问题介绍
要在 Java 代码中实现类似 SQL 中的 GroupBy 分组聚合运算,是比较繁琐的,通常先要声明数据结构(Java 实体类),然后用 Java 集合进行循环遍历,最后根据分组条件添加到某个子集合中。Java 8 有了 Lambda(stream)代码简洁了许多,分组后往往还要跟着聚合操作,仍然需要单写聚合函数 sum(),count(*),topN()等。这些还都是最常规的分组和聚合运算,遇到对位分组、枚举分组、多重分组等非常规分组加上其他聚集函数 (FIRST,LAST…),代码就变得非常冗长且不通用。如果能有一个中间件专门负责这类计算,采用类似 SQL 脚本做算法描述,在 Java 中直接调用脚本并返回结果集就好了。Java 版集算器和 SPL 脚本,就是这样的机制,下面举例说明如何使用。
SPL 实现
常规分组
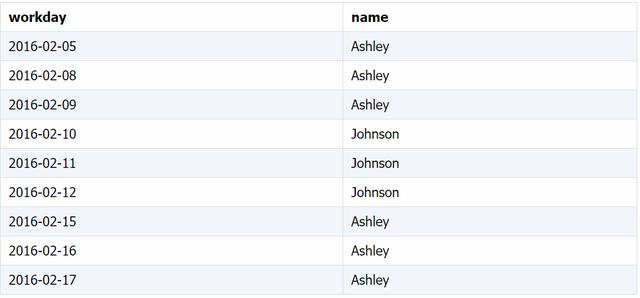
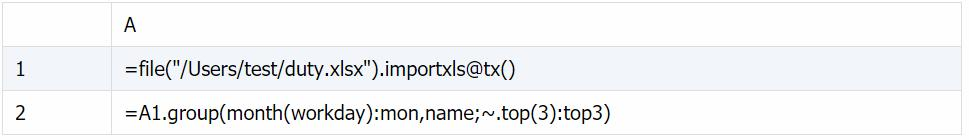
duty.xlsx 文件中保存着每个人的加班记录:
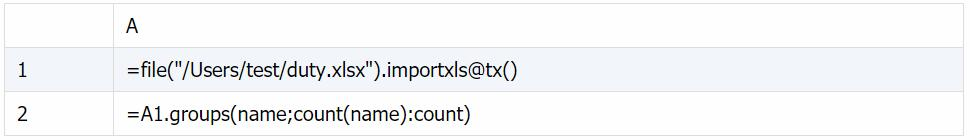
汇总每个人的值班天数:

保存脚本文件CountName.dfx(嵌入 Java 会用到)
每组 TopN
取每个月、每个人、头三天的加班记录
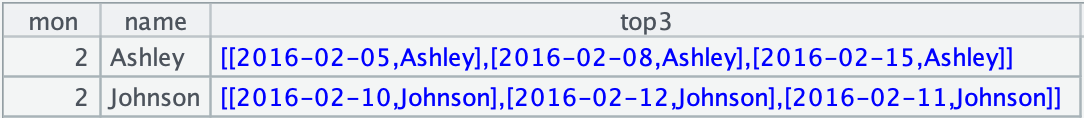
保存脚本文件RecMonTop3.dfx(嵌入 Java 会用到)
Java 调用
SPL 嵌入到 Java 应用程序十分方便,通过 JDBC 调用存储过程方法加载,用常规分组保存的文件CountName.dfx,示例调用如下:
...
Connection con = null;
Class.forName("com.esproc.jdbc.InternalDriver");
con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esproc:local://");
//调用存储过程,其中CountName是dfx的文件名
st =(com. esproc.jdbc.InternalCStatement)con.prepareCall("call CountName()");
//执行存储过程
st.execute();
//获取结果集
ResultSet rs = st.getResultSet();
...
...
Connection con = null;
Class.forName("com.esproc.jdbc.InternalDriver");
con= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:esproc:local://");
//调用存储过程,其中CountName是dfx的文件名
st =(com. esproc.jdbc.InternalCStatement)con.prepareCall("call CountName()");
//执行存储过程
st.execute();
//获取结果集
ResultSet rs = st.getResultSet();
... 替换成 RecMonTop3.dfx 是同样的道理,只需 call RecMonTop3() 即可,也可同时返回两个结果集。这里只用 Java 片段粗略解释了如何嵌入 SPL,详细步骤请参阅 Java 如何调用 SPL 脚本 ,也非常简单,不再赘述。同时,SPL 也支持 ODBC 驱动,集成到支持 ODBC 的语言,嵌入过程类似。
拓展节选
之前没有相关的总结,其实关于数据分组,细分起来其实还有很多种,对位分组、枚举分组、多重分组…,在乾学院 SPL 官方论坛都有总结和示例,这里节选其中两种。
SPL 对位分组
示例 1:按顺序分别列出使用 Chinese、English、French 作为官方语言的国家数量
MySQL8:
with t(name,ord) as (select 'Chinese',1
union all select 'English',2
union all select 'French',3)
select t.name, count(countrycode) cnt
from t left join world.countrylanguage s on t.name=s.language
where s.isofficial='T'
group by name,ord
order by ord;
MySQL8:
with t(name,ord) as (select 'Chinese',1
union all select 'English',2
union all select 'French',3)
select t.name, count(countrycode) cnt
from t left join world.countrylanguage s on t.name=s.language
where s.isofficial='T'
group by name,ord
order by ord; 注意:表的字符集和数据库会话的字符集要保持一致。
(1) show variables like ’character_set_connection’查看当前会话字符集
(2) show create table world.countrylanguage 查看表的字符集
(3) set character_set_connection=[字符集] 更新当前会话字符集
集算器 SPL:
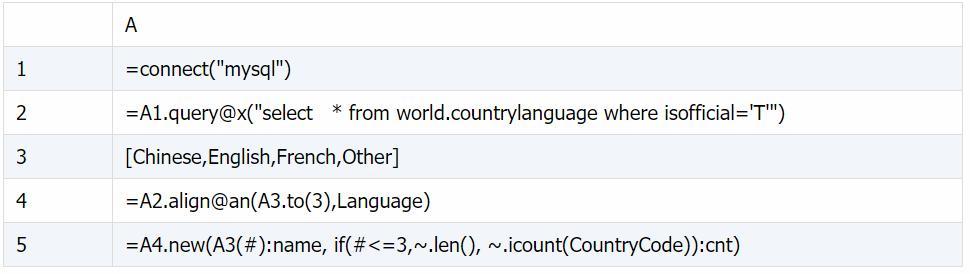
A1: 连接数据库
A2: 查询出所有官方语言的记录
A3: 需要列出的语言
A4: 将所有记录按 Language 对位到 A3 相应位置
A5: 构造以语言和使用此语言为官方语言的国家数量的序表

