInfo = leaseToRenew.getHolder(); //获取实例的基本信息
if (instanceInfo != null) { //实例基本信息不为空
// touchASGCache(instanceInfo.getASGName());
//获取实例的运行状态
InstanceStatus overriddenInstanceStatus = this.getOverriddenInstanceStatus(
instanceInfo, leaseToRenew, isReplication);
if (overriddenInstanceStatus == InstanceStatus.UNKNOWN) { //如果运行状态未知,也返回续约失败
logger.info("Instance status UNKNOWN possibly due to deleted override for instance {}"
+ "; re-register required", instanceInfo.getId());
RENEW_NOT_FOUND.increment(isReplication);
return false;
}
//如果当前请求的实例信息
if (!instanceInfo.getStatus().equals(overriddenInstanceStatus)) {
logger.info(
"The instance status {} is different from overridden instance status {} for instance {}. "
+ "Hence setting the status to overridden status", instanceInfo.getStatus().name(),
overriddenInstanceStatus.name(),
instanceInfo.getId());
instanceInfo.setStatusWithoutDirty(overriddenInstanceStatus);
}
}
//更新上一分钟的续约数量
renewsLastMin.increment();
leaseToRenew.renew(); //续约
return true;
}
}The realization of contract renewal is to update the time when the server received the last heartbeat request.
public void renew() {
lastUpdateTimestamp = System.currentTimeMillis() + duration;
}Eureka's self-protection mechanism
In fact, the heartbeat detection mechanism has certain uncertainties. For example, the service provider may be normal, but due to network communication problems, the heartbeat request is not received within 90s, which will cause the healthy service to be killed by mistake.
In order to avoid this problem, Eureka provides a self-protection mechanism Simply put, after the self-protection mechanism is turned on, Eureka Server will protect these service instances to avoid the problem of expiration and removal of instances, thereby ensuring that the Eurreka cluster is more robust and stable.
After entering the self-protection state, the following situations will occur
Eureka Server no longer removes from the registration list expired services that should be removed because they have not received a heartbeat for a long time. If the service happens to be abnormally offline during the protection period, the service consumer will take it. To an invalid service instance, the call will fail at this time. For this problem, the service consumer needs to have some fault tolerance mechanisms, such as retry, circuit breaker, etc.!Eureka Server can still accept new service registration and query requests, but it will not be synchronized to other nodes, ensuring that the current node is still available.
Eureka self-protection mechanism, by configuring eureka.server.enable-self-preservation to [ true ] open / [ false disabled] self-protection mechanism, the default open state, it is recommended to open this configuration in the production environment.
How should the self-protection mechanism be designed to more accurately control the communication delay caused by the "network abnormality" instead of service downtime?Eureka does this: If less than 85% of the client nodes do not have a normal heartbeat, then Eureka Server thinks that there is a network failure between the client and the registry, and Eureka Server automatically enters the self-protection state .
Among them, 85% can be set by the following configuration# 自我保护续约百分比,默认是0.85
eureka.server.renewal-percent-threshold=0.85But there is still a question, whose 85% is more than that? There is an expected number of contract renewals. The calculation formula for this number is as follows:
//自我保护阀值 = 服务总数 * 每分钟续约数(60S/客户端续约间隔) * 自我保护续约百分比阀值因子Assuming that there are 100 services, the renewal interval is 30S , and the self-protection threshold is 0.85 , then its expected number of renewals is:
自我保护阈值 =100 * 60 / 30 * 0.85 = 170。Threshold setting for automatic renewal
Threshold setting for automatic renewalIn EurekaServerBootstrap this class contextInitialized approach, calls initEurekaServerContext initialize
public void contextInitialized(ServletContext context) {
try {
initEurekaEnvironment();
initEurekaServerContext();
context.setAttribute(EurekaServerContext.class.getName(), this.serverContext);
}
catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot bootstrap eureka server :", e);
}
}Continue to look down.
protected void initEurekaServerContext() throws Exception {
EurekaServerConfig eurekaServerConfig = new DefaultEurekaServerConfig();
//...
registry.openForTraffic(applicationInfoManager, registryCount);
}In the openForTraffic method expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews will be initialized. The meaning of this value is: number of clients expected to receive renewal every minute depends on the number of services registered on the eureka server@Override
public void openForTraffic(ApplicationInfoManager applicationInfoManager, int count) {
// Renewals happen every 30 seconds and for a minute it should be a factor of 2.
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count; //初始值是1.
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
logger.info("Got {} instances from neighboring DS node", count);
logger.info("Renew threshold is: {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);
this.startupTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (count > 0) {
this.peerInstancesTransferEmptyOnStartup = false;
}
DataCenterInfo.Name selfName = applicationInfoManager.getInfo().getDataCenterInfo().getName();
boolean isAws = Name.Amazon == selfName;
if (isAws && serverConfig.shouldPrimeAwsReplicaConnections()) {
logger.info("Priming AWS connections for all replicas..");
primeAwsReplicas(applicationInfoManager);
}
logger.info("Changing status to UP");
applicationInfoManager.setInstanceStatus(InstanceStatus.UP);
super.postInit();
}updateRenewsPerMinThreshold
updateRenewsPerMinThresholdThen call the updateRenewsPerMinThreshold method to update the minimum number of renewals per minute, which is the threshold for the total number of client instance renewals that Eureka Server expects to receive every minute. If it is less than this threshold, it will trigger the self-protection mechanism.
