本文对Vue和Vuex有一定基础的同学更容易掌握,如对Vue和Vuex不是很熟悉的同学,请先移步Vue官网自行学习
在这个教程中,我们会通过构建一个小米便签应用来学习怎么使用Vuex,开始我会简单的介绍Vuex的一些基础内容,什么时候使用以及用Vuex怎么组织代码,然后一步一步的把这些概念应用到小米便签应用里面。
废话不多说,先给大家看一下小米便签应用的截图:
你可以从GitHub上下载源码,这里是项目源代码的地址和在线预览地址,安装成功后推荐使用chrome的设备模式查看效果更佳。
Vuex概述
Vuex 是一个专门为 Vue.js 应用所设计的集中式状态管理架构,它借鉴了 Flux 和 Redux 的设计思想,但简化了概念,并且采用了一种为能更好发挥 Vue.js 数据响应机制而专门设计的实现。
如果你不太理解 Vue.js 应用里的状态是什么意思的话,你可以想象一下你此前写的 Vue 组件里面的 data 字段。Vuex 把状态分成组件内部状态和应用级别状态:
- 组件内部状态:仅在一个组件内使用的状态(data 字段)
- 应用级别状态:多个组件共用的状态
举个例子:比如说有一个父组件,它有两个子组件。这个父组件可以用 props 向子组件传递数据,这条数据通道很好理解。
那如果这两个子组件相互之间需要共享数据呢?或者子组件需要向父组件传递数据呢?这两个问题在应用体量较小的时候都好解决,只要用自定义事件即可。
但是随着应用规模的扩大:
- 追踪这些事件越来越难了。这个事件是哪个组件触发的?谁在监听它?
- 业务逻辑遍布各个组件,导致各种意想不到的问题。
- 由于要显式地分发和监听事件,父组件和子组件强耦合。
Vuex 要解决的就是这些问题,Vuex 背后有四个核心的概念:
- State: 包含所有应用级别状态的对象
- Getters: 在组件内部获取 store 中状态的函数
- Mutations: 修改状态的事件回调函数
- Actions: 组件内部用来分发 mutations 事件的函数
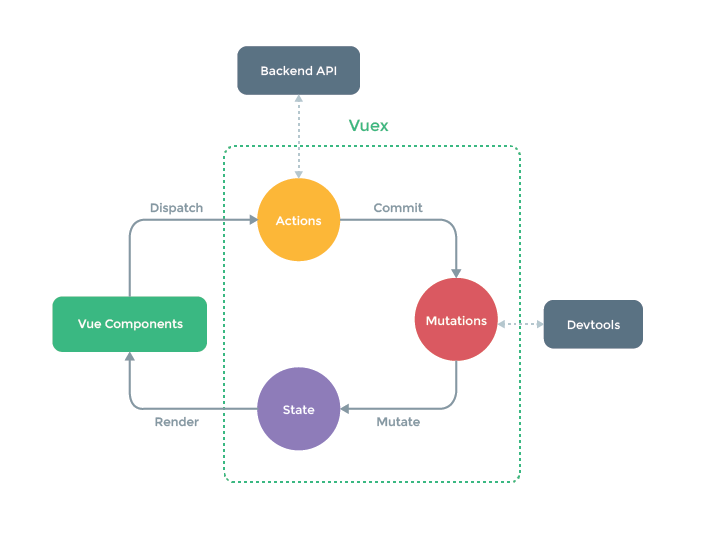
下面这张图完美地解释了一个 Vuex 应用内部的数据流动:
这张图的重点:
数据流动是单向的
- 组件可以调用 actions
- Actions 是用来分发 mutations 的
- 只有 mutations 可以修改状态
- store 是反应式的,即,状态的变化会在组件内部得到反映
搭建项目
项目结构:
项目主要文件存放于src目录下:
- assets/公共图片,css文件
- components/包含所有组件
- libs/扩展文件
- router/路由文件
- store/vuex相关文件(state,actions,getters,mutation)
- App.vue根组件
- main.js应用总入口
新建项目:
使用vue-cli脚手架,可用于快速搭建大型单页应用。该工具为现代化的前端开发工作流提供了开箱即用的构建配置。只需几分钟即可创建并启动一个带热重载、保存时静态检查以及可用于生产环境的构建配置的项目:
# 安装vue
npm install vue
# 全局安装 vue-cli
npm install --global vue-cli
# 创建一个基于 webpack 模板的新项目
vue init webpack notepad-xiaomi
# 安装依赖,走你
cd notepad-xiaomi
# 安装依赖
npm install muse-ui vue-awesome --save
# 安装vuex
npm install vue vuex --save
# 运行
npm run dev使用vue-cli脚手架创建项目时,一定要安装vue-router插件。
安装依赖后再main.js中引用
创建Vuex Store
在store文件夹下创建第一个index.js:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import state from './state'
import mutations from './mutation'
import * as getters from './getters'
import * as actions from './actions'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations,
getters,
actions
})现在我用下面这张图把应用分解成多个组件,并把组件内部需要的数据对应到 store.js 里的 state。
App根组件,第一幅图中的红色盒子
Header头部组件,第一幅图中的绿色盒子
NoteList列表组件,第一幅图中的橙色盒子
ToolBar工具栏组件,第一幅图中的蓝色盒子(包括删除和移动按钮)
Editor编辑组件,第二幅图,
NoteFolder便签夹组件,第三幅图
TrashHeader废纸篓头部组件,第四幅图蓝色盒子
TrashNoteList废纸篓列表组件,第四幅图灰色盒子
TrashToolBar废纸篓工具栏组件,第四幅图黄色盒子
state.js里面的状态对象会包含所有应用级别的状态,也就是各个组件需要共享的状态。
笔记列表(notes: [])包含了 NodesList 组件要渲染的 notes 对象。当前便签(activeNote: {})则包含当前编辑的便签对象,多个组件都需要这个对象。
聊完了状态state,我们来看看 mutations, 我们要实现的 mutation 方法包括:
- 添加标签到notes数组中
- 编辑选中便签
- 删除便签
- 便签布局
- 勾选便签
- 全部/取消勾选便签
- 保存便签
- 勾选废纸篓便签
- 全部/取消勾选废纸篓便签
- 恢复废纸篓便签
mutation-types中用于将常量放在单独的文件中,方便协作开发。
export const NEW_NOTE = 'NEW_NOTE'
export const EDIT_NOTE = 'EDIT_NOTE'
export const TOGGLE_NOTE = 'TOGGLE_NOTE'
export const CANCEL_CHECK = 'CANCEL_CHECK'
