Spring的核心思想是IOC(Inversion of Control),DI其实就是IOC的另外一种说法。所谓IoC,对于spring框架来说,就是由spring来负责控制对象的生命周期和对象间的关系。当一个对象需要使用其它对象时,通过Spring容器动态的向这个对象提供它所需要的其他对象。这一点是通过DI(Dependency Injection,依赖注入)来实现的。
这里提到Spring IOC主要是为了说明Spring IOC中的(Convention over configuration) -- 约定优于配置的一个体现,那就是类型转换。Spring把它包装得太好了,可能大家都没有意识到。我下面简单的举一个例子:
1、User.java -- 实体类
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer age;
// getter and setter
}2、beans.xml -- Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.carlzone.springboot.mybatis.User">
<property name="name" value="carl" />
<property name="age" value="27" />
</bean>
</beans>3、Main.java 测试类
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("test-beans.xml");
User user = context.getBean(User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}结果毫无疑问,控制台会把User类的name和age输出出来。但是大家有不有想过这样一个问题,在对象实体User中,我们的属性类型这里有String,也有Integer.当然这里举了2个简单的数据类型,Spring还支持更加复杂的数据类型。Spring是如何把我们配置在xml里面的属性转换成我们需要的类型呢?是不是之前没有想过这个问题,下面我们就来分析一下Spring内部是如何这个类型转换的。
1、缘由
其实我之前在看Spring 源码的时候,对于Spring IOC这块一直都看得不是很明白。直到之前看公司代码的时候让我看到了项目中使用了 FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean这个对象。其实这个对象是一个Factory Bean,如果大家对于这个概念不太明白可以看我之前的blog -- Spring bean 之 FactoryBean。通过对这个对象的源码分析让我明白了Spring的类型转换是如果实现的。
2、Type Conversion SPI
Spring从Spring 3开始新添加了一个包core.conver用来提供一般类型的转换系统。这个系统中定义了SPI在运行时期来实现类型转换逻辑。在Spring容器中,这个系统可以使用PropertyEditors把bean的属性值转换成需要的类型。同样的这个API同样会在你的应用中被使用到。下面我们来看一下Spring的类型转换API。
2.1 Converter SPI
这个SPI用于实现类型转换逻辑。
package org.springframework.core.convert.converter;
public interface Converter<S, T> {
T convert(S source);
} 2.2 Formatter SPI
Formatter SPI用于实现格式化逻辑。
package org.springframework.format;
public interface Formatter<T> extends Printer<T>, Parser<T> {
}Formatter是继承自Printer,Parser接口
public interface Printer<T> {
String print(T fieldValue, Locale locale);
}import java.text.ParseException;
public interface Parser<T> {
T parse(String clientValue, Locale locale) throws ParseException;
}不难看出虽然Format接口其实是Converter接口的一个子集,它只是类型转换的一种特例。
- Format : Printer接口实现 T -> String,而Parser接口实现 String -> T.
- Converter : 而Converter接口是实现 S -> T,从任意对象转换成任意对象。
这里只是简单的介绍了一下Spring关于的Spring Type Conversion与Spring Field Formatting接口方便后续的分析。如果大家想要了解更多详情可以查看Spring官网的介绍。下面我们就来看看Spring类型转换的内部实现。
3、Type Converter Internal
我们还是首先来看看我们最开始提到的类,FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean。最开始也说到这个类其实是一个FactoryBean。Spring IOC在进行容器初始的时候会通过它的getObject()获取到它想创建的对象。所以说我的目标就转换到了FormattingConversionService这个对象。其实Spring真正创建的对象是DefaultFormattingConversionService。下面我们就来看一下它的类继承体系。
3.1 相关接口与类
其实我们看类继承体系(e.g.:这里只画出了相关接口),主要还是看它实现的接口,这样就可以大概知道这个类干了哪些事。这个体系里面有4个接口。
- ConversionService:类型转换服务,提供判断类型之间是否可以转换,以及转换方法。
- ConverterRegistry :类型转换服务注册接口,提供类型转换服务的注册接口。
- ConfigurableConversionService:这个是个空接口,只是同时继承了ConversionService与ConverterRegistry接口。
- FormatterRegistry:Formatter服务接口注册接口。
其实这里最需要关注的还转换服务的注册以及转换服务的获取。在解释这2个方法之前,再来介绍2个类:
1、GenericConverter
格式转换包装类,包装Formatter以及Converter.内部类ConvertiblePair提供这两种的索引。
public interface GenericConverter {
Set<ConvertiblePair> getConvertibleTypes();
Object convert(Object source, TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
final class ConvertiblePair {
private final Class<?> sourceType;
private final Class<?> targetType;
public ConvertiblePair(Class<?> sourceType, Class<?> targetType) {
Assert.notNull(sourceType, "Source type must not be null");
Assert.notNull(targetType, "Target type must not be null");
this.sourceType = sourceType;
this.targetType = targetType;
}
public Class<?> getSourceType() {
return this.sourceType;
}
public Class<?> getTargetType() {
