前言
紧接着上一篇的初始化,有一些问题还没有解决,和native有关的问题如下:
- (10) nativeInit作用?bundle是什么,如何加载?
- (12)flutter中的so库具体有哪些,有什么作用?
- (13)native中的初始化流程?
- (14)这里并没有看到一行代码有和绘制图形有关,那么在哪里调用?是否都是在native中调用,怎么调用的?
下载源码
因为前一篇的android版本可以直接在as中反编译源码,所以很多情况下都可以直接使用as查看。这里要分析so库就只能去官方下载源码。
https://github.com/flutter/en...
下载之后的结构:
这里我们当然是紧接着分析android部分的native代码
load分析
JNI_OnLoad
了解jni开发的读者,应该知道JNI_OnLoad为so库加载的入口函数,在System.load(xxx)方法的时候调用,参考这里:
https://blog.csdn.net/zerokkq...
// This is called by the VM when the shared library is first loaded.
JNIEXPORT jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved) {
// Initialize the Java VM.
fml::jni::InitJavaVM(vm);
JNIEnv* env = fml::jni::AttachCurrentThread();
bool result = false;
// Register FlutterMain.
result = shell::FlutterMain::Register(env);
FXL_CHECK(result);
// Register PlatformView
result = shell::PlatformViewAndroid::Register(env);
FXL_CHECK(result);
// Register VSyncWaiter.
result = shell::VsyncWaiterAndroid::Register(env);
FXL_CHECK(result);
return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
}InitJavaVM
看下InitJavaVM
void InitJavaVM(JavaVM* vm) {
FML_DCHECK(g_jvm == nullptr);
g_jvm = vm;
}这里初始化的作用实际是保存一个JavaVM的指针,以便将来使用
FML_DCHECK 这个宏是什么?
#ifndef NDEBUG
// 不是debug版本
#define FML_DLOG(severity) FML_LOG(severity)
#define FML_DCHECK(condition) FML_CHECK(condition)
#else
//debug版本
#define FML_DLOG(severity) FML_EAT_STREAM_PARAMETERS(true)
#define FML_DCHECK(condition) FML_EAT_STREAM_PARAMETERS(condition)
#endif看下debug版本的,release版本暂时先不看
#define FML_EAT_STREAM_PARAMETERS(ignored) \
true || (ignored) \
? (void)0 \
: ::fml::LogMessageVoidify() & \
::fml::LogMessage(::fml::LOG_FATAL, 0, 0, nullptr).stream()替换进去:
true || (g_jvm == nullptr) ?
0 :
::fml::LogMessageVoidify() & ::fml::LogMessage(::fml::LOG_FATAL, 0, 0, nullptr).stream()所以FML_DCHECK的意思是检查下条件是不是真,如果不是真则打印日志出来,并返回stream以便还可以输出内容。
AttachCurrentThread
JNIEnv* AttachCurrentThread() {
FML_DCHECK(g_jvm != nullptr)
<< "Trying to attach to current thread without calling InitJavaVM first.";
JNIEnv* env = nullptr;
jint ret = g_jvm->AttachCurrentThread(&env, nullptr);
FML_DCHECK(JNI_OK == ret);
return env;
}这里程序的意思是拿到JNIEnv的指针,以便将来使用
关于AttachCurrentThread,参考这里:
https://blog.csdn.net/stefzeu...
shell::FlutterMain::Register(env);
bool FlutterMain::Register(JNIEnv* env) {
static const JNINativeMethod methods[] = {
{
.name = "nativeInit",
.signature = "(Landroid/content/Context;[Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/"
"lang/String;)V",
.fnPtr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(&Init),
},
{
.name = "nativeRecordStartTimestamp",
.signature = "(J)V",
.fnPtr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(&RecordStartTimestamp),
},
};
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/FlutterMain");
if (clazz == nullptr) {
return false;
}
return env->RegisterNatives(clazz, methods, arraysize(methods)) == 0;
}这里注册了给java调用的两个方法,我们在上一篇文章中均有提到,关于在native中注册给java调用的方法参考这里:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/216...
这两个方法具体干啥的,先留着。
shell::PlatformViewAndroid::Register(env);
bool PlatformViewAndroid::Register(JNIEnv* env) {
if (env == nullptr) {
return false;
}
g_flutter_view_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/FlutterView"));
...
g_flutter_native_view_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/FlutterNativeView"));
...
g_surface_texture_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(
env, env->FindClass("android/graphics/SurfaceTexture"));
...
static const JNINativeMethod native_view_methods[] = {
...代码略过
};
static const JNINativeMethod view_methods[] = {
...代码略过
};
if (env->RegisterNatives(g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(),
native_view_methods,
arraysize(native_view_methods)) != 0) {
return false;
}
if (env->RegisterNatives(g_flutter_view_class->obj(), view_methods,
arraysize(view_methods)) != 0) {
return false;
}
g_handle_platform_message_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(),
"handlePlatformMessage", "(Ljava/lang/String;[BI)V");
if (g_handle_platform_message_method == nullptr) {
return false;
}
g_handle_platform_message_response_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(),
"handlePlatformMessageResponse", "(I[B)V");
...