export const ALL_CHECK = 'ALL_CHECK'
export const DELETE_NOTE = 'DELETE_NOTE'
export const BACK_SAVE = 'BACK_SAVE'
export const TOGGLE_TRASHNOTE = 'TOGGLE_TRASHNOTE'
export const CANCEL_TRASHCHECk = 'CANCEL_TRASHCHECk'
export const ALL_TRASHCHECK = 'ALL_TRASHCHECK'
export const DELETE_TRASHNOTE = 'DELETE_TRASHNOTE'
export const RECOVERY_NOTE = 'RECOVERY_NOTE'首先,创建一条新的便签,我们需要做的是:
- 新建一个对象
- 初始化属性
- push到state.notes数组中
[types.NEW_NOTE](state) {
let newNote = {
id: +new Date(),
date: new Date().Format('yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm'),
content: '',
done: false
}
state.notes.push(newNote)
}然后,编辑便签需要用笔记内容 content 作参数:
[types.EDIT_NOTE](state, note) {
state.activeNote = note;
}剩下的这些 mutations 很简单就不一一赘述了。整个 store/mutation.js 如下:
import Format from '../libs/dateFormat'
import * as types from './mutation-types';
const mutations = {
[types.NEW_NOTE](state) {
let newNote = {
id: +new Date(),
date: new Date().Format('yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm'),
content: '',
done: false
}
state.notes.push(newNote)
},
[types.EDIT_NOTE](state, note) {
state.activeNote = note;
},
[types.TOGGLE_NOTE](state, note) {
state.notes.map((item, i) => {
if (item.id == note.id) {
item.done = !note.done;
}
})
if (note.done) {
state.deleteNotes.push(note);
} else {
state.deleteNotes.splice(state.deleteNotes.indexOf(note), 1);
}
},
[types.CANCEL_CHECK](state) {
state.notes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = false;
})
state.deleteNotes = [];
state.isCheck = false;
},
[types.ALL_CHECK](state, done) {
state.deleteNotes = [];
state.notes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = done;
if (done) {
state.deleteNotes.push(item);
} else {
state.deleteNotes = [];
}
})
},
[types.DELETE_NOTE](state) {
state.deleteNotes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = false;
state.notes.splice(state.notes.indexOf(item), 1);
state.trashNotes.push(item)
})
state.isCheck = false;
state.deleteNotes = [];
},
[types.BACK_SAVE](state, note) {
if (note.content != '') return;
state.notes.splice(state.notes.indexOf(note), 1);
},
[types.TOGGLE_TRASHNOTE](state, note) {
state.trashNotes.map((item, i) => {
if (item.id == note.id) {
item.done = !note.done;
}
})
if (note.done) {
state.deleteTrashNotes.push(note);
} else {
state.deleteTrashNotes.splice(state.deleteTrashNotes.indexOf(note), 1);
}
},
[types.CANCEL_TRASHCHECk](state) {
state.trashNotes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = false;
})
state.deleteTrashNotes = [];
state.isTrashCheck = false;
},
[types.ALL_TRASHCHECK](state, done) {
state.deleteTrashNotes = [];
state.trashNotes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = done;
if (done) {
