原文链接:22 Essential CSS Recipes
更多译文将陆续推出,欢迎点赞+收藏+关注我的专栏,未完待续……
大家好,今天我们将会介绍一些非常实用的CSS小技巧,让我们开始吧!
混合模式
不久之前Firefox和Safari浏览器已经开始支持类似Photoshop的混合模式,但是在Chrome和Opera浏览器中需要添加前缀。举个栗子:
// 你也可以尝试不同的样式
.blend {
background: #fff;
}
.blend img {
mix-blend-mode: darken;
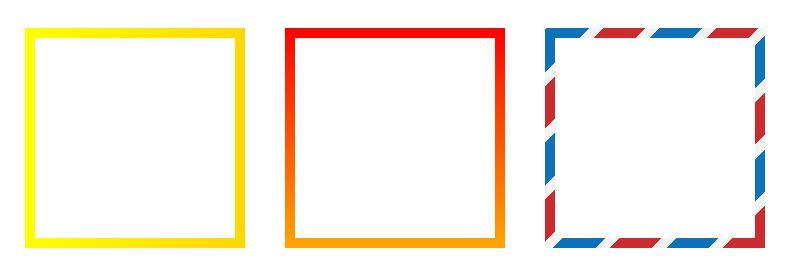
}渐变边框
现在,你甚至可以在边框中使用渐变。
要使用渐变边框非常简单,只需要设置一个更低z-index的伪元素即可:
.box {
margin: 80px 30px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: relative;
background: #fff;
float: left;
}
.box:before {
content: '';
z-index: -1;
position: absolute;
width: 220px;
height: 220px;
top: -10px;
left: -10px;
background-image: linear-gradient(90deg, yellow, gold);
}具体的例子可以看这里,或者看这里使用的是background-clip和background-origin属性。在不久的将来,也许所有浏览器都将支持border-image属性,最终的代码会和下面一样:
.box {
border-image: linear-gradient(to bottom, #000000 0%, #FFFFFF 100%);
border-image-slice: 1; /* set internal offset */
}z-index的过渡
也许你不知道z-index同样支持过渡!在过渡的每一步中,它的值都不发生改变,所以你以为它不支持过渡——但其实它支持。
举个栗子
currentColor
我们可以使用这个方法来侦测当前的颜色,以避免经常地重复定义它。
这个方法在使用SVG图标的时候非常有用,因为它们的颜色由其父元素决定。通常我们是这么做的:
.button {
color: black;
}
.button:hover {
color: red;
}
.button:active {
color: green;
}
.button svg {
fill: black;
}
.button:hover svg {
fill: red;
}
.button:active svg {
fill: green;
}但我们可以使用currentColor这么做:
svg {
fill: currentColor;
}
.button {
color: black;
border: 1px solid currentColor;
}
.button:hover {
color: red;
}
.button:active {
color: green;
}附上其它带有伪元素的例子:
a {
color: #000;
}
a:hover {
color: #333;
}
a:active {
color: #666;
}
a:after,
a:hover:after,
a:active:after {
background: currentColor;
...
}Object Fit
你是否还记得为了解决一些问题而给一幅背景图设置background-size属性的时刻呢?现在你可以使用object-fit属性啦,webkit浏览器都支持它,Firefox也将在近期予以支持。
.image__contain {
object-fit: contain;
}
.image__fill {
object-fit: fill;
}
.image__cover {
object-fit: cover;
}
.image__scale-down {
object-fit: scale-down;
}单选框和复选框的样式
让我们一起不使用图片来设置复选框的样式:
<!-- html -->
<input type="checkbox" id="check" name="check" />
<label for="check">Checkbox</label><!-- css -->
input[type=checkbox] {display: none;}
input[type=checkbox] + label:before {
content: "";
border: 1px solid #000;
font-size: 11px;
line-height: 10px;
margin: 0 5px 0 0;
height: 10px;
width: 10px;
text-align: center;
vertical-align: middle;
}
input[type=checkbox]:checked + label:before {
content: "\2713";
}
正如你所看见的,我们隐藏了原有的复选框,改为使用伪元素和伪类:checked(IE9+)来表现它。当它被选中时,一个设置在content里的Unicode编码的字符将会显示出来。
值得注意的是,Unicode编码在CSS和HTML中的写法是不一样的。在CSS中它是一个以反斜杠为开始的十六进制数,而在HTML中它是十进制的,比如
✓。
接着为我们的复选框添加一些动画效果:
<!-- checkbox -->
input[type=checkbox] + label:before {
content: "\2713";
color: transparent;
transition: color ease .3s;
}
input[type=checkbox]:checked + label:before {
color: #000;
}
<!-- radio -->
input[type=radio] + label:before {
content: "\26AB";
border: 1px solid #000;
border-radius: 50%;
font-size: 0;
transition: font-size ease .3s;
}
input[type=radio]:checked + label:before {
font-size: 10px;
}CSS中的计数器
总所周知CSS中是可以使用计数器的:
<!-- html -->
<ol class="list">