return this.targetType;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object other) {
if (this == other) {
return true;
}
if (other == null || other.getClass() != ConvertiblePair.class) {
return false;
}
ConvertiblePair otherPair = (ConvertiblePair) other;
return (this.sourceType == otherPair.sourceType && this.targetType == otherPair.targetType);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (this.sourceType.hashCode() * 31 + this.targetType.hashCode());
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return (this.sourceType.getName() + " -> " + this.targetType.getName());
}
}
}2、ConditionalConverter
转换条件类,判断这个GenericConverter对象是否可以进行转换。
public interface ConditionalConverter {
boolean matches(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType);
}3.2 注册
其实类型转换的具体实现是在分为Formatter与Converter的注册。
- Converter的注册发生在GenericConversionService类中。也就是里面各种不同的重载方法
addConverter(). - Formatter的注册发生在FormattingConversionService类中。也就是里面各种不同的
addFormatterXXX()方法。
它会把这两个接口的实现都会转换成上面提到的GenericConverter接口实现,并且注册到GenericConversionService.Converters对象中,里面有2个属性。converters与globalConverters这两个属性中。
private static class Converters {
private final Set<GenericConverter> globalConverters = new LinkedHashSet<GenericConverter>();
private final Map<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair> converters =
new LinkedHashMap<ConvertiblePair, ConvertersForPair>(36);
public void add(GenericConverter converter) {
Set<ConvertiblePair> convertibleTypes = converter.getConvertibleTypes();
if (convertibleTypes == null) {
Assert.state(converter instanceof ConditionalConverter,
"Only conditional converters may return null convertible types");
this.globalConverters.add(converter);
}
else {
for (ConvertiblePair convertiblePair : convertibleTypes) {
ConvertersForPair convertersForPair = getMatchableConverters(convertiblePair);
convertersForPair.add(converter);
}
}
}
public GenericConverter find(TypeDescriptor sourceType, TypeDescriptor targetType) {
// Search the full type hierarchy
List<Class<?>> sourceCandidates = getClassHierarchy(sourceType.getType());
List<Class<?>> targetCandidates = getClassHierarchy(targetType.getType());
for (Class<?> sourceCandidate : sourceCandidates) {
for (Class<?> targetCandidate : targetCandidates) {
ConvertiblePair convertiblePair = new ConvertiblePair(sourceCandidate, targetCandidate);
GenericConverter converter = getRegisteredConverter(sourceType, targetType, convertiblePair);
if (converter != null) {
return converter;
}
}
}
return null;
}
}当你实现Formatter、Converter接口时,它会把转换接口以转换源对象sourceType(Class<?>)与转换目标对象targetType(Class<?>)生成ConvertiblePair对象插入到一个converters属性中。如果你实现GenericConverter接口分为两种情况:
1) 如果实现的getConvertibleTypes()返回你需要转换的源对象与目标对象构成的Set<ConvertiblePair>不为空。它就会把转换对象添加到converters属性中。
2) 如果实现的getConvertibleTypes()返回你需要转换的源对象与目标对象构成的Set<ConvertiblePair>为空。它会检查它的类型是不是ConditionalConverter。所以如果你要实现GenericConverter并且实现getConvertibleTypes()方法返回为空,那么你同时需要实现ConditionalConverter。Spring提供了实现了这2个接口的接口ConditionalGenericConverter,你只需要实现它就行了。而且它会把这个转换器添加到globalConverters属性中。
3.3 查询
在Spring中的自定义转换中,当首先会查询GenericConversionService.Converters中的converters属性,然后才会查询GenericConversionService.Converters中的globalConverters属性。所以说实现ConditionalGenericConverter的方法getConvertibleTypes()如果返回为空,那么它就是一个备胎。
4、Spring IOC Type Converter
Spring IOC在进行类型转换的时候最终会调用在TypeConverterDelegate类的convertIfNecessary方法。下面我们来看一这个方法的具体实现。
class TypeConverterDelegate {
public <T> T convertIfNecessary(String propertyName, Object oldValue, Object newValue,
Class<T> requiredType, TypeDescriptor typeDescriptor) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// Custom editor for this type?
