监听的定义: 服务器等待来自任意远端的连接请求.
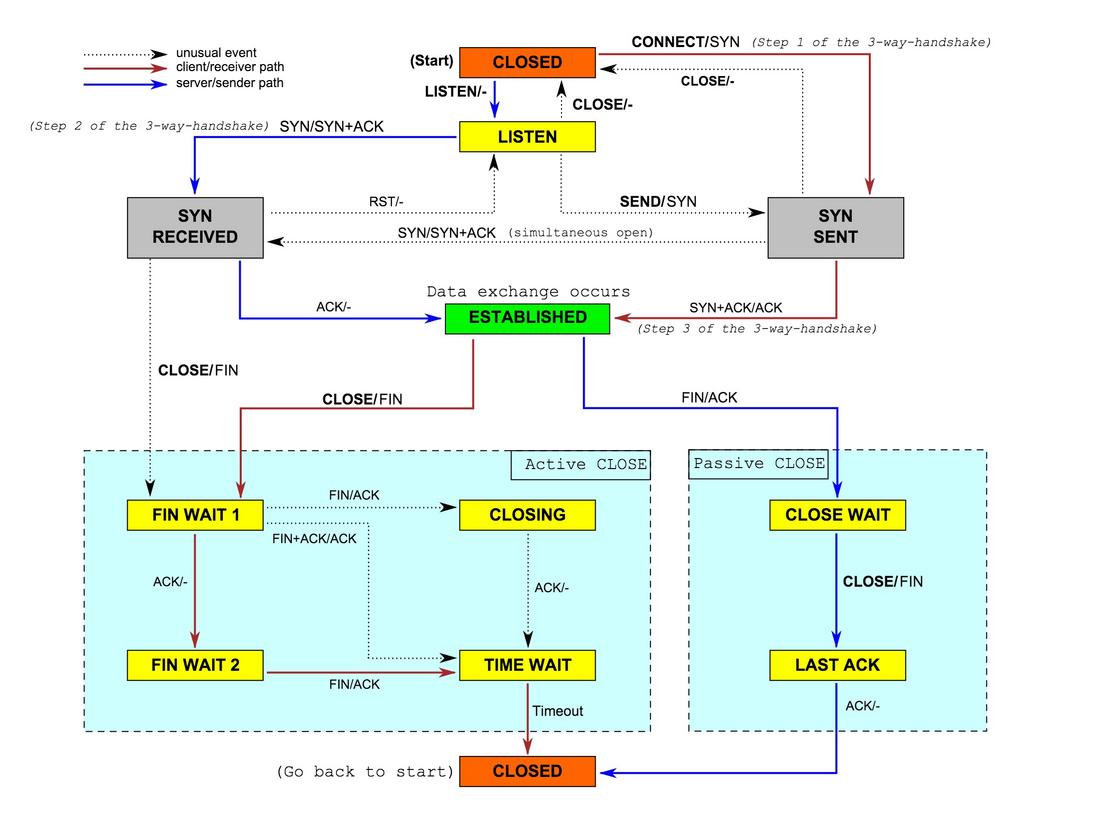
这张图的信息量很大, 可以仔细研究. 图中顶部黄色的 LISTEN 方块就是监听器的所处的位置.
监听器
一个监听器是一组进程, 它的用途是在一个指定的端口上监听新的TCP连接. 它管理着一个接收器进程池, 池中的每个接收器一直持续不断的接受连接. 当一个新的连接到达时, 它启动一个新的进程来执行协议处理代码, 所有的套接字编程通过使用传输处理模块进行抽象.
监听器关注于监控所有的接收器和连接进程, 允许开发者把关注点放在构建应用程序上.
启动一个监听器
默认 Ranch 什么都不会做, 要求 Ranch 监听连接是应用开发者的事情.
监听器可以启动和停止, 当启动一个监听器的时候, 要求许多不同的设置:
一个本地的标识名称, 通过这个名称能与监听器交互.
资源池中的接收器的数量.
一个传输处理器以及关联的选项.
一个协议处理器以及关联的选项.
Ranch 包括 TCP 和 SSL 传输处理器, 分别为 ranch_tcp 和 ranch_ssl 模块.
监听器可以通过调用 ranch:start_listener/6 函数来启动, 在这之前, 请确保 ranch 应用程序已经启动.
启动 Ranch 应用程序
ok = application:start(ranch).现在就可以启动监听器了, 给这个监听器一个名字, 叫他 tcp_echo. 它有一个包含 100 个接收器的资源池, 使用TCP传输, 并转发连接到 echo_protolcol 处理器.
在端口 5555 启动一个监听器
{ok, _} = ranch:start_listener(
tcp_echo, %% 监听器的名称
100, %% 100 个 Acceptors
ranch_tcp, %% 使用TCP传输
[{port, 5555}], %% 监听器选项
echo_protocol, %% 协议处理模块
[] %% 协议处理模块选项
).可以在项目目录的 examples 目录测试并编译运行 tcp_echo 这个例子. 打开终端在 examples/tcp_echo 目录下运行下面的命令:
$ make run可以通过 telnet 命令连接并查看服务器的响应. 可用 Ctrl+] 组合键转义 telnet 命令行, 并输入 quit 退出.
使用 telnet 连接到监听器
$ telnet localhost 5555
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
Hello!
Hello!
It works!
It works!
^]
telnet> quit
Connection closed.停止监听器
只需要调用 ranch:stop_listener/1 函数停止一个监听器, 它接受一个监听器的名字作为参数, 之前使用名称 tcp_echo 启动了这个监听器, 现在停止它.
