In the last chapter, we introduced the Axios source code - request . In this chapter, let's introduce the part where Axios actually initiates the network request, that is, the dispatchRequest method.
dispatchRequest
The definition of this method is also relatively simple (as shown below)
Line 29 - Cancel the request
Let's break down what each line of code does, line by line, starting with the cancellation request on line 29. (as follows)
throwIfCancellationRequested(config);This action is not only done once before making a formal request, but also once when the request succeeds and when the request fails.
As long as it is cancel , it will not enter the success or failure callback processing. (As shown below)
throwIfCancellationRequested function does, is to detect whether the request was canceled, throw an error if it is canceled, and prevent the code from continuing down the line. (as follows)
function throwIfCancellationRequested(config) {
if (config.cancelToken) {
// 检测请求是否被取消,然后决定是否抛出错误
config.cancelToken.throwIfRequested();
}
if (config.signal && config.signal.aborted) {
// 抛出错误
throw new Cancel('canceled');
}
}Of course, CancelToken is still somewhat complicated (complex in callback processing). If anyone is interested, you can talk about the processing of this part separately, and I will not expand it here.
Lines 35 ~ 40 - process the request data
config.data = transformData.call(
config,
config.data,
config.headers,
config.transformRequest
);transformData method is used here. The main function is to merge data , and it can transformRequest method (as shown below).
The transformData method is to traverse the incoming transformRequest method, use data and headers as the transformRequest parameters of 061e3f3b915feb, and then copy the returned result to config.data data content to be sent in the final request.
Lines 43 ~ 54 - merge request headers
config.headers = utils.merge(
config.headers.common || {},
config.headers[config.method] || {},
config.headers
);
utils.forEach(
['delete', 'get', 'head', 'post', 'put', 'patch', 'common'],
function cleanHeaderConfig(method) {
delete config.headers[method];
}
);The above code mainly does two things:
- The first thing is to merge the general
headers(common headers) with the corresponding methodheadersand the originalheaders; - The second thing is to delete the
headers
Lines 56 ~ 58 - make the real request
var adapter = config.adapter || defaults.adapter;
return adapter(config).then(function onAdapterResolution(response) {
// ...
});adapter is used here, which is actually the method to initiate the request.
For example two default request method for use in running the browser when the end is XMLHttpRequest , in Node use terminal runtime http module.
Know what this configuration can do?
