概述
DiffUtil是recyclerview support library v7 24.2.0版本中新增的类,根据Google官方文档的介绍,DiffUtil的作用是比较两个数据列表并能计算出一系列将旧数据表转换成新数据表的操作。这个概念比较抽象,换一种方式理解,DiffUtil是一个工具类,当你的RecyclerView需要更新数据时,将新旧数据集传给它,它就能快速告知adapter有哪些数据需要更新。
那么相比直接调用adapter.notifyDataSetChange()方法,使用DiffUtil有什么优势呢?它能在收到数据集后,提高UI更新的效率,而且你也不需要自己对新老数据集进行比较了。
顾名思义,凡是数据集的比较DiffUtil都能做,所以用处并不止于更新RecyclerView。DiffUtil也提供了回调让你可以进行其他操作。本文只介绍使用DiffUtil更新RecyclerView。
DiffUtil简介
在使用DiffUtil前我们先简单看看DiffUtil的特性。DiffUtil使用Eugene W. Myers的Difference算法来计算出将一个数据集转换为另一个的最小更新量,也就是用最简单的方式将一个数据集转换为另一个。除此之外,DiffUtil还可以识别一项数据在数据集中的移动。Eugene的算法对控件进行了优化,在查找两个数据集间最少加减操作时的空间复杂度为O(N),时间复杂度为O(N+D^2)。而如果添加了对数据条目移动的识别,复杂度就会提高到O(N^2)。所以如果数据集中数据不存在移位情况,你可以关闭移动识别功能来提高性能。当数据集较大时,你应该在后台线程计算数据集的更新。
如何使用
DiffUtil类
DiffUtil.Callback:这是最核心的类,你可以将它理解成比较新老数据集时的规则。
DiffUtil:通过静态方法
DiffUtil.calculateDiff(DiffUtil.Callback)来计算数据集的更新。DiffResult:是DiffUtil的计算结果对象,通过
DiffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(RecyclerView.Adapter)来进行更新。
代码模式为
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallBack(mDatas, newDatas), true);
mAdapter.setDatas(newDatas);
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);dispatchUpdatesTo()方法它会自动计算新老数据集的差异,并根据差异情况,自动调用以下四个方法
adapter.notifyItemRangeInserted(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemRangeRemoved(position, count);
adapter.notifyItemMoved(fromPosition, toPosition);
adapter.notifyItemRangeChanged(position, count, payload);DiffUtil.Callback抽象类
public abstract static class Callback {
/**
* 返回旧数据集的大小
*
* @return The size of the old list.
*/
public abstract int getOldListSize();
/**
* 返回新数据集的大小
*
* @return The size of the new list.
*/
public abstract int getNewListSize();
/**
* 比较两个Item对象是否是同一个对象
*
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list
* @return True if the two items represent the same object or false if they are different.
*/
public abstract boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition);
/**
* 比较两个Item对象的内容是否相同
* Called by the DiffUtil when it wants to check whether two items have the same data.
* DiffUtil uses this information to detect if the contents of an item has changed.
* <p>
* DiffUtil uses this method to check equality instead of {@link Object#equals(Object)}
* so that you can change its behavior depending on your UI.
* For example, if you are using DiffUtil with a
* {@link android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView.Adapter RecyclerView.Adapter}, you should
* return whether the items' visual representations are the same.
* <p>
* This method is called only if {@link #areItemsTheSame(int, int)} returns
* {@code true} for these items.
*
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list which replaces the
* oldItem
* @return True if the contents of the items are the same or false if they are different.
*/
public abstract boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition);
/**
* areItemsTheSame()返回true而areContentsTheSame()返回false时调用,也就是说两个对象代表的数据是一条,但是内容更新了。
* When {@link #areItemsTheSame(int, int)} returns {@code true} for two items and
* {@link #areContentsTheSame(int, int)} returns false for them, DiffUtil
* calls this method to get a payload about the change.
* <p>
* For example, if you are using DiffUtil with {@link RecyclerView}, you can return the
* particular field that changed in the item and your
* {@link android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView.ItemAnimator ItemAnimator} can use that
* information to run the correct animation.
* <p>
* Default implementation returns {@code null}.
*
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list
*
* @return A payload object that represents the change between the two items.
*/
@Nullable
public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
return null;
}
}DiffUtil步骤
自定义类继承DiffUtil.Callback,通过重写特定方法给出数据比较逻辑。
调用
DiffUtil.calculateDiff(DiffUtil.Callback callback,boolean detectMove)来计算更新,得到DiffResult对象。第二个参数可省,意为是否探测数据的移动,是否关闭需要根据数据集情况来权衡。当数据集很大时,此操作可能耗时较长,需要异步计算。在UI线程中调用DiffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(RecyclerView.Adapter),而后Adapter的onBindViewHolder(RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder, int position, Listpayloads)。注意这个方法比必须覆盖的onBindViewHolder(RecyclerView.ViewHolder holder, int position)方法多一个参数payloads,而里面存储了数据的更新。
示例
初始化RecyclerView
新建一个Bean为Item:
package com.michael.materialdesign.bean;
/**
* Created by liuguoquan on 2016/10/18.
