上一篇讲了ELF文件的总体布局,以及section和segment的概念。按照计划,今天继续讲 ELF header。
讲新的内容之前,先更正一个错误:上一篇中讲section header table中的条目和文件中的section是一一对应的,其实这么讲是不对的。一个section必定有一个section header来描述它,但一个section header不一定在文件中有对应的section,因为有的section是不占用文件字节的。segment也是这个道理。
这篇文章本来应该上周写的,但上周忙于突击考试,周末又自我放纵,看了两天《相声有新人》,所以今天赶紧补上。
ELF header的定义可以在 /usr/include/elf.h 中找到。Elf32_Ehdr是32位 ELF header的结构体。Elf64_Ehdr是64位ELF header的结构体。
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number和其它信息 */
Elf32_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf32_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf32_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf32_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf32_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf32_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf32_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf32_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf32_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf32_Ehdr;
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf64_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf64_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf64_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf64_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf64_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf64_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf64_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf64_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf64_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf64_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf64_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf64_Ehdr;
64位和32位只是个别字段长度不同,比如 Elf64_Addr 和 Elf64_Off 都是64位无符号整数。而Elf32_Addr 和 Elf32_Off是32位无符号整数。这导致ELF header的所占的字节数不同。32位的ELF header占52个字节,64位的ELF header占64个字节。
ELF header详解
-
e_ident占16个字节。前四个字节被称作ELF的Magic Number。后面的字节描述了ELF文件内容如何解码等信息。等一下详细讲。 -
e_type,2字节,描述了ELF文件的类型。以下取值有意义:ET_NONE, 0, No file type ET_REL, 1, Relocatable file(可重定位文件,通常是文件名以.o结尾,目标文件) ET_EXEC, 2, Executable file (可执行文件) ET_DYN, 3, Shared object file (动态库文件,你用gcc编译出的二进制往往也属于这种类型,惊讶吗?) ET_CORE, 4, Core file (core文件,是core dump生成的吧?) ET_NUM, 5,表示已经定义了5种文件类型 ET_LOPROC, 0xff00, Processor-specific ET_HIPROC, 0xffff, Processor-specific从
ET_LOPROC到ET_HIPROC的值,包含特定于处理器的语义。 -
e_machine,2字节。描述了文件面向的架构,可取值如下(因为文档较老,现在有更多取值,参见/usr/include/elf.h中的EM_开头的宏定义):EM_NONE, 0, No machine EM_M32, 1, AT&T WE 32100 EM_SPARC, 2, SPARC EM_386, 3, Intel 80386 EM_68K, 4, Motorola 68000 EM_88K, 5, Motorola 88000 EM_860, 7, Intel 80860 EM_MIPS, 8, MIPS RS3000 ... ... -
e_version,2字节,描述了ELF文件的版本号,合法取值如下:EV_NONE, 0, Invalid version EV_CURRENT, 1, Current version,通常都是这个取值。 EV_NUM, 2, 表示已经定义了2种版本号 -
e_entry,(32位4字节,64位8字节),执行入口点,如果文件没有入口点,这个域保持0。 -
e_phoff, (32位4字节,64位8字节),program header table的offset,如果文件没有PH,这个值是0。 -
e_shoff, (32位4字节,64位8字节), section header table 的offset,如果文件没有SH,这个值是0。 -
e_flags, 4字节,特定于处理器的标志,32位和64位Intel架构都没有定义标志,因此eflags的值是0。 -
e_ehsize, 2字节,ELF header的大小,32位ELF是52字节,64位是64字节。 -
e_phentsize,2字节。program header table中每个入口的大小。 -
e_phnum, 2字节。如果文件没有program header table, e_phnum的值为0。e_phentsize乘以e_phnum就得到了整个program header table的大小。 -
e_shentsize, 2字节,section header table中entry的大小,即每个section header占多少字节。 -
e_shnum, 2字节,section header table中header的数目。如果文件没有section header table, e_shnum的值为0。e_shentsize乘以e_shnum,就得到了整个section header table的大小。 -
e_shstrndx, 2字节。section header string table index. 包含了section header table中section name string table。如果没有section name string table,e_shstrndx的值是SHN_UNDEF.
注意:program header table一般译为程序头表,section header table 一般译为节头表,因为这样的翻译无助于理解,所以我倾向于不翻。
e_ident
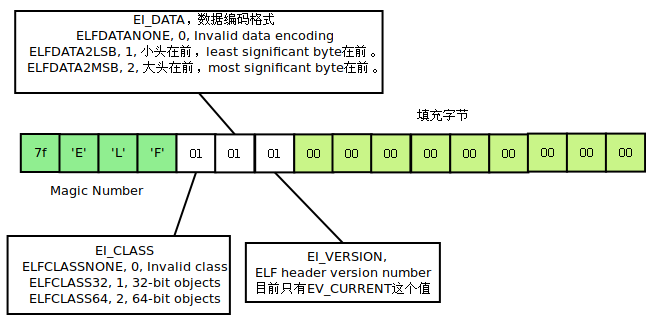
回过头来,我们仔细看看文件前16个字节,也是e_ident。
如图,前4个字节是ELF的Magic Number,固定为7f 45 4c 46。
第5个字节指明ELF文件是32位还是64位的。
第6个字节指明了数据的编码方式,即我们通常说的little endian或是big endian。little endian我喜欢称作小头在前,低位字节在前,或者直接说低位字节在低位地址,比如0x7f454c46,存储顺序就是46 4c 45 7f。big endian就是大头在前,高位字节在前,直接说就是高位字节在低位地址,比如0x7f454c46,在文件中的存储顺序是7f 45 4c 46。
第7个字节指明了ELF header的版本号,目前值都是1。
第8-16个字节,都填充为0。
readelf读取ELF header
我们使用readelf -h <elffile>可以读取文件的ELF header信息。
比如我本地有执行文件hello,我执行reaelf -h hello,结果如下:
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: Advanced Micro Devices X86-64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0x1050
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 14768 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 11
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 29
Section header string table index: 28
这是我用gcc生成的执行文件,但注意它的Type是DYN (Shared object file),这大概是因为,这个文件不能直接执行,是依赖于解释器和c库才能运行。真正的可执行文件是解释器,而hello相对于解释器来说也是个共享库文件。这是我的推断,需要后面深入学习后验证。
今天就讲到这了,这周结束前计划写本系列第三篇,关于目标文件内section的知识。
2018-10-22 Mon


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。