(更新时间 - 2017-03-20 9:00)
Inject 装饰器的作用
在 Angular 2 中,Inject 是参数装饰器,用来在类的构造函数中描述非 Type 类型的参数对象。
Angular 2 中 Type 类型:
// Type类型 - @angular/core/src/type.ts
export const Type = Function;
export function isType(v: any): v is Type<any> {
return typeof v === 'function';
}
export interface Type<T> extends Function { new (...args: any[]): T; }
Angular 2 中常用的非 Type 类型 Token:字符串、OpaqueToken对象、InjectionToken对象等。
/*
* 用于创建OpaqueToken实例
* export const CONFIG = new OpaqueToken('config');
*/
export class OpaqueToken {
constructor(protected _desc: string) {}
toString(): string { return `Token ${this._desc}`; }
}
/*
* 用于创建InjectionToken实例,使用泛型描述该Token所关联的依赖对象的类型
* const API_URL = new InjectionToken<string>('apiUrl');
*/
export class InjectionToken<T> extends OpaqueToken {
private _differentiate_from_OpaqueToken_structurally: any;
constructor(desc: string) { super(desc); }
toString(): string { return `InjectionToken ${this._desc}`; }
}
(备注:各种 Token 类型的区别,请参照 Angular 2 OpaqueToken & InjectionToken)
Inject 装饰器的使用
config.ts
export const CONFIG = new OpaqueToken('config');
app.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core';
@Injectable()
export class AppService {
constructor() { }
}
app.component.ts
import { Component, Inject, ViewChild, HostListener, ElementRef } from '@angular/core';
import { CONFIG } from './config';
import { AppService } from './app.service';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `<h1 #greet> Hello {{ name }} </h1>`,
})
export class AppComponent {
name = 'Angular';
@ViewChild('greet')
private greetDiv: ElementRef;
@HostListener('click', ['$event'])
onClick($event: any) {
console.dir($event);
}
constructor(public appService: AppService,
@Inject(CONFIG) config: any) {
}
}
编译后的 ES5 代码片段:
var __decorate = (this && this.__decorate) || function (decorators, target, key, desc) {...};
var __metadata = (this && this.__metadata) || function (k, v) {
if (typeof Reflect === "object" && typeof Reflect.metadata === "function")
return Reflect.metadata(k, v);
};
var __param = (this && this.__param) || function (paramIndex, decorator) {
return function (target, key) { decorator(target, key, paramIndex); }
};
var AppComponent = (function () {
// 构造函数
function AppComponent(appService, config) {
this.appService = appService;
this.name = 'Angular';
}
AppComponent = __decorate([
core_1.Component({ // 调用ComponentDecoratorFactory返回TypeDecorator
selector: 'my-app',
template: "<h1 #greet> Hello {{ name }} </h1>",
}),
// 调用ParamDecoratorFactory返回ParamDecorator
__param(1, core_1.Inject(config_1.CONFIG)),
// 保存构造函数参数的类型
__metadata('design:paramtypes', [app_service_1.AppService, Object])
], AppComponent);
return AppComponent;
}());
exports.AppComponent = AppComponent;
Inject 装饰器实现
Inject、InjectDecorator 接口及 Inject 函数:
// Inject接口定义
export interface Inject { token: any; }
// InjectDecorator接口定义
export interface InjectDecorator {
(token: any): any;
new (token: any): Inject; // 构造函数的签名
}
// Inject装饰器:即示例中转成ES5代码后的 core_1.Inject 对象 - core_1.Inject(config_1.CONFIG)
export const Inject: InjectDecorator = makeParamDecorator('Inject', [['token', undefined]]);
makeParamDecorator函数片段:
/*
* 创建ParamDecorator工厂
*
* 调用 makeParamDecorator('Inject', [['token', undefined]])后返回ParamDecoratorFactory
*/
function makeParamDecorator(name, props, parentClass) {
// name: 'Inject', props: [['token', undefined]]
// 创建Metadata构造函数
var metaCtor = makeMetadataCtor(props);
// __param(1, core_1.Inject(config_1.CONFIG))
function ParamDecoratorFactory() {
// 解析参数并创建annotationInstance实例
var args = [];
// arguments: {0: CONFIG}
for (var _i = 0; _i < arguments.length; _i++) {
args[_i - 0] = arguments[_i];
}
if (this instanceof ParamDecoratorFactory) {
// args: [CONFIG]
metaCtor.apply(this, args);
return this;
}
...
