In recent years, with the rapid development of information technology and the popularization of mobile Internet applications, more and more applications collect and use personal information in large quantities, which brings convenience to people's lives. At the same time, illegal collection and abuse of personal information also occur. , leakage and other issues, personal information security is facing serious threats. In January 2019, the Central Cyberspace Administration of China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, the Ministry of Public Security, and the State Administration for Market Regulation jointly issued the "Announcement on Carrying out Special Governance of the Illegal Collection and Use of Personal Information by Apps" (hereinafter referred to as the "Announcement"). In order to implement the relevant deployment of the "Announcement", entrusted by the four departments, the National Information Security Standardization Technical Committee, the China Consumers Association, the Internet Society of China, and the China Cyberspace Security Association established a special governance working group for the illegal collection and use of personal information by Apps (hereinafter referred to as "" App Special Governance Working Group”), which specifically promotes the evaluation of the illegal collection and use of personal information by Apps.
The review of each application market is also very strong. There are often problems that applications are rejected due to the collection of personal information. Let’s look at a few examples and describe the reasons for rejection:
App treasure:
(1) Collection of personal information beyond the scope
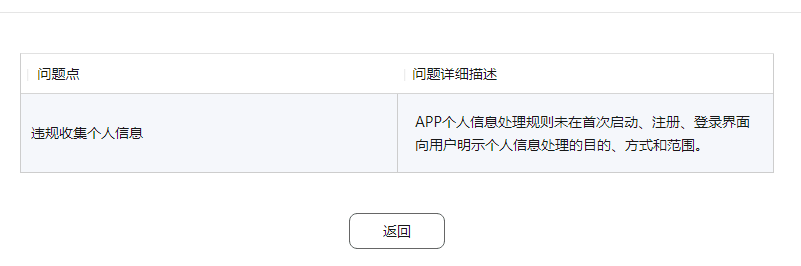
Question 1: The APP has not notified the user without the user's consent. In some functions, there is behavior to collect information such as address book, text message, call record, camera, etc., which is not necessary for the service and has no reasonable application scenarios. The stated purpose of the personal information is directly or reasonably related to the scope.
Question 2: When the APP is running, it does not inform the user and without the user's consent, the location information is read every 30s, which is not necessary for the service and has no reasonable application scenarios, and exceeds the minimum necessary to realize the business function of the product or service. frequency.
Question 3: The APP does not inform the user and without the user's consent, in a silent state or when running in the background, there is behavior to collect information such as address book, text message, call record, camera, etc., which is not necessary for the service and has no reasonable application scenarios , beyond the scope that is directly or reasonably related to the purpose for which the personal information was collected.
Question 4: The APP does not inform the user and without the user's consent, in a silent state or when running in the background, there is a behavior of collecting location information, IMEI, address book, text messages, pictures and other information at a certain frequency, which is not necessary for the service. and no reasonable application)
(2) APP frequently self-start and associated startup .
Question 1: The APP does not express to the user that it is not consented by the user, and there is no reasonable usage scenario, and there are frequent self-starting or associated startup behaviors.
Question 2: Although the APP has an explicit link to the user and obtained the user's consent, frequent self-starting or associated startup occurs before the user's consent.
Problem 3: The APP is not necessary for the service or has no reasonable application scenarios, and the third-party APP is frequently started automatically or associated with it outside the scope.
Huawei AppGallery:
How to solve it?
1. When the APP is launched for the first time, the "Privacy Policy" and "User Agreement" must pop up first, and provide an agree or reject button. After the user agrees, the third-party sdk (map, push, etc.) is initialized. These third-party services usually involve to collect personal information. Any code that collects personal information cannot be triggered without the user's consent.
2. The APP privacy policy should clearly describe the scenarios and purposes of all personal information used. The third-party sdk used can go to the third-party official website to view their privacy agreement.
Reference documentation:

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。