PropertyEditor editor = this.propertyEditorRegistry.findCustomEditor(requiredType, propertyName);
ConversionFailedException conversionAttemptEx = null;
// No custom editor but custom ConversionService specified?
ConversionService conversionService = this.propertyEditorRegistry.getConversionService();
if (editor == null && conversionService != null && newValue != null && typeDescriptor != null) {
TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue);
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) {
try {
return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor);
}
catch (ConversionFailedException ex) {
// fallback to default conversion logic below
conversionAttemptEx = ex;
}
}
}
Object convertedValue = newValue;
// Value not of required type?
if (editor != null || (requiredType != null && !ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue))) {
if (typeDescriptor != null && requiredType != null && Collection.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType) &&
convertedValue instanceof String) {
TypeDescriptor elementTypeDesc = typeDescriptor.getElementTypeDescriptor();
if (elementTypeDesc != null) {
Class<?> elementType = elementTypeDesc.getType();
if (Class.class == elementType || Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(elementType)) {
convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue);
}
}
}
if (editor == null) {
editor = findDefaultEditor(requiredType);
}
convertedValue = doConvertValue(oldValue, convertedValue, requiredType, editor);
}
boolean standardConversion = false;
if (requiredType != null) {
// Try to apply some standard type conversion rules if appropriate.
if (convertedValue != null) {
if (Object.class == requiredType) {
return (T) convertedValue;
}
else if (requiredType.isArray()) {
// Array required -> apply appropriate conversion of elements.
if (convertedValue instanceof String && Enum.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType.getComponentType())) {
convertedValue = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) convertedValue);
}
return (T) convertToTypedArray(convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType.getComponentType());
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Collection) {
// Convert elements to target type, if determined.
convertedValue = convertToTypedCollection(
(Collection<?>) convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType, typeDescriptor);
standardConversion = true;
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Map) {
// Convert keys and values to respective target type, if determined.
convertedValue = convertToTypedMap(
(Map<?, ?>) convertedValue, propertyName, requiredType, typeDescriptor);
standardConversion = true;
}
if (convertedValue.getClass().isArray() && Array.getLength(convertedValue) == 1) {
convertedValue = Array.get(convertedValue, 0);
standardConversion = true;
}
if (String.class == requiredType && ClassUtils.isPrimitiveOrWrapper(convertedValue.getClass())) {
// We can stringify any primitive value...
return (T) convertedValue.toString();
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof String && !requiredType.isInstance(convertedValue)) {
if (conversionAttemptEx == null && !requiredType.isInterface() && !requiredType.isEnum()) {
try {
Constructor<T> strCtor = requiredType.getConstructor(String.class);
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(strCtor, convertedValue);
}
catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
// proceed with field lookup
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No String constructor found on type [" + requiredType.getName() + "]", ex);
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Construction via String failed for type [" + requiredType.getName() + "]", ex);
}
}
}
String trimmedValue = ((String) convertedValue).trim();
if (requiredType.isEnum() && "".equals(trimmedValue)) {
// It's an empty enum identifier: reset the enum value to null.
return null;
}
convertedValue = attemptToConvertStringToEnum(requiredType, trimmedValue, convertedValue);
standardConversion = true;
}
else if (convertedValue instanceof Number && Number.class.isAssignableFrom(requiredType)) {
convertedValue = NumberUtils.convertNumberToTargetClass(
(Number) convertedValue, (Class<Number>) requiredType);
standardConversion = true;
}
}
else {
// convertedValue == null
if (javaUtilOptionalEmpty != null && requiredType == javaUtilOptionalEmpty.getClass()) {
convertedValue = javaUtilOptionalEmpty;
}
}
if (!ClassUtils.isAssignableValue(requiredType, convertedValue)) {
if (conversionAttemptEx != null) {
// Original exception from former ConversionService call above...
throw conversionAttemptEx;
}
else if (conversionService != null) {
// ConversionService not tried before, probably custom editor found
// but editor couldn't produce the required type...