<li>a</li>
<li>b</li>
<li>c</li>
</ol> <!-- css -->
.list {
counter-reset: i; //reset conunter
}
.list > li {
counter-increment: i; //counter ID
}
.list li:after {
content: "[" counter(i) "]"; //print the result
}我们定义了一个ID在counter-reset属性中作为初始值(默认为0)。你可以设置另一个值在counter-increment属性中作为每一步的递增值。
高级CSS计数器
你可以计算出有多少个复选框被用户勾选了:
<!-- html -->
<div class="languages">
<input id="c" type="checkbox"><label for="c">C</label>
<input id="C++" type="checkbox"><label for="C++">C++</label>
<input id="C#" type="checkbox"><label for="C#">C#</label>
<input id="Java" type="checkbox"><label for="Java">Java</label>
<input id="JavaScript" type="checkbox"><label for="JavaScript">JavaScript</label>
<input id="PHP" type="checkbox"><label for="PHP">PHP</label>
<input id="Python" type="checkbox"><label for="Python">Python</label>
<input id="Ruby" type="checkbox"><label for="Ruby">Ruby</label>
</div>
<p class="total">
Total selected:
</p> <!-- css -->
.languages {
counter-reset: characters;
}
input:checked {
counter-increment: characters;
}
.total:after {
content: counter(characters);
} 你也可以制作一个简单的计算器:
<!-- html -->
<div class="numbers">
<input id="one" type="checkbox"><label for="one">1</label>
<input id="two" type="checkbox"><label for="two">2</label>
<input id="three" type="checkbox"><label for="three">3</label>
<input id="four" type="checkbox"><label for="four">4</label>
<input id="five" type="checkbox"><label for="five">5</label>
<input id="one-hundred" type="checkbox"><label for="one-hundred">100</label>
</div>
<p class="sum">
Sum
</p> <!-- css -->
.numbers {
counter-reset: sum;
}
#one:checked { counter-increment: sum 1; }
#two:checked { counter-increment: sum 2; }
#three:checked { counter-increment: sum 3; }
#four:checked { counter-increment: sum 4; }
#five:checked { counter-increment: sum 5; }
#one-hundred:checked { counter-increment: sum 100; }
.sum::after {
content: '= ' counter(sum);
} 不使用图片的菜单图标
你记得你有多么经常被迫需要一个“汉堡”图标吗?
这里有至少3个方式去实现它:
1、 Shadows
.shadow-icon {
position: relative;
}
.shadow-icon:after {
content: "";
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: -50px;
height: 100%;
width: 100%;
box-shadow: 0 5px 0 #000, 0 15px 0 #fff, 0 25px 0 #000, 0 35px 0 #fff, 0 45px 0 #000;
}2、 Gradient
.gradient-icon {
background: linear-gradient(to bottom, #000 0%, #000 20%, transparent 20%, transparent 40%, #000 40%, #000 60%, transparent 60%, transparent 80%, #000 80%, #000 100%);
}3、 UTF-8
你可以直接使用标准符号:☰ (Unicode: U+2630, HTML: ☰)。你也可以像其他元素那样灵活设置它的颜色或大小。看例子。
你也可以使用SVG,字体图标,或者通过伪元素设置的border边框。
@Supports
这是一个新的叫做supports的CSS表达式。顾名思义,它可以检测某些设定是否被浏览器所支持,并非所有的浏览器都支持它,但是你仍然可以使用它作为基本的检测手段:
@supports (display: flex) {
div { display: flex; }
}
/*You can check prefixes*/
@supports (display: -webkit-flex) or (display: -moz-flex) or (display: flex) {
section {
display: -webkit-flex;
display: -moz-flex;
display: flex;
float: none;
}
}visibility: visible
依你估计,把一个设置为visibility: visible的元素放在一个设置为visibility: hidden的元素里面,会发生什么?