state.deleteTrashNotes.push(item);
} else {
state.deleteTrashNotes = [];
}
})
},
[types.DELETE_TRASHNOTE](state) {
state.deleteTrashNotes.map((item, i) => {
state.trashNotes.splice(state.trashNotes.indexOf(item), 1);
})
state.deleteTrashNotes = [];
state.isTrashCheck = false;
},
[types.RECOVERY_NOTE](state) {
state.deleteTrashNotes.map((item, i) => {
item.done = false;
state.notes.unshift(item)
state.trashNotes.splice(state.trashNotes.indexOf(item), 1);
})
state.deleteTrashNotes = [];
state.isTrashCheck = false;
}
}
export default mutations;接下来聊 actions, actions 是组件内用来分发 mutations 的函数。它们接收 store 作为第一个参数。比方说,当用户点击 Toolbar 组件的添加按钮时,我们想要调用一个能分发NEW_NOTE mutation 的 action。现在我们在 store/文件夹下创建一个 actions.js 并在里面写上 newNote函数:
// 创建新便签
export const newNote = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.NEW_NOTE)
}其他的这些actions都类似,整个store/actions.js如下:
import * as types from './mutation-types';
//创建新便签
export const newNote = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.NEW_NOTE)
}
//编辑便签
export const editNote = ({ commit }, note) => {
commit(types.EDIT_NOTE, note)
}
//勾选便签
export const toggleNote = ({ commit }, note) => {
commit(types.TOGGLE_NOTE, note)
}
//取消勾选便签
export const cancelCheck = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.CANCEL_CHECK)
}
//全部勾选
export const allCheck = ({ commit }, done) => {
commit(types.ALL_CHECK, done)
}
//删除便签
export const deleteNote = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.DELETE_NOTE)
}
//返回自动保存
export const backSave = ({ commit }, note) => {
commit(types.BACK_SAVE, note)
}
//勾选废纸篓便签
export const toggleTrashNote = ({ commit }, note) => {
commit(types.TOGGLE_TRASHNOTE, note)
}
//取消勾选废纸篓便签
export const cancelTrashCheck = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.CANCEL_TRASHCHECk)
}
//全选废纸篓便签
export const allTrashCheck = ({ commit }, done) => {
commit(types.ALL_TRASHCHECK, done)
}
//删除废纸篓便签
export const deleteTrashNote = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.DELETE_TRASHNOTE)
}
//恢复便签
export const recoveryNote = ({ commit }) => {
commit(types.RECOVERY_NOTE)
}最后说一下getters,在Store仓库里,state就是用来存放数据,若是对数据进行处理输出,比如数据要过滤,一般我们可以写到computed中。但是如果很多组件都使用这个过滤后的数据,比如饼状图组件和曲线图组件,我们是否可以把这个数据抽提出来共享?这就是getters存在的意义。我们可以认为,getters是store的计算属性
// 搜索过滤便签
export const filterNote = (state) => {
if (state.search != '' && state.notes.length > 0) {
return state.notes.filter(note => note.content.indexOf(state.search) > -1) || {}
} else {
return state.notes || {}
}
}
// 当前编辑的便签
export const activeNote = (state) => {
return state.activeNote
}
// 便签列表布局
export const layout = state => state.layout
// 便签选中状态
export const isCheck = state => state.isCheck
// 废纸篓便签选中状态
