1.vue的开始
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app', // el: 用来挂载 Vue 实例的元素
data: {}, // data: 要绑定的资料
props: {}, // props: 用来接收外部资料的属性
methods: {}, // methods: 用来定义在 Vue 实例内使用的函数(方法)
watch: {}, // watch: 用来观察 Vue 实例内资料的变动
computed: {}, // compoted: 自动为内部资料计算过的属性
template: "...", // template: 提供 Vue 实例编译后的样板
components: {} // components: 用来定义子元件
});
2.组件注册
组件注册分为两种:局部注册 和 全局注册
2.1 组件局部注册
<div class="app">
<my-component></my-component>
<my-component></my-component>
<my-component></my-component>
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script>
// 组件的局部注册,在 new Vue() 里面
var app = new Vue({
el: '.app',
components: {
// 注册组件
'my-component': {
template: '<div class="myComponent">这是一个注册组件</div>'
}
}
});
</script>2.2 组件全局注册
<div class="se_app">
<global-component></global-component>
</div>
<script>
// 组件的全局注册
Vue.component('global-component', {
template: '<div class="global">这是一个全局注册的组件</div>'
});
var se_app = new Vue({
el: '.se_app'
});
</script>2.3 复杂组件的打包?
// 子组件怎么做?怎么用?
// 对于复杂的组件,可以将其用下面的方法打包
var app2 = new Vue({
el: '.app2',
components: {
CustomHeader: Vue.extend({ // extend 是构造一个组件的语法器. 你给它参数 他给你一个组件
template: '<div class="header">header</div>'
}),
CustomMain: Vue.extend({
template:
'<div class="Main">' +
'<div style="margin: 10px;">Main</div>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'</div>',
components: {
CustomBlock: Vue.extend({
template: '<div class="block">B</div>'
})
}
}),
CustomAside: Vue.extend({
template: '<div class="aside">Aside</div>'
})
}
});3.将网页模板封装成 Component
3.1 将 HTML 模板封装在js中
var CustomMain = Vue.extend({
template:
'<div class="Main">' +
'<div style="margin: 10px;">Main</div>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'<custom-block></custom-block>' +
'</div>',
components: {
CustomBlock
}
});3.2 将 HTML 模板封装在HTML的Script标签中
<div id="app3">
<my-component></my-component>
</div>
<script type="text/x-template" id="my-components">
// 模板的最外层只能有一个标签包着(根节点)
<div>
<div class="component">1 A custom component of Vue!</div>
<div class="component">2 A custom component of Vue!</div>
<div class="component">3 A custom component of Vue!</div>
<div class="component">4 A custom component of Vue!</div>
</div>
</script>
<script>
Vue.component('my-component', {
template: '#my-components'
});
// create a root instance 创建一个根实例
new Vue({
el: '#app3'
})
</script>3.3 render function ?
Vue的template模板 其实最后会被vue引擎编译为 render function,最终渲染到网页上