*/
public class Item {
public int id = 0;
public String name;
public Item(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}新建Adapter
public class DiffUtilAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<DiffUtilAdapter.DiffItemHolder> {
private Context mContext;
private List<Item> mDatas;
public DiffUtilAdapter(Context context, List<Item> datas) {
this.mContext = context;
this.mDatas = datas;
}
public void setDatas(List<Item> mDatas) {
this.mDatas = mDatas;
}
@Override public DiffItemHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.item_diff_util, parent, false);
return new DiffItemHolder(view);
}
@Override public void onBindViewHolder(DiffItemHolder holder, int position) {
Item info = mDatas.get(position);
holder.mInfo.setText(info.getName());
Log.d("lgq","onBindViewHolder");
}
//payloads就是DiffUtil.Callback中的getChangePayload方法返回的数据集
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(DiffItemHolder holder, int position, List<Object> payloads) {
if (payloads.isEmpty()) {
onBindViewHolder(holder,position);
} else {
//更新item
Bundle bundle = (Bundle) payloads.get(0);
for(String key : bundle.keySet()) {
switch (key) {
case "name":
holder.mInfo.setText((CharSequence) bundle.get(key));
break;
}
}
}
}
@Override public int getItemCount() {
return mDatas != null ? mDatas.size() : 0;
}
static class DiffItemHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
@BindView(R.id.info) TextView mInfo;
public DiffItemHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
ButterKnife.bind(this, itemView);
}
}
}初始化ReyclerView
private void initView() {
for(int i = 0; i < 20;i++) {
Item item = new Item(i,"liu"+i);
mDatas.add(item);
}
mAdapter = new DiffUtilAdapter(this,mDatas);
mList.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(this,LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL,false));
mList.setItemAnimator(new DefaultItemAnimator());
mList.setAdapter(mAdapter);
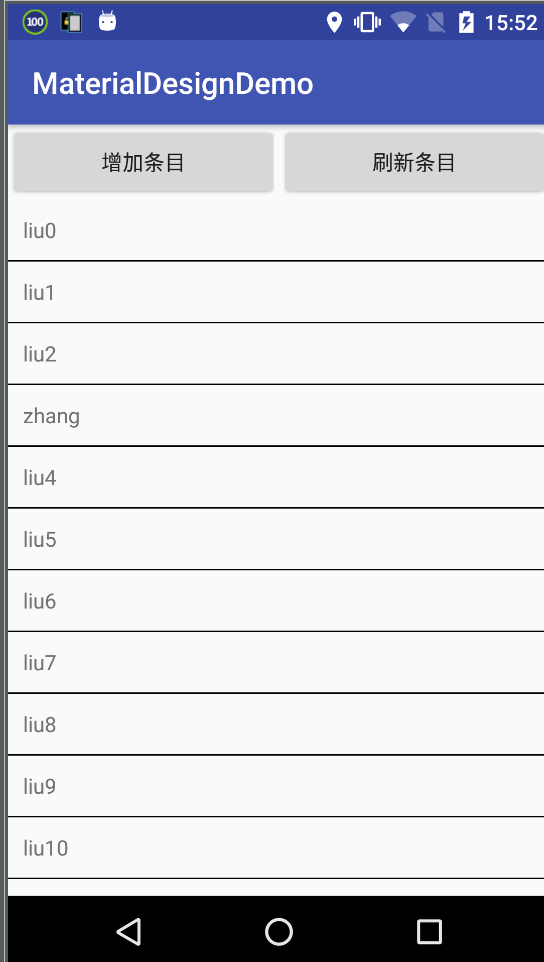
}初始化RecyclerView后效果为:
实现DiffUtil.Callback
新建类继承DiffUtil.Callback
private class DiffCallback extends DiffUtil.Callback {
private List<Item> mOldDatas;
private List<Item> mNewDatas;
//传入旧数据和新数据的集合
public DiffCallback(List<Item> oldDatas,List<Item> newDatas) {
this.mOldDatas = oldDatas;
this.mNewDatas = newDatas;
}
@Override public int getOldListSize() {
return mOldDatas != null ? mOldDatas.size() : 0;
}
@Override public int getNewListSize() {
return mNewDatas != null ? mNewDatas.size() : 0;
}
/**
* 被DiffUtil调用,用来判断 两个对象是否是相同的Item。
* 例如,如果你的Item有唯一的id字段,这个方法就 判断id是否相等。
* 本例判断id字段是否一致
*/
@Override public boolean areItemsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
boolean is = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition).id == mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition).id;
Log.d("lgq","areItemsTheSame " +oldItemPosition + " " + newItemPosition + " " + is);
return is;
}
/*
* 被DiffUtil调用,用来检查 两个item是否含有相同的数据
* 这个方法仅仅在areItemsTheSame()返回true时,才调用。
* @param oldItemPosition The position of the item in the old list
* @param newItemPosition The position of the item in the new list which replaces the
* oldItem
* @return True if the contents of the items are the same or false if they are different.