export const isTrashCheck = state => state.isTrashCheck这样,在 store文件夹里面要写的代码就都写完了。这里面包括了 state.js 中的 state 和 mutation.js中的mutations,以及 actions.js 里面用来分发 mutations 的 actions,和getters.js中的处理输出。
构建Vue组件
最后这个小结,我们来实现四个组件 (App, Header,Toolbar, NoteList 和 Editor) 并学习怎么在这些组件里面获取 Vuex store 里的数据以及调用 actions。
创建根实例 - main.js
main.js是应用的入口文件,里面有根实例,我们要把 Vuex store 加到到这个根实例里面,进而注入到它所有的子组件里面:
// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command
// (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias.
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store/index'
/* 第三方插件 */
import MuseUI from 'muse-ui'
import 'muse-ui/dist/muse-ui.css'
import 'muse-ui/dist/theme-teal.css'
import Icon from 'vue-awesome/components/Icon'
import 'vue-awesome/icons/flag'
import 'vue-awesome/icons'
Vue.use(MuseUI)
Vue.component('icon', Icon);
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})App - 根组件
根组件 App 作为总的路由入口:
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
Notepad
Notepad 组件会 import 其余三个组件:Header,NoteList和ToolBar:
<template>
<div class="notepad">
<Header />
<NoteList />
<ToolBar />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Header from './Header'
import NoteList from './NoteList'
import ToolBar from './ToolBar'
export default {
name: 'Notepad',
data () {
return {
}
},
components:{
Header,
NoteList,
ToolBar,
}
}
</script>Header
Header组件提供搜索和便签勾选和取消,并统计勾选数量功能,如图:
对于Header组件来说,搜索框中输入查询内容时,需要对便签列表中的数据进行过滤,在创建state.js的时候就添加了search字段,用于存储搜索内容,而在getters.js中通过filterNote方法对便签列表进行过滤,筛选出符合条件的便签并返回,这时候我们在NoteList组件中就直接遍历filterNote方法就可以实现搜索功能。
store/getters中实现filterNote方法
// 搜索过滤便签
export const filterNote = (state) => {
if (state.search != '' && state.notes.length > 0) {
return state.notes.filter(note => note.content.indexOf(state.search) > -1) || {}
} else {
return state.notes || {}
}
}NoteList组件中遍历filterNote
<li v-for="note in filterNote" :key="note.id" @mousedown="gtouchstart(note)" @mouseup="gtouchend(note)" @touchstart="loopstart(note)" @touchend="clearLoop">
<h4>{{note.date}}</h4>
<p>{{note.content}}</p>
<mu-checkbox label="" v-model="note.done" class="checkbox" v-show="isCheck"/>
</li>Header组件:
...mapGetters中的...是es6的扩展运算符,不懂的可以查阅es6文档
<template>
<header class="header" :class="{visible:isVisible}">
<mu-flexbox class="headerTool" :class="{visible:isVisible}">
<mu-flexbox-item order="0" class="flex">
<mu-raised-button v-if="isCheck" label="取消" @click="cancelCheck" class="raised-button"/>
<span v-else class="icon" @click="openFolder"><icon name="folder-open"></icon></span>
</mu-flexbox-item>
<mu-flexbox-item order="1" class="flex" style="text-align:center">
<span v-if="isCheck">{{checkTitle}}</span>
<span v-else>{{title}}</span>
</mu-flexbox-item>