.hidden {
visibility: hidden;
}
.hidden .visible {
visibility: visible;
}你可能会认为两个元素都不显示——然而事实上整个父元素都被隐藏了,而子元素不会。请看DEMO。
position: sticky
我们发现了一个新的特性,你可以新建一个sticky属性的元素。它的运行效果和fixed相同,但不会挡住任何元素。你最好看看例子
只有Mozilla和Safari浏览器支持这一属性,但你也可以像下面那样使用它:
.sticky {
position: static;
position: sticky;
top: 0px;
}我们将会在支持的浏览器中得到一个sticky属性的元素,而在不支持的浏览器中它将会是一个普通的元素。这在你需要建立一个不可替代的,可以移动的元素的移动端页面的时候非常实用。
新的尺寸单位
不久之前,一些新的用以描述不同元素大小的尺寸单位问世了,它们是:
vw (viewport width) - 浏览器窗口宽度的1%。
vh (viewport height) - 同上,只不过用来描述高度。
vmin and vmax 设置介于vh和vw之间的最大最小值。
有趣的是,几乎所有的现代浏览器都能很好地支持它们,所以你可以放心地使用。
为什么我们需要这些新的单位?因为它们可以让不同的尺寸更容易被定义,你不要为父元素指定任何的百分比或者别的什么,请看例子:
.some-text {
font-size: 100vh;
line-height: 100vh;
}
或者你可以设置一个漂亮的弹出框在屏幕中间:
.blackSquare {
background: black;
position: fixed;
height: 50vh;
width: 50vw;
left: 25vw;
top: 25vh;
}这看起来酷毙了,看看在codepen的例子吧~
但是目前仍然有一些关于这些新单位的不足之处:
IE9应该用vm而不是vmin。
iOS7在使用vh的时候可能会有bug。
vmax至今并未得到全面的支持。
文字修饰
我们可以通过几行代码修改文字被选中时的效果:
*::selection {
color: #fff;
background: #000;
}
*::-moz-selection {
/*Only Firefox still needs a prefix*/
color: #fff;
background: #000;
}你不仅可以定义文字被选中时的颜色,还能定义阴影或者背景颜色。
触摸屏当中的元素滚动
如果你需要在触摸屏当中为一些元素设置内滚动,那么你不仅需要overflow: scroll / auto ,还需要-webkit-overflow-scrolling: touch;
实际上,移动端浏览器在某些时候并不能正确执行overflow: scroll / auto ,它可能会滚动整个页面而不是你想要的那部分。-webkit-overflow-scrolling解决了这个问题,你可以在你的实际项目中体验一下。
使用硬件加速
有时候动画可能会导致用户的电脑卡顿,你可以在特定元素中使用硬件加速来避免这个问题:
.block {
transform: translateZ(0);
}你并不会察觉有什么不同,但浏览器会为这个元素进行3D硬件加速,在will-change这个特殊属性未被全面支持之前,这个方法还是很有用的。
Unicode Classes
你可以用Unicode符号明名class:
.❤ {
...
}
.☢ {
...
}
.☭ {
...
}
.★ {
...
}
.☯ {
...
}但这其实是用来搞笑的,千万不要在大型项目中使用,因为不是所有的电脑都支持Unicode符号。
垂直方向的百分比边距
实际上垂直方向的排列计算是基于父元素的宽度而不是高度。定义两个元素:
<!-- html -->
<div class="parent">
<div class="child"></div>
</div> <!-- css -->
.parent {
height: 400px;
width: 200px;
}
.child {
height: 50%;
padding-top: 25%;
padding-bottom: 25%;
width: 100%;
}理论上,子元素的高会是父元素高的一半,但是看看我们实际得到的情况:
记住,子元素的百分比是相对于父元素的宽度。
火狐浏览器的按钮边距
Firefox用它自己的方式去计算按钮的边距。这听起来有点奇怪,但它会自动地添加一些边距进去:
可以用以下方法来修复这个问题:
button::-moz-focus-inner,
input[type="reset"]::-moz-focus-inner,
input[type="button"]::-moz-focus-inner,
input[type="submit"]::-moz-focus-inner {
border: none;
padding:0;
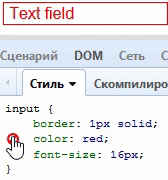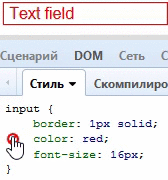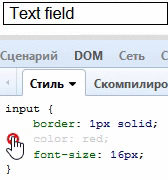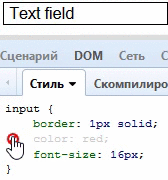
}Color + Border = Border-Color
很少人知道,定义了一个元素的文字颜色,意味着这个元素的边框颜色也被定义了:
input[type="text"] {
color: red;
border: 1px solid;
}古老浏览器的彩蛋
如果你仍需要适配IE7或者类似的古老浏览器,你可以在定义hack的时候使用笑脸符号,像这样:
body {
:) background: pink;
}是不是很有趣?
如果你觉得我翻译得不错,请点赞收藏并关注我的专栏,我会陆续推出更多精彩的内容。如发现任何的错漏欢迎指正,我们下次见!











**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。