TypeDescriptor sourceTypeDesc = TypeDescriptor.forObject(newValue);
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor)) {
return (T) conversionService.convert(newValue, sourceTypeDesc, typeDescriptor);
}
}
// Definitely doesn't match: throw IllegalArgumentException/IllegalStateException
StringBuilder msg = new StringBuilder();
msg.append("Cannot convert value of type '").append(ClassUtils.getDescriptiveType(newValue));
msg.append("' to required type '").append(ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType)).append("'");
if (propertyName != null) {
msg.append(" for property '").append(propertyName).append("'");
}
if (editor != null) {
msg.append(": PropertyEditor [").append(editor.getClass().getName()).append(
"] returned inappropriate value of type '").append(
ClassUtils.getDescriptiveType(convertedValue)).append("'");
throw new IllegalArgumentException(msg.toString());
}
else {
msg.append(": no matching editors or conversion strategy found");
throw new IllegalStateException(msg.toString());
}
}
}
if (conversionAttemptEx != null) {
if (editor == null && !standardConversion && requiredType != null && Object.class != requiredType) {
throw conversionAttemptEx;
}
logger.debug("Original ConversionService attempt failed - ignored since " +
"PropertyEditor based conversion eventually succeeded", conversionAttemptEx);
}
return (T) convertedValue;
}
}这个Spring IOC类型转换分为以下4个步骤:
- 通过Java中的PropertyEditor的内省机制对Spring的对象属性进行类型转换
- 通过Spring中的ConversionService的自定义类型转换实现对象属性进行类型转换
- 通过一般类型判断对对象的属性进行类型转换(Array, Collection, Map, String, Number, Optional)
- 报错(不遵循COC -- 约定大于配置)。
5、应用
在Spring通过它的约定大于配置,它帮助我们实现了一些默认的类型转换。具体的默认的类型转换在DefaultFormattingConversionService接口。可以如果你的包依赖中没有joda-time,Spring就不会提供String转换Date的转换服务。下面我们就来自定义类型转换服务:
5.1 Order.java -- 实体类
public class Order {
private Date createDt;
public Date getCreateDt() {
return createDt;
}
public void setCreateDt(Date createDt) {
this.createDt = createDt;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Order{" +
"createDt=" + createDt +
'}';
}
}5.2 StringToDateConverter -- 实现Formatter接口
public class StringToDateConverter implements Formatter<Date> {
private String pattern;
public StringToDateConverter(String pattern) {
this.pattern = pattern;
}
@Override
public Date parse(String text, Locale locale) throws ParseException {
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern, locale);
return dateFormat.parse(text);
}
@Override
public String print(Date date, Locale locale) {
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat(pattern, locale);
return dateFormat.format(date);
}
}5.3 ConverterController.java
@RestController
public class ConverterController {
@InitBinder
public void init(DataBinder dataBinder){
dataBinder.addCustomFormatter(new StringToDateConverter("yyyy-MM-dd"));
}
@RequestMapping("converter")
public Order converter(Order order){
return order;
}
}5.4 SpringBootMybatisApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootMybatisApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootMybatisApplication.class, args);
}
}5.4 测试
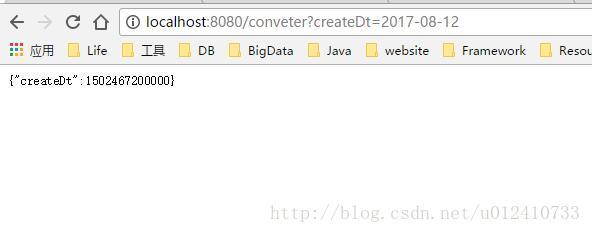
通过访问http://localhost:8080/conveter?createDt=2017-08-12,根据以上的测试代码就会返回以下的结果。
在Spring MVC中因为前端HttpServletRequest的传值只会涉及到String,所以在Spring MVC在进行数据绑定的时候只开放的Formatter接口,而没有开放Converter接口。
但是我们可以使用FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean来注册Converter接口。
public class FormattingConversionServiceFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<FormattingConversionService>, EmbeddedValueResolverAware, InitializingBean {
private Set<?> converters;
private Set<?> formatters;
private Set<FormatterRegistrar> formatterRegistrars;
}它可以注册Converter与Formatter接口.Spring会在容器开始依赖注入之前检测容器中是否有名称有conversionService,就会把conversionService设计到BeanFactory当中,当类型转换的时候就会把这个对象设置进去。
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}可以看到在代码最开始的时候就是判断容器是否有这个对象。如果有就设置到BeanFactory里面。代码的最后面才是Spring容器初始化单例bean的逻辑。
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。