1、Plist 文件概述
直接将数据直接写在代码里面,不是一种合理的做法。如果数据经常改,就要经常翻开对应的代码进行修改, 造成代码扩展性低。
因此,可以考虑将经常变的数据放在文件中进行存储,程序启动后从文件中读取最新的数据。如果要变动数 据,直接修改数据文件即可,不用修改代码。
一般可以使用属性列表文件存储 NSArray 或者 NSDictionary 之类的数据,这种属性列表文件的扩展名是 plist, 因此也成为“Plist 文件”。
2、创建 Plist 文件
在创建 Plist 文件的时候要特别注意名称当中不能带“info”,如果带了“info”会导致 xcode 把它误当作一个项 目中某个文件而出现问题。,导致文件加载不进来。
3、 解析Plist文件
(1)获得 Plist 文件的全路径
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
NSString *path =
[bundle pathForResource:@"imageData(文件名)" ofType:@"plist(扩展名)"];(2)加载 plist 文件
//如果从网络加载可以用:
//_images = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfUrl:url];
_images = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
- (NSArray *)images
{
if (_images == nil)
{
//可以利用 mainBundle 获取手机里面的任何资源
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
NSString *path =
[bundle pathForResource:@"imageData" ofType:@"plist"]; self.imageData = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
}
return _images;
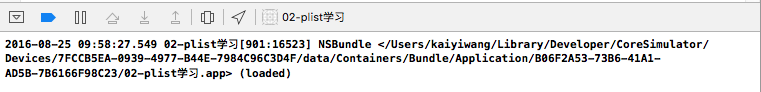
}打印项目所在Mac的路径:
// 获得项目的路径
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
NSLog(@"%@", bundle);获得项目目录下的plist文件路径
// 获得项目目录下的plist文件路径
NSString *path = [bundle pathForResource:@"images" ofType:@"plist"];
NSLog(@"%@", path);
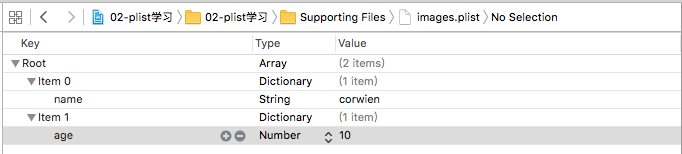
plist添加数据:
Root为数组类型,里边包含两个字典
完整代码:
//
// ViewController.m
// 02-plist学习
//
// Created by kaiyi wang on 16/8/25.
// Copyright © 2016年 Corwien. All rights reserved.
//
#import "ViewController.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 1.获得plist文件的全路径
NSBundle *bundle = [NSBundle mainBundle];
NSString *path = [bundle pathForResource:@"images" ofType:@"plist"];
// NSLog(@"%@", path);
NSArray *myPlist = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSLog(@"%@", myPlist); // 打印plist
// NSNumber *num = @0;
// 获取数组的第一个元素,字典类型
NSDictionary *mydict = [myPlist objectAtIndex:0];
NSLog(@"%@", mydict[@"name"]);
}
@end
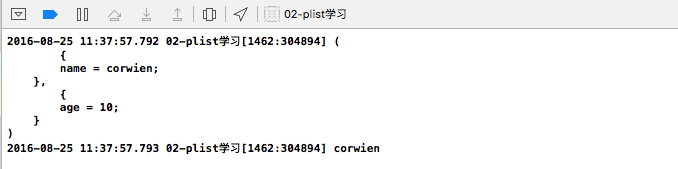
打印结果:
是把 plist 文件转成一个 NSArray,里面存放各 Dictionary。以后可以根据索引从 dictArray 中取出对应 Dictionary, 再根据字段取出对应数据。


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。