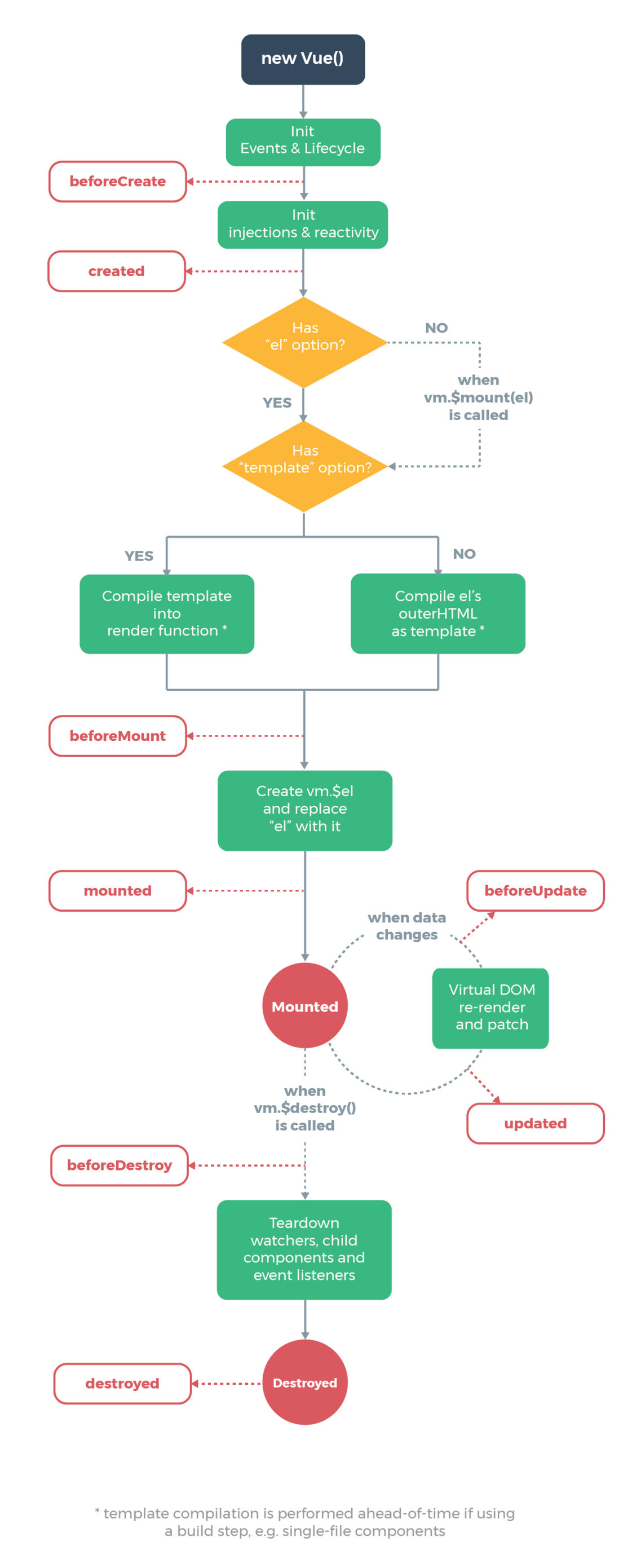
4.Vue元件生命周期
<div id="app">
<h1>{{ count }}</h1>
<button @click="updateEvent">Update</button>
</div>
<button id="del">Del</button>
<script>
var vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
count: 0
},
methods: {
updateEvent: function(){
this.count += 1;
}
},
beforeCreate: function(){
// 元件实体刚被建立,属性计算之前。
console.log('beforeCreate - this.count: ', this.count); // undefined
console.log('beforeCreate - this.$el: ', this.$el); // undefined
},
created: function(){
// 元件实体已建立,属性已绑定,但 DOM 还没生成。
console.log('created - this.count: ', this.count); // 0
console.log('created - this.$el: ', this.$el); // undefined
},
beforeMount: function(){
// 模板 (template) 编译或挂载至 HTML 之前 // DOM内的代码仍然是Vue源码,DOM内的 data 属性尚未编译,仍是{{ count }}
console.log('beforeMount - this.$el: ', this.$el); // <div id="app"></div>
},
mounted: function(){
// 模板 (template) 编译或挂载至 HTML 之后 // DOM内的代码已编译,DOM内的 data 属性尚已编译,替换为需要的 0
console.log('mounted - this.$el: ', this.$el); // <div id="app"></div>
},
beforeUpdate: function(){
// 元件被更新之前
console.log('beforeUpdate: ',
this.$el.querySelector('h1').innerText,
this.count );
},
updated: function(){
// 元件被更新之后
console.log('updated: ',
this.$el.querySelector('h1').innerText,
this.count );
},
// activated: function(){
// // keep-alive 用,元件被启动时呼叫
// },
// deactivated: function(){
// // keep-alive 用,元件被移除时呼叫
// },
beforeDestroy: function(){
// 移除 vue instance (实例) 之前
console.log('beforeDestroy');
},
destroyed: function(){
// 移除 vue instance (实例) 之后
console.log('destroyed');
// destroy 做的事情就是,把 watch,child components 和 event listeners 拿掉,
// 让 vue 和 DOM 脱钩(不相互关联),但是不会移除它生成的 DOM,这个 vue 实例无法再对DOM操作
}
});
document.getElementById('del').addEventListener('click',function(){
vm.$destroy();
})
// Vue.js 教學 - 從 Vuejs 初探 Web Component 的世界 (HD)
// https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T2JsTE0Hq58&list=PLYrA-SsMvTPNPhv8KeSNtPTY8q85-SSJA&index=3
// 40:22
// 2018-10-12 19:17:25
</script>
4.2追踪物件变化
Object.defineProperty() 的MDN文档
资料变动检测
5.props 从外部接受指定的资料
// props 案例1
<div id="app">
<my-component v-bind:parent-msg="msg"></my-component>
</div>
<script type="text/x-template" id="my-component">
<div class="component">
<div> ParentMsg: {{ parentMsg }} </div>
<div> ChildMsg: {{ msg }} </div>
</div>
</script>
<script>
// register
Vue.component("my-component", {
props: ["parentMsg"],
template: "#my-component",
data: function(){
return {
msg: "Msg of child!"