You can pass a custom request method here, e.g. use fetch wrapper instead of XMLHttpRequest on the client side.
You can also pass in a mock method that you have encapsulated here, which returns all local json data for mock data, so that you don't need to build an additional mock service.
......
Closer to home, we take a look axios default two adapter it, this article will focus on explaining the client adapter - xhrAdapter .
Client adapter - xhrAdapter
By convention, we adapter - xhrAdapter line by line.
Preparation before making a request
| Rows | describe |
|---|---|
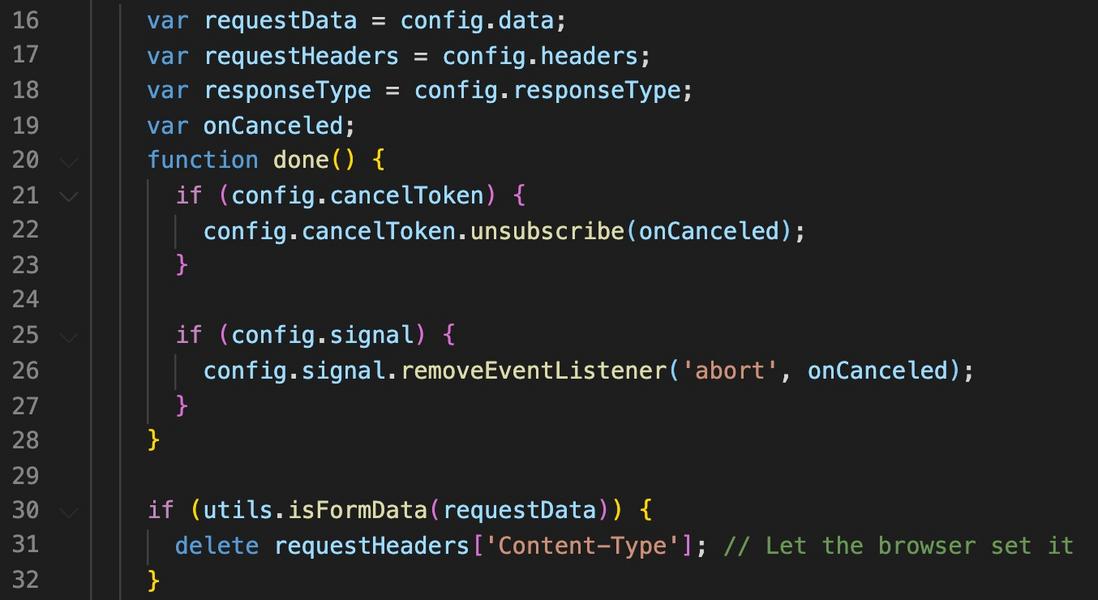
line 16 ~ 18 | Collect request data information ( requestData ), request header information ( requestHeaders ), return body type ( responseType ) |
line 19 ~ 28 | For cancelToken done deal, cancel the subscription at the time of the completion of the request, free up memory; as well as to signal treatment, this signal in the document could not see, it should also be used abort request. |
line 30 ~ 32 | For FormData requests, remove the Content-Type request header and let the browser automatically set the request header. |
Set authentication information
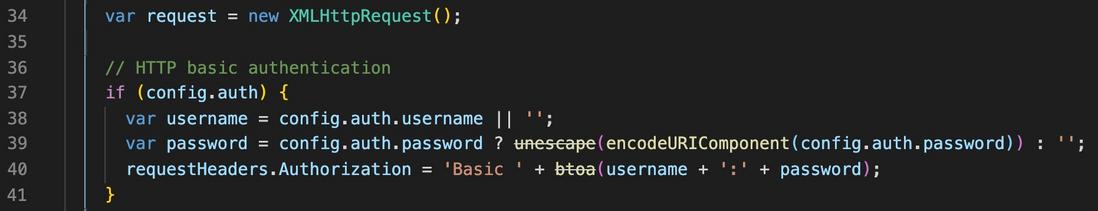
First, at 34 , an XMLHttpRequest created for subsequent network requests.
Then take the first 37 ~ 41 line, set for HTTP basic authentication information authentication, we can learn from this passage simply HTTP basic authentication authentication knowledge.
First password be encodeURLComponent escape coding, then the user name and password in accordance with the rules of stitching, using btoa the user name and password turned into base64 coding.
If you want to do this kind of thing yourself in the future, you can turn to this chapter again to find the content of this part of the code and copy it again.
splicing request url
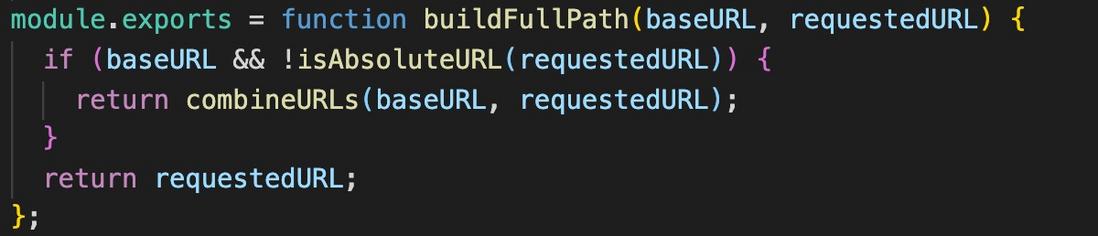
The first is to concatenate the complete request url buildFullPath method. (As shown below)
It can be seen that this method will not concatenate baseURL url ( isAbsoluteURL() ).
Then, axios also uses the buildURL method to params parameter into url - which is what we often call the query parameter. (as follows)
function buildURL(url, params, paramsSerializer) {
/*eslint no-param-reassign:0*/
if (!params) {
return url;
}
var serializedParams;
if (paramsSerializer) {
serializedParams = paramsSerializer(params);
} else if (utils.isURLSearchParams(params)) {
serializedParams = params.toString();
} else {
// ...
serializedParams = parts.join('&');
}
if (serializedParams) {
// ...
// 在这里,将处理后的参数作为 query 查询参数拼接到 url 中
url += (url.indexOf('?') === -1 ? '?' : '&') + serializedParams;
}
return url;
};This is why when axios GET method should be set in the params field.