protected void updateRenewsPerMinThreshold() {
this.numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold = (int) (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews
* (60.0 / serverConfig.getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds())
* serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold());
}
//自我保护阀值 = 服务总数 * 每分钟续约数(60S/客户端续约间隔) * 自我保护续约百分比阀值因子getExpectedClientRenewalIntervalSeconds, the client renewal interval, the default is 30sgetRenewalPercentThreshold, self-protection renewal percentage threshold factor, default 0.85. In other words, the number of renewals per minute must be greater than 85%
Trigger mechanism for changes in expected value
Trigger mechanism for changes in expected valueexpectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews and numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold will change with the triggering of new service registration and service offline.
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.cancel
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.cancelWhen the service provider takes the initiative to go offline, it means that Eureka-Server will remove the address of the service provider at this time, and it also means that the heartbeat renewal threshold will change. So you can see the data update PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.cancel
Call path PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.cancel -> AbstractInstanceRegistry.cancel->internalCancelAfter the service goes offline, it means that the number of clients that need to send renewals decreases, so modify it here
protected boolean internalCancel(String appName, String id, boolean isReplication) {
//....
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {
// Since the client wants to cancel it, reduce the number of clients to send renews.
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews - 1;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
}PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.register
PeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.registerWhen a new service provider is registered on eureka-server, the number of renewed clients needs to be increased, so it will be processed in the register method
register ->super.register(AbstractInstanceRegistry)public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) {
//....
// The lease does not exist and hence it is a new registration
synchronized (lock) {
if (this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews > 0) {
// Since the client wants to register it, increase the number of clients sending renews
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews + 1;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
}Refresh the self-protection threshold every 15 minutes
Refresh the self-protection threshold every 15 minutesPeerAwareInstanceRegistryImpl.scheduleRenewalThresholdUpdateTaskEvery 15 minutes, update the self-protection threshold!
private void updateRenewalThreshold() {
try {
// 1. 计算应用实例数
Applications apps = eurekaClient.getApplications();
int count = 0;
for (Application app : apps.getRegisteredApplications()) {
for (InstanceInfo instance : app.getInstances()) {
if (this.isRegisterable(instance)) {
++count;
}
}
}
synchronized (lock) {
// Update threshold only if the threshold is greater than the
// current expected threshold or if self preservation is disabled.
//当节点数量count大于最小续约数量时,或者没有开启自我保护机制的情况下,重新计算expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews和numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold
if ((count) > (serverConfig.getRenewalPercentThreshold() * expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews)
|| (!this.isSelfPreservationModeEnabled())) {
this.expectedNumberOfClientsSendingRenews = count;
updateRenewsPerMinThreshold();
}
}
logger.info("Current renewal threshold is : {}", numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Cannot update renewal threshold", e);
}
}Self-protection mechanism trigger
Self-protection mechanism triggerIn AbstractInstanceRegistry of postInit method, will open a EvictionTask task, the task is to detect whether the need to open the self-protection mechanism.
This method is also triggered when the EurekaServerBootstrap method starts.protected void postInit() {
renewsLastMin.start(); //开启一个定时任务,用来实现每分钟的续约数量,每隔60s归0重新计算
if (evictionTaskRef.get() != null) {
evictionTaskRef.get().cancel();
}
evictionTaskRef.set(new EvictionTask()); //启动一个定时任务EvictionTask,每隔60s执行一次
evictionTimer.schedule(evictionTaskRef.get(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs(),
serverConfig.getEvictionIntervalTimerInMs());
}Among them, the code of EvictionTask is as follows.
private final AtomicLong lastExecutionNanosRef = new AtomicLong(0l);
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//获取补偿时间毫秒数
long compensationTimeMs = getCompensationTimeMs();
logger.info("Running the evict task with compensationTime {}ms", compensationTimeMs);
evict(compensationTimeMs);
} catch (Throwable e) {
logger.error("Could not run the evict task", e);
}
}evict method
evict methodpublic void evict(long additionalLeaseMs) {
logger.debug("Running the evict task");
// 是否需要开启自我保护机制,如果需要,那么直接RETURE, 不需要继续往下执行了
if (!isLeaseExpirationEnabled()) {
logger.debug("DS: lease expiration is currently disabled.");
return;
}
//这下面主要是做服务自动下线的操作的。
}isLeaseExpirationEnabled
isLeaseExpirationEnabledWhether the self-protection mechanism is enabled, if not, skip it, the default is to enableCalculate whether self-protection needs to be turned on, and determine whether the number of renewals received in the last minute is greater thannumberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold
public boolean isLeaseExpirationEnabled() {
if (!isSelfPreservationModeEnabled()) {
// The self preservation mode is disabled, hence allowing the instances to expire.
return true;
}
return numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold > 0 && getNumOfRenewsInLastMin() > numberOfRenewsPerMinThreshold;
}Copyright statement: All articles in this blog, except for special statements, adopt the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license agreement. Please indicate the reprint from Mic takes you to learn architecture!
If this article is helpful to you, please help me to follow and like. Your persistence is the motivation for my continuous creation. Welcome to follow the WeChat public account of the same name for more technical dry goods!
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。