理解Store
1.什么是
Store?
上一篇文章说了,
Vuex就是提供一个仓库,Store仓库里面放了很多对象。其中state就是数据源存放地,对应于与一般Vue对象里面的data(后面讲到的actions和mutations对应于methods)。在使用
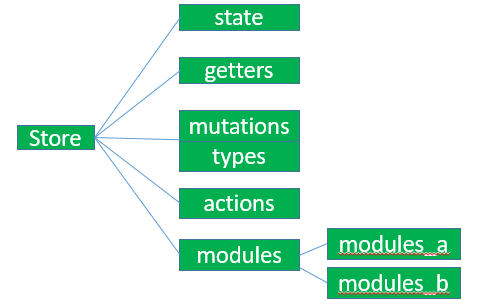
Vuex的时候通常会创建Store实例new Vuex.store({state,getters,mutations,actions})有很多子模块的时候还会使用到modules。总结,
Store类就是存储数据和管理数据方法的仓库,实现方式是将数据和方法已对象形式传入其实例中。要注意一个应用或是项目中只能存在一个Store实例!!
2.
Store源码分析
class Store{
constructor (options = {}) {
1.部分2个‘断言函数’判断条件
assert(Vue, `must call Vue.use(Vuex) before creating a store
instance.`) // 在Store实例化之前一定要确保Vue的存在
assert(typeof Promise !== 'undefined', `vuex requires a Promise polyfill in this browser.`)
//确保promise存在
2.结构赋值拿到options里面的state,plugins和strict
const {
state = {}, //rootState
plugins = [], // 插件
strict = false //是否严格模式
} = options
3.Store internal state创建store内部属性
this._options = options //存储参数
this._committing = false //标识提交状态,保证修改state只能在mutation里面,不能在外部随意修改
this._actions = Object.create(null) //存储用户定义的actions
this._mutations = Object.create(null) //存储用户定义的mutations
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null) //存储用户定义的getters
this._runtimeModules = Object.create(null) //存储运行时的modules
this._subscribers = [] //存储所有堵mutation变化的订阅者
this._watcherVM = new Vue() //借用Vue实例的方法,$watch来观测变化
4.将dispatch和commit的this指向当前store实例
const store = this
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)}
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)}}后面文章逐步分析每一个模块。
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。