Then, a request is initiated request.open
response callback function
The next step is to compare the core response callback function (as shown below)
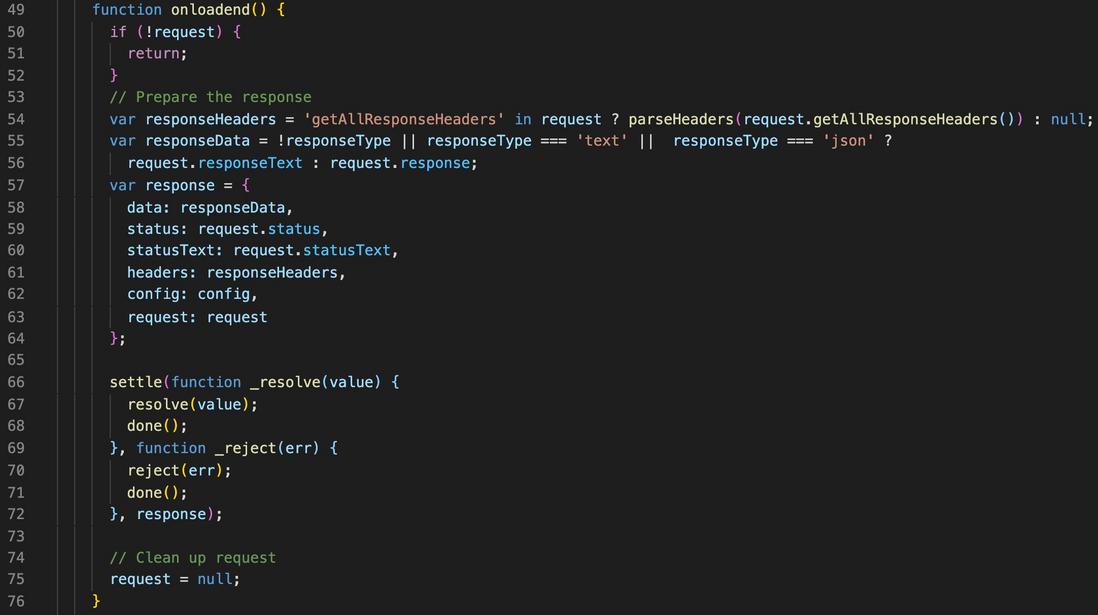
| Rows | describe |
|---|---|
line 54 | get all response headers |
line 55 | get response content |
line 57 ~ 64 | Set the promise resolve , the things you often console.log , you should be familiar |
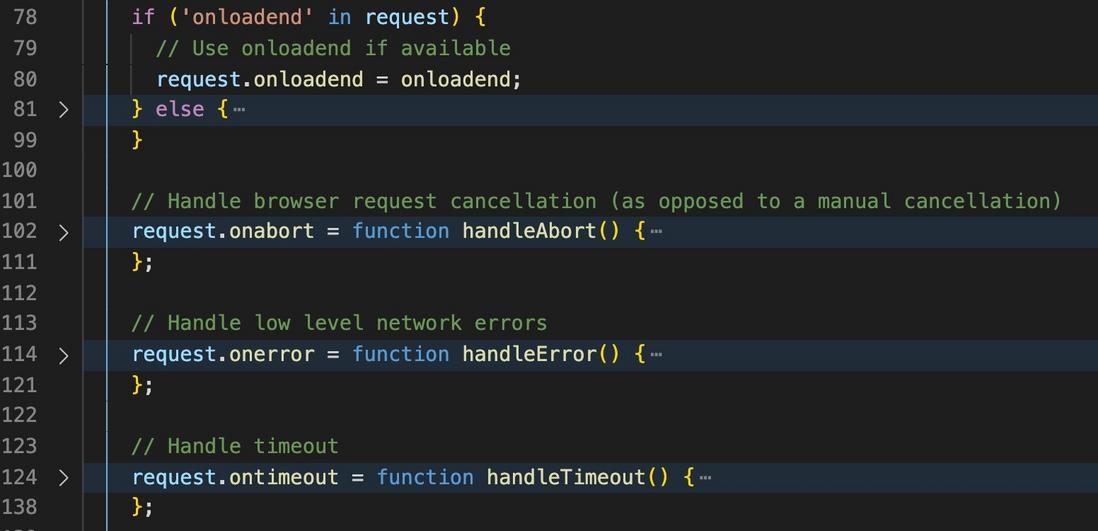
Set other callback functions
The following are basically some callback functions that XMLHttpRequest (As shown below)
XMLHttpRequest are relatively late to the front end may not be clear about what these events of the 061e3f3b916501 instance do. You can refer to the XMLHttpRequest document .
Finally, send this request. (as follows)
request.send(requestData);back to dispatchRequest
As can be seen from the above, dispatchRequest calls adapter , the following data is obtained.
{
data: responseData,
status: request.status,
statusText: request.statusText,
headers: responseHeaders,
config: config,
request: request
};Then let's take a look at how dispatchRequest handles this piece of data internally. (As shown below)
| Rows | describe |
|---|---|
line 59/72 | Process CancelToken , if the request has been canceled, it will not continue down |
line 62~67 | Convert the response result through transformResponse to get the processed response data |
line 69 | return the response |
In this way, the entire axios is sorted out clearly. Let's draw a flowchart to sort it out. (As shown below)
Here on Node end of adapter not be launched explained, and the main difference is that the client following points:
- The request is
Nodethehttp - A proxy server can be
proxy, and the request will be sent to the proxy server.
summary
Well, our interpretation of the source code of axios
It can be seen that axios is the most popular and powerful network request framework at present, the source code looks relatively clean and easy to read. It is recommended that you follow the ideas of the article.
The next chapter, we will achieve a simple axios framework contains axios some of the core functions of the axios source Interpretation series ending.
one last thing
If you have seen this, I hope you will give a like and go~
Your likes are the greatest encouragement to the author, and can also allow more people to see this article!
If you think this article is helpful to you, please help to light up star github to encourage it!








**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。