}
}
});
new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: "Msg of parent!"
}
});
</script>// props 案例2
<div id="myApp">
<h1>你的成绩评价</h1>
<test-result :score="50"></test-result>
<test-result :score="65"></test-result>
<test-result :score="90"></test-result>
<test-result :score="100"></test-result>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component('test-result', {
props: ['score'],
template: '<div><strong>{{score}}分,{{testResult}}</strong></div>',
computed: {
testResult: function(){
var strResult = "";
if (this.score < 60)
strResult = '不及格';
else if (this.score < 90)
strResult = '中等生';
else if (this.score <= 100)
strResult = '优秀生';
return strResult;
}
}
});
var myApp = new Vue({
el: "#myApp"
})
</script>5.1 Prop 接收参数验证
组件可以为 props 指定验证要求。如果未指定验证要求,Vue 会发出警告。当组件给其他人使用时这很有用。
prop 是一个对象而不是字符串数组时,它包含验证要求:
<div id="app">
<my-component :pro-c="msg" :prop-d="num"></my-component>
</div>
<script type="text/x-template" id="my-component">
<div class="component">
{{ propD }}
</div>
</script>
<script>
// 09-data-props-validation
// register
Vue.component("my-component", {
props: {
parentMsg: null, // null 代表不验证类别
propA: Number, // 限定数字
propB: [String, Number], // 多重条件可用 [] 隔开
propC: {
// 必要栏位,且限定字串类别
type: String,
require: true
},
propD: {
// 数字类型,且有预设值
type: Number,
default: 100
},
propE: {
// Object 类型,代表可接受的是对象或者数组
type: Object,
default: function(){
return {
message: 'hello'
}
}
},
propF: {
// 自定义的条件验证
validator: function(value){
return value > 10
}
}
},
template: '#my-component',
data: function(){
return {
msg: 'Msg of Child!'
}
}
});
// a root instance 一个根实例
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
msg: 'true',
num: 123456
}
});
</script>5.2 单向数据流
所有的 prop 都使得其父子 prop 之间形成了一个单向下行绑定:父级 prop 的更新会向下流动到子组件中,但是反过来则不行。这样会防止从子组件意外改变父级组件的状态,从而导致你的应用的数据流向难以理解。
额外的,每次父级组件发生更新时,子组件中所有的 prop 都将会刷新为最新的值。这意味着你不应该在一个子组件内部改变 prop。如果你这样做了,Vue 会在浏览器的控制台中发出警告。
<div id="app">
单向数据流:<br>
Parent: {{ message }} <input v-model="message">
<hr>
Child:
<my-component :parent-message="message"></my-component>
</div>
<script>
Vue.component("my-component", {
props: {
parentMessage: String
},
template: "<span>{{ parentMessage }}<input v-model='message'></span>",
data: function(){
return {
message: this.parentMessage
}
}
})
var vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
message: "hello!"
}
});
</script>



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。