g_update_semantics_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(), "updateSemantics",
"(Ljava/nio/ByteBuffer;[Ljava/lang/String;)V");
...
g_update_custom_accessibility_actions_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(), "updateCustomAccessibilityActions",
"(Ljava/nio/ByteBuffer;[Ljava/lang/String;)V");
...
g_on_first_frame_method = env->GetMethodID(g_flutter_native_view_class->obj(),
"onFirstFrame", "()V");
...
g_attach_to_gl_context_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "attachToGLContext", "(I)V");
...
g_update_tex_image_method =
env->GetMethodID(g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "updateTexImage", "()V");
...
g_get_transform_matrix_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "getTransformMatrix", "([F)V");
...
g_detach_from_gl_context_method = env->GetMethodID(
g_surface_texture_class->obj(), "detachFromGLContext", "()V");
...
return true;
}这个方法比较长,为了节省篇幅,把一些判断代码去掉。
我们在里面看到了熟悉的代码,这个方法主要做了几件事情:
- 保存FlutterView、FlutterNativeView、SurfaceTexture的引用
- 注册FlutterView、FlutterNativeView中的调用native的方法,以便将来在java端调用native
- 保存FlutterNativeView中的java方法handlePlatformMessage,handlePlatformMessageResponse,updateSemantics,updateCustomAccessibilityActions,onFirstFrame,attachToGLContext,updateTexImage,getTransformMatrix,detachFromGLContext的引用,以便将来在native中直接调用
shell::VsyncWaiterAndroid::Register(env);
bool VsyncWaiterAndroid::Register(JNIEnv* env) {
static const JNINativeMethod methods[] = {{
.name = "nativeOnVsync",
.signature = "(JJJ)V",
.fnPtr = reinterpret_cast<void*>(&OnNativeVsync),
}};
jclass clazz = env->FindClass("io/flutter/view/VsyncWaiter");
if (clazz == nullptr) {
return false;
}
g_vsync_waiter_class = new fml::jni::ScopedJavaGlobalRef<jclass>(env, clazz);
FXL_CHECK(!g_vsync_waiter_class->is_null());
g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_ = env->GetStaticMethodID(
g_vsync_waiter_class->obj(), "asyncWaitForVsync", "(J)V");
FXL_CHECK(g_async_wait_for_vsync_method_ != nullptr);
return env->RegisterNatives(clazz, methods, arraysize(methods)) == 0;
}这里做了:
- 查找VsyncWaiter这个类,并引用之
- 注册java端调用native方法nativeOnVsync
- 保存asyncWaitForVsync这个方法的引用。
问题
- (15) VsyncWaiter作用?
这段代码总结:
- 初始化环境,特别是获取到了环境变量
JavaVM* g_jvm = nullptr;
JNIEnv* env
- 引用java中相关类,并引用了它们的方法,并注册native调用
native启动流程分析
这里也就是上面一篇遗留的问题:
- (10)nativeInit作用?
- (13)native中的初始化流程?
回过头再看下
Application#onCreate:
Activity#onCreate:
分别分析:
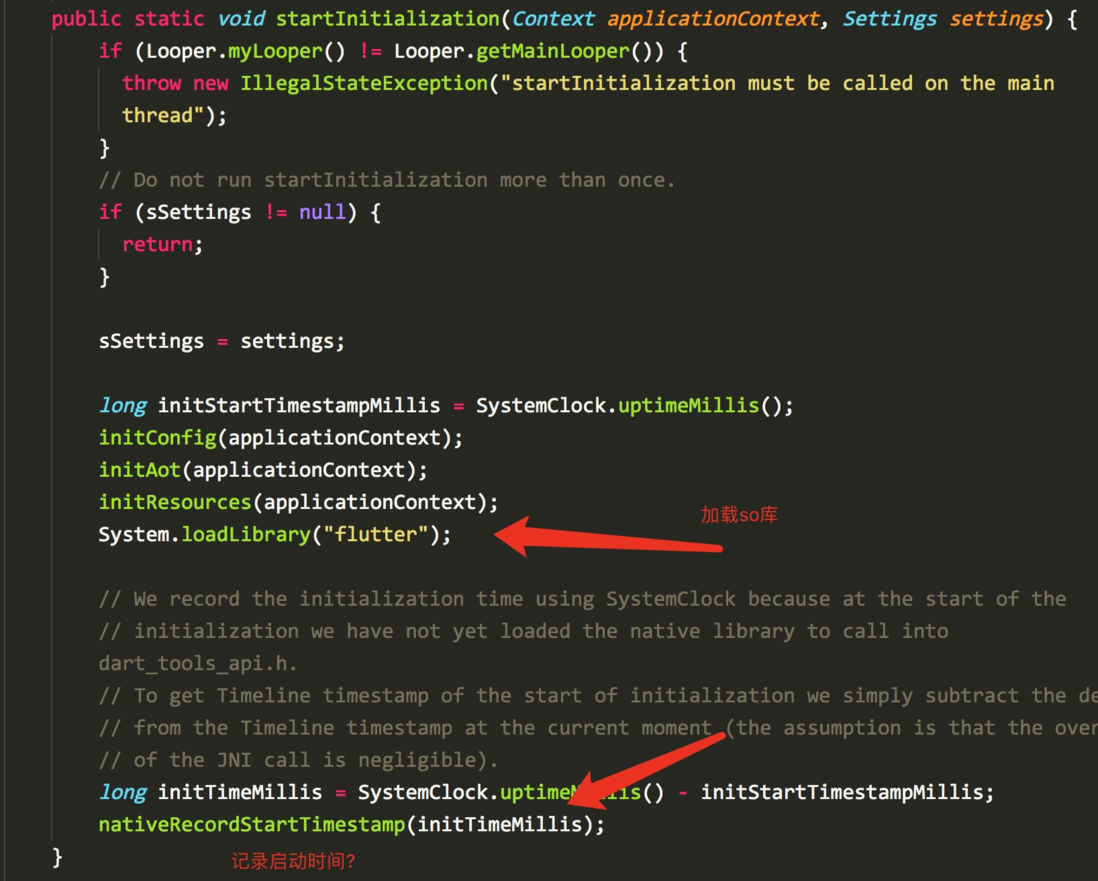
nativeRecordStartTimestamp=>FlutterMain::RecordStartTimestamp
static void RecordStartTimestamp(JNIEnv* env,