*/
@Override public boolean areContentsTheSame(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
String oldName = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition).getName();
String newName = mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition).getName();
Log.d("lgq","areContentsTheSame"
+ " " +oldName + " " + newName);
if (!oldName.equals(newName)) {
Log.d("lgq","false");
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
* areItemsTheSame()返回true而areContentsTheSame()返回false,也就是说两个对象代表的数据是一条,但是内容更新了。
* @param oldItemPosition
* @param newItemPosition
* @return
*/
@Nullable @Override public Object getChangePayload(int oldItemPosition, int newItemPosition) {
String oldItem = mOldDatas.get(oldItemPosition).getName();
String newItem = mNewDatas.get(newItemPosition).getName();
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
if (!oldItem.equals(newItem)) {
bundle.putString("name",newItem);
}
if (bundle.size() == 0) {
return null;
}
Log.d("lgq","getChangePayload");
return bundle;
}
}使用DiffUtil
下面通过两种不同的改变RecyclerView条目来介绍DiffUtil的使用。
增加或删除条目
这种情况下,数据集的大小改变,反映在RecyclerView的效果就是增加或者删除条目
private void add() {
mNewDatas.clear();
mNewDatas.addAll(mDatas);
mNewDatas.add(new Item(89,"xiao"));
mNewDatas.add(new Item(90,"xia"));
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallback(mDatas,mNewDatas),true);
mAdapter.setDatas(mNewDatas);
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);
mDatas.clear();
mDatas.addAll(mNewDatas);
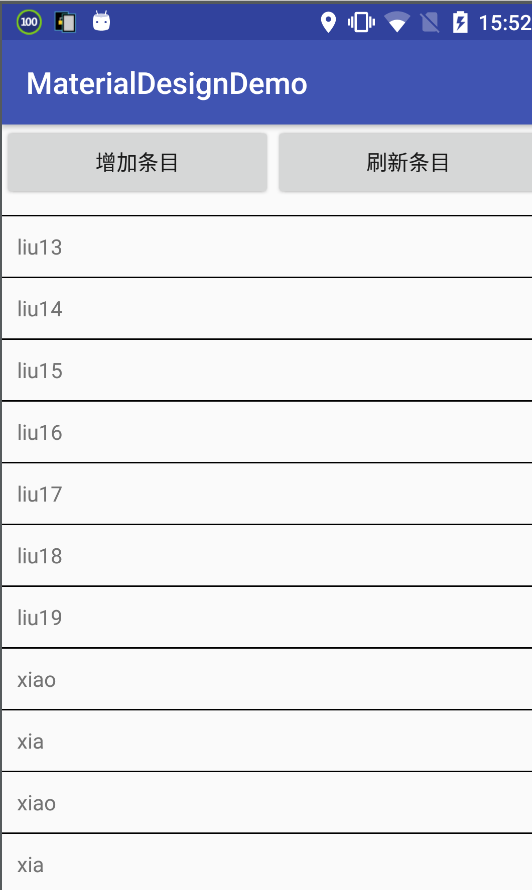
}增加条目后的RecyclerView的效果为:
更新具体的条目
这种情况下数据集大小不改变,改变数据集中条目的内容,反映在RecyclerView的效果就是更新具体的条目,这回调用Callback中的getChangePayload方法,而Adapter必须要实现public void onBindViewHolder(DiffItemHolder holder, int position, List<Object> payloads)方法。
private void refresh() {
mNewDatas.clear();
mNewDatas.addAll(mDatas);
//改变第三个位置的对象
Item item = new Item(3,"zhang");
mNewDatas.remove(3);
mNewDatas.add(3,item);
DiffUtil.DiffResult diffResult = DiffUtil.calculateDiff(new DiffCallback(mDatas,mNewDatas),true);
//将新数据给Adapter
mAdapter.setDatas(mNewDatas);
diffResult.dispatchUpdatesTo(mAdapter);
mDatas.clear();
mDatas.addAll(mNewDatas);
}更新条目后的RecyclerView效果为:
由图可知,第四个位置的条目显示变为zhang。
结语
DiffUtil可用于高效进行RecyclerView的数据更新,但DiffUtil本身的作用是计算数据集的最小更新。DiffUtil有强大的算法支撑,可以利用DiffUtil完成许多其他功能。
示例代码
参考文章:

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。