停止一个监听器
ranch:stop_listener(tcp_echo).默认传输选项
默认套接字设置为使用 {active, false}, {packet, raw}, {reuseaddr, true} 选项返回 binary 数据. 这些选项可以在启动监听器的时候覆盖, 同时也可以在协议处理模块中调用 Transport:setopts/2 来覆盖.
It will also set
{backlog, 1024}and{nodelay, true}, which can be overriden at listener startup.
如果还要设置 {backlog, 1024} 和 {nodelay, true}, 在监听器启动的时候可以覆盖.
监听一个随机端口
You do not have to specify a specific port to listen on. If you give the port number 0, or if you omit the port number entirely, Ranch will start listening on a random port.
如果在监听的时候不必指定端口, 如果你指定端口为 0, 或者完全省略端口号, Ranch 将监听在随机端口上.
You can retrieve this port number by calling ranch:get_port/1. The argument is the name of the listener you gave in ranch:start_listener/6.
可以嗲用 ranch:get_port/1 获取端口号, 参数为 监听器的名称, 即: 启动监听器是传递给 ranch:start_listener/6 的第一个参数.
Starting a listener for TCP connections on a random port
{ok, _} = ranch:start_listener(tcp_echo, 100,
ranch_tcp, [{port, 0}],
echo_protocol, []
).
Port = ranch:get_port(tcp_echo).在特权端口上监听
Some systems limit access to ports below 1024 for security reasons. This can easily be identified by an {error, eacces} error when trying to open a listening socket on such a port.
1024 一下的端口在多数 Linux/Unix 系统上都要求具有 Root 权限, 如果你没有 Root 权限, 在 1024 一下打开一个监听套接字的时候, 将会抛出错误 {error, eacces}.
The methods for listening on privileged ports vary between systems, please refer to your system’s documentation for more information.
不同的系统, 在特权端口上监听都不大相同, 细节请参考系统文档
We recommend the use of port rewriting for systems with a single server, and load balancing for systems with multiple servers. Documenting these solutions is however out of the scope of this guide.
推荐单服务器使用端口重新, 多服务器使用负载均衡. 这些方案与本文无关就不做讨论了.
从现有的套接字接受连接
如果想要在已经存在的套接字上接受连接, 可以使用 socket 传输选项. 对于传输或套接字库(gen_tcp:connect, ssl:connect), 其应该只是从连接函数返回的相关的数据. accept 函数调用传入的套接字. 应该以 {active, false} 模式连接套接字.
因为SSL的BUG, 在R16之前, 无法改变一个SSL监听套接字的所有权. SSL套接字的创建者作为该套接字的所有者, 并不影响 accept 行为,除非该套接字的所有者挂了.
限制并发连接数
max_connections 传输选项允许限制并发连接的数量. 默认为 1024, 目的是防止系统过载, 以保证所有的连接都能够的快速的处理.
自定义最大并发连接数
{ok, _} = ranch:start_listener(tcp_echo, 100,
ranch_tcp, [{port, 5555}, {max_connections, 100}],
echo_protocol, []
).可以通过设置并发连接数为 infinity 禁用并发连接限制(不推荐)
{ok, _} = ranch:start_listener(tcp_echo, 100,
ranch_tcp, [{port, 5555}, {max_connections, infinity}],
echo_protocol, []
).在某些情况下, 并不总是期望某个连接被计入 max_connections, 例如长连接和短连接混用的时候.
要删除连接计数, 从连接进程内调用 ranch:remove_connection/1, 唯一的参数为监听器的名字.
ranch:remove_connection(Ref).可以通过 ranch:set_max_connections/2 设置监听器的最大连接数
ranch:set_max_connections(tcp_echo, MaxConns).修改即时生效.
使用 Supervisor 作为连接进程
Ranch allows you to define the type of process that will be used for the connection processes. By default it expects a worker. When the connection_type configuration value is set to supervisor, Ranch will consider that the connection process it manages is a supervisor and will reflect that in its supervision tree.
Ranch 可以定义用于连接进程的进程类型. 默认为 worker 类型. 当 connection_type 的值设置为 supervisor 时, Ranch 会认为它所管理的连接进程是一个 Supervisor, 并且挂载到监控树中.
Connection processes of type supervisor can either handle the socket directly or through one of their children. In the latter case the start function for the connection process must return two pids: the pid of the supervisor you created (that will be supervised) and the pid of the protocol handling process (that will receive the socket).
supervisor 类型的连接进程能够直接处理套接字, 或者通过其子进程处理套接字. 对于通过其子进程处理套接字, 连接进程的 start 函数必须返回两个 pid: 你创建的 supervisor 的 (被监听器监控的) pid 和 协议处理进程的 pid(接收套接字).
Instead of returning {ok, ConnPid}, simply return {ok, SupPid, ConnPid}.
这种情况下, 返回的 是 {ok, SupPid, ConnPid} 而不是 {ok, ConnPid}
It is very important that the connection process be created under the supervisor process so that everything works as intended. If not, you will most likely experience issues when the supervised process is stopped.
升级
Ranch 允许在运行时升级协议选项. 这对后续的连接立马生效.
要升级协议选项, 需要调用 ranch:set_protocol_options/2 函数, 监听器的名称作为第一个参数, 新的选项作为第二个参数.
升级协议选项
ranch:set_protocol_options(tcp_echo, NewOpts).所有后续建立的连接将会使用新的选项
也可以调用 ranch:get_protocol_options/1 获取当前的协议选项.
获取当前的协议选项
Opts = ranch:get_protocol_options(tcp_echo).参考资料
https://github.com/ninenines/ranch/blob/master/doc/src/guide/listeners.asciidoc
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transmission_Control_Protocol#Protocol_operation
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。