return ParamDecorator;
function ParamDecorator(cls, unusedKey, index) {
// 获取类已经定义的metadata信息
var parameters = Reflect.getOwnMetadata('parameters', cls) || [];
while (parameters.length <= index) {
parameters.push(null);
}
// parameters是一个二维数组,因为支持同时应用多个装饰器
// eg: @Inject(CONFIG) @Optional() @SkipSelf() config: any
parameters[index] = parameters[index] || [];
parameters[index].push(annotationInstance);
Reflect.defineMetadata('parameters', parameters, cls);
return cls;
}
var _a;
}
return ParamDecoratorFactory;
}
makeMetadataCtor 函数:
// 生成Metadata构造函数: var metaCtor = makeMetadataCtor(props);
// props: [['token', undefined]]
function makeMetadataCtor(props) {
return function ctor() {
/*
* metaCtor.apply(this, args);
*/
var _this = this;
var args = [];
for (var _i = 0; _i < arguments.length; _i++) {
args[_i - 0] = arguments[_i];
}
props.forEach(function (prop, i) { // prop: ['token', undefined]
var argVal = args[i];
if (Array.isArray(prop)) { // prop: ['token', undefined]
// prop[0]: token, argVal: CONFIG - {_desc: "config"}
_this[prop[0]] = argVal === undefined ? prop[1] : argVal;
}
else {
for (var propName in prop) {
_this[propName] =
argVal && argVal.hasOwnProperty(propName) ?
argVal[propName] : prop[propName];
}
}
});
};
}
接下来我们可以在控制台输入 window['__core-js_shared__'] ,查看通过 Reflect API 保存后的metadata信息
最后我们来了解一下,Angular 如何获取 AppComponent 构造函数中,通过 @Inject 装饰器设置的 metadata信息。
// @angular/core/src/reflection/reflection_capabilities.ts
export class ReflectionCapabilities implements PlatformReflectionCapabilities {
// 获取ParamDecorator函数中通过Reflect.defineMetadata('parameters', parameters, cls)
// 保存的metadata信息
parameters(type: Type<any>): any[][] {
if (!isType(type)) { return []; }
const parentCtor = getParentCtor(type);
let parameters = this._ownParameters(type, parentCtor);
if (!parameters && parentCtor !== Object) {
parameters = this.parameters(parentCtor);
}
return parameters || [];
}
}
private _ownParameters(type: Type<any>, parentCtor: any): any[][] {
/*
* constructor(
* public appService: AppService,
* @Inject(CONFIG) config: any) {
* }
*/
if (this._reflect != null && this._reflect.getOwnMetadata != null) {
// @Inject(CONFIG) config: any -> 'parameters'
const paramAnnotations = this._reflect.getOwnMetadata('parameters', type);
// appService: AppService -> 'design:paramtypes'
const paramTypes = this._reflect.getOwnMetadata('design:paramtypes', type);
if (paramTypes || paramAnnotations) {
return this._zipTypesAndAnnotations(paramTypes, paramAnnotations);
}
}
}
我有话说
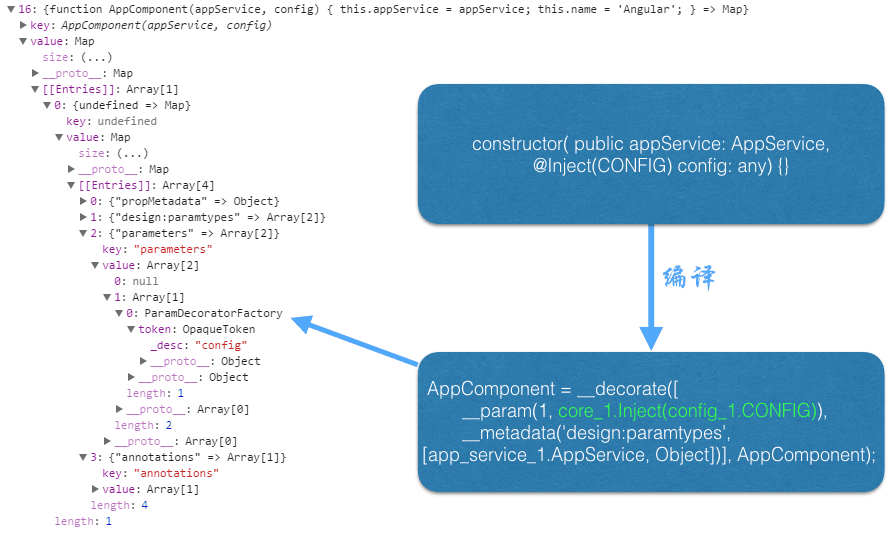
1.为什么在构造函数中,非 Type 类型的参数只能用 @Inject(Something) 的方式注入 ?