jclass jcaller,
jlong initTimeMillis) {
int64_t initTimeMicros =
static_cast<int64_t>(initTimeMillis) * static_cast<int64_t>(1000);
blink::engine_main_enter_ts = Dart_TimelineGetMicros() - initTimeMicros;
}这里记录一下启动时间
nativeInit=>FlutterMain::Init
void FlutterMain::Init(JNIEnv* env,
jclass clazz,
jobject context,
jobjectArray jargs,
jstring bundlePath) {
std::vector<std::string> args;
args.push_back("flutter");
for (auto& arg : fml::jni::StringArrayToVector(env, jargs)) {
args.push_back(std::move(arg));
}
auto command_line = fxl::CommandLineFromIterators(args.begin(), args.end());
auto settings = SettingsFromCommandLine(command_line);
settings.assets_path = fml::jni::JavaStringToString(env, bundlePath);
if (!blink::DartVM::IsRunningPrecompiledCode()) {
// Check to see if the appropriate kernel files are present and configure
// settings accordingly.
auto platform_kernel_path =
fml::paths::JoinPaths({settings.assets_path, "platform.dill"});
auto application_kernel_path =
fml::paths::JoinPaths({settings.assets_path, "kernel_blob.bin"});
if (files::IsFile(application_kernel_path)) {
settings.application_kernel_asset = application_kernel_path;
if (files::IsFile(platform_kernel_path)) {
settings.platform_kernel_path = platform_kernel_path;
}
}
}
settings.task_observer_add = [](intptr_t key, fxl::Closure callback) {
fml::MessageLoop::GetCurrent().AddTaskObserver(key, std::move(callback));
};
settings.task_observer_remove = [](intptr_t key) {
fml::MessageLoop::GetCurrent().RemoveTaskObserver(key);
};
// Not thread safe. Will be removed when FlutterMain is refactored to no
// longer be a singleton.
g_flutter_main.reset(new FlutterMain(std::move(settings)));
}这里做了几件事情:
- 解析java传过来的参数
- 创建Setting,保存配置
- 创建FlutterMain
总结
本篇分析了native中的初始化过程,看下前面的问题哪些解决了?
- (1)
FlutterNativeView和FlutterView有啥区别和联系 - (2)UserLeaveHintListener作用?
- (3)ViewFactory#retainFlutterNativeView作用?
- (4)BinaryMessenger作用
- (5)TextureRegistry作用
- (6)
FlutterView究竟如何创建的 - (7)retainFlutterNativeView有什么作用
- (8)
sResourceExtractor.waitForCompletion();在干什么? - (9)
new FlutterView(this.activity, (AttributeSet)null, nativeView);这里是否可以解释前面的问题(1) - (10)
nativeInit作用?bundle是什么,如何加载? - (11)sIsPrecompiledAsBlobs && sIsPrecompiledAsSharedLibrary这两个参数具体代表什么含义,为什么不能同时存在?和flutter的hotload有关吗,和flutter是调试版本还是发布版本有关吗?
- (12)
flutter中的so库具体有哪些,有什么作用? - (13)
native中的初始化流程? - (14)这里并没有看到一行代码有和绘制图形有关,那么在哪里调用?是否都是在native中调用,怎么调用的?
- (15) VsyncWaiter作用?
下一篇文章应该开始分析图形绘制前,即第一帧之前flutter干了什么。
如有疑问,请加qq群854192563讨论


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。