<mu-flexbox-item order="2" class="flex" style="text-align:right">
<mu-raised-button v-if="isCheck" :label="checkBtnTxt" @click="allCheck(!allChecked)" class="raised-button"/>
<span v-else>
<span class="icon" v-if="layout=='grid'" @click="changeLayout"><icon name="list"></icon></span>
<span class="icon" v-else @click="changeLayout"><icon name="th-large"></icon></span>
</span>
</mu-flexbox-item>
</mu-flexbox>
<div class="search">
<div class="icon"><icon name="search"></icon></div>
<input type="text" v-model="searchTxt" @keyup="search" @focus="searchFocus" @blur="searchBlur"/>
</div>
</header>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions,mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Header',
data(){
return {
title:'便签',
checkBtnTxt:'全选',
searchTxt:'',
isVisible:false
}
},
computed:{
...mapGetters([
'layout',
'isCheck'
]),
//获取便签勾选状态
allChecked(){
return this.$store.state.notes.every(note => note.done)
},
//便签选中数量提示
checkTitle(){
return `已选择${this.$store.state.deleteNotes.length}项`
}
},
methods:{
//显示搜索框
searchFocus(){
this.isVisible = true;
},
//隐藏搜索框
searchBlur(){
this.isVisible = false;
},
//搜索
search(){
this.$store.state.search = this.searchTxt
},
//切换布局
changeLayout(){
if(this.$store.state.layout == 'list'){
this.$store.state.layout = 'grid'
}else{
this.$store.state.layout = 'list'
}
},
//取消勾选
cancelCheck(){
this.$store.dispatch('cancelCheck')
},
//全选切换
allCheck(done){
this.checkBtnTxt = done?'取消全选':'全选'
this.$store.dispatch('allCheck',done)
},
//打开便签夹
openFolder(){
this.$router.push({path:'noteFolder'})
}
}
}
</script>
NoteList
NotesList 组件主要有三个功能:
- 渲染便签列表
- 对便签进行勾选或取消
- 点击编辑便签
<template>
<ul class="noteList" :class="layout">
<li v-for="note in filterNote" :key="note.id" @mousedown="gtouchstart(note)" @mouseup="gtouchend(note)" @touchstart="loopstart(note)" @touchend="clearLoop">
<h4>{{note.date}}</h4>
<p>{{note.content}}</p>
<mu-checkbox label="" v-model="note.done" class="checkbox" v-show="isCheck"/>
</li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters,mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'NoteList',
data(){
return {
timeOutEvent: 0,
Loop:null
}
},
computed:{
...mapGetters([
'filterNote',
'layout',
'isCheck'
])
},
methods:{
//编辑&选中
editNote(note){
if(this.isCheck){
this.$store.dispatch('toggleNote',note);
}else{
this.$store.dispatch('editNote',note);
this.$router.push({path:'/editor'})
}
},
//鼠标按下,模拟长按事件
gtouchstart(note){
var _this = this;
this.timeOutEvent = setTimeout(function(){
_this.longPress(note)
},500);//这里设置定时器,定义长按500毫秒触发长按事件,时间可以自己改,个人感觉500毫秒非常合适
return false;
},
//鼠标放开,模拟长按事件
gtouchend(note){
clearTimeout(this.timeOutEvent);//清除定时器
if(this.timeOutEvent!=0){
//这里写要执行的内容(尤如onclick事件)
this.editNote(note);