因为只有是 Type 类型的对象,才会被 TypeScript 编译器编译。具体参照下图:
2.为什么 TypeScript 会自动保存 metadata 信息 ?
因为我们在 tsconfig.json 文件中,进行如下配置:
{
"compilerOptions": {
...,
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true
}
}
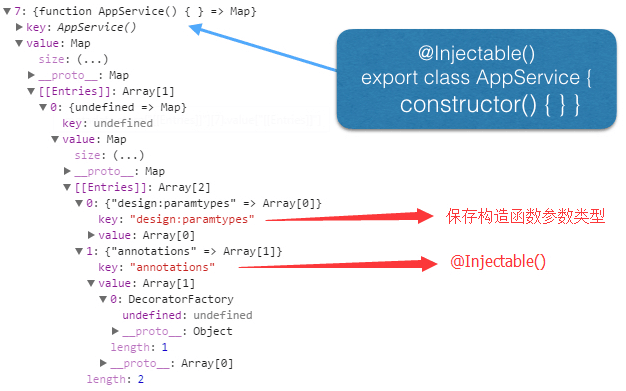
3.AppService 中 @Injectable() 是必须的么 ?
如果 AppService 不依赖于其他对象,是可以不用使用 Injectable 类装饰器。当 AppService 需要在构造函数中注入依赖对象,就需要使用 Injectable 类装饰器。比较推荐的做法不管是否有依赖对象,service 中都使用 Injectable 类装饰器。
4.Reflect 对象还有哪些方法 ?
Reflect
.defineMetadata(metadataKey, metadataValue, target, propertyKey?) -> void
.getMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey?) -> var
.getOwnMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey?) -> var
.hasMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey?) -> bool
.hasOwnMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey?) -> bool
.deleteMetadata(metadataKey, target, propertyKey?) -> bool
.getMetadataKeys(target, propertyKey?) -> array
.getOwnMetadataKeys(target, propertyKey?) -> array
.metadata(metadataKey, metadataValue) -> decorator(target, targetKey?) -> void
Reflect API 使用示例
var O = {};
Reflect.defineMetadata('foo', 'bar', O);
Reflect.ownKeys(O); // => []
Reflect.getOwnMetadataKeys(O); // => ['foo']
Reflect.getOwnMetadata('foo', O); // => 'bar'
5.使用 Reflect API 有什么好处 ?
使用 Reflect API 我们能够方便的对类相关的 metadata 信息进行保存和读取
Reflect API 把类相关的 metadata 信息保存在 window['__core-js_shared__'] 对象中,避免对类造成污染。
6.在构造函数中,Type 类型的参数能用 @Inject(Type) 的方式注入么?
Type 类型的参数也能使用 @Inject(Type) 的方式注入,具体如下:
constructor(@Inject(Http) private http) { }
同样也可以使用以下方式:
constructor(@Inject(Http) private http: Http) { }
第一种方式虽然可以正常编译,但 IDE 会有如下的提示信息:
[ts] Parameter 'http' implicitly has an 'any' type.
第二种方式,虽然 Angular 内部会合并 design:paramtypes 与 parameters 内的 metadata 信息,但本人觉得是有点冗余了。 总而言之,若果是 Type 类型的参数,推荐使用下面的方式:
constructor(private http: Http) { }
总结
本文通过一个示例,一步步分析 Inject 装饰器的作用及内部实现原理,此外我们还解释了在构造函数中为什么非 Type 类型的参数只能通过 @Inject(Something) 的方式注入及 Injectable装饰器的使用场景,最后我们还简单介绍了Reflect API。希望通过这篇文章,能让读者更好地理解 Inject 装饰器。
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。