}
return false;
},
longPress(note){
this.timeOutEvent = 0;
this.$store.state.isCheck = true;
this.$store.dispatch('toggleNote',note);
},
//手按住开始,模拟长按事件
loopstart(note){
var _this = this;
clearInterval(this.Loop);
this.Loop = setTimeout(function(){
_this.$store.state.isCheck = true;
_this.$store.dispatch('toggleNote',note);
},500);
},
//手放开结束,模拟长按事件
clearLoop(){
clearTimeout(this.Loop);
}
}
}
</script>
ToolBar
Toolbar组件提供给用户三个按钮:创建便签,编辑便签和移动便签(移动便签功能还没有做):
<template>
<div class="toolBar">
<div class="toolBtn" v-if="isCheck">
<span class="icon" @click="deleteNote"><icon name="trash-alt"></icon></span>
<span class="icon"><icon name="dolly"></icon></span>
</div>
<div class="addNote" v-else>
<div class="float-button mu-float-button" @click="addNote"><icon name="plus"></icon></div>
</div>
<mu-dialog :open="dialog" title="删除便签" @close="close">
您确定删除所选便签吗?
<mu-flat-button slot="actions" @click="close" primary label="取消"/>
<mu-flat-button slot="actions" primary @click="deleteConfirm" label="确定"/>
</mu-dialog>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters,mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'ToolBar',
data(){
return {
dialog: false
}
},
computed:{
...mapGetters([
'isCheck'
])
},
methods:{
//添加便签
addNote(){
this.$store.dispatch('newNote');
this.$router.push({path:'editor'});
},
//删除便签
deleteNote(){
this.dialog = true;
},
//关闭窗口
close () {
this.dialog = false;
},
//确定删除
deleteConfirm(){
this.dialog = false;
this.$store.dispatch('deleteNote');
}
}
}
</script>Editor
Editor 组件是最简单的,它只做两件事:
从 store 获取当前笔记activeNote,把它的内容展示在 textarea
在用户更新笔记的时候,调用 editNote() action
以下是完整的 Editor.vue:
<template>
<div class="edit-panel">
<div class="edit-tool">
<span class="back-list" @click="backList"><icon name="angle-left"></icon></span>
<span class="date" v-text="activeNote.date"></span>
<span class="saveNote" v-show="isShow" @click="backList">完成</span>
</div>
<textarea v-focus class="edit-area" v-model="activeNote.content" @keyup="editorNote"></textarea>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Editor',
data(){
return {
content:'',
isShow:false
}
},
created(){
this.content = this.activeNote.content
},
computed:{
//获取正在操作的便签
...mapGetters([
'activeNote'
])
},
directives:{
focus:{
inserted(el){
el.focus();
}
}
},
methods:{
//返回便签列表
backList(){
this.$router.push({path:'/'})
this.$store.dispatch('backSave',this.activeNote)
},
//完成按钮显示&隐藏
editorNote(){
if(this.content != this.activeNote.content){
this.isShow = true;
}else{
this.isShow = false;
}
}
}
}
</script>这就是一个小米便签的创建和编辑,还有删除以及废纸篓功能这里就不多说了,功能都很简单不明白的地方可以看源代码,然后自己实战操作一番,如有写的不对的地方大家提出来,互相学习互相帮助嘛,谢谢!
来都来了点一下赞吧,你的赞是对我最大的鼓励^_^









**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。