示例 2:按顺序分别列出使用 Chinese、English、French 及其它语言作为官方语言的国家数量
MySQL8:
with t(name,ord) as (select 'Chinese',1 union all select 'English',2
union all select 'French',3 union all select 'Other', 4),
s(name, cnt) as (
select language, count(countrycode) cnt
from world.countrylanguage s
where s.isofficial='T' and language in ('Chinese','English','French')
group by language
union all
select 'Other', count(distinct countrycode) cnt
from world.countrylanguage s
where isofficial='T' and language not in ('Chinese','English','French')
)
select t.name, s.cnt
from t left join s using (name)
order by t.ord;
MySQL8:
with t(name,ord) as (select 'Chinese',1 union all select 'English',2
union all select 'French',3 union all select 'Other', 4),
s(name, cnt) as (
select language, count(countrycode) cnt
from world.countrylanguage s
where s.isofficial='T' and language in ('Chinese','English','French')
group by language
union all
select 'Other', count(distinct countrycode) cnt
from world.countrylanguage s
where isofficial='T' and language not in ('Chinese','English','French')
)
select t.name, s.cnt
from t left join s using (name)
order by t.ord; 集算器 SPL:
A4: 将所有记录按 Language 对位到 A3.to(3) 相应位置,并追加一组用于存放不能对位的记录
A5: 第 4 组计算不同 CountryCode 的数量

SPL 枚举分组
示例 1:按顺序列出各类型城市的数量
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN'),
segment(class,start,end) as (select 'tiny', 0, 200000
union all select 'small', 200000, 1000000
union all select 'medium', 1000000, 2000000
union all select 'big', 2000000, 100000000
)
select class, count(1) cnt
from segment s join t on t.population>=s.start and t.population<s.end
group by class, start
order by start;
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN'),
segment(class,start,end) as (select 'tiny', 0, 200000
union all select 'small', 200000, 1000000
union all select 'medium', 1000000, 2000000
union all select 'big', 2000000, 100000000
)
select class, count(1) cnt
from segment s join t on t.population>=s.start and t.population<s.end
group by class, start
order by start; 集算器 SPL:
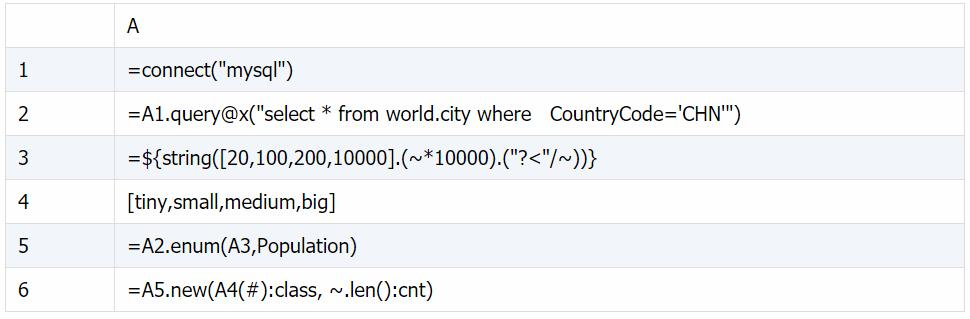
A3: ${…} 宏替换,以大括号内表达式的结果作为新表达式进行计算,结果为序列 [“?<200000”,“?<1000000”,“?<2000000”,“?<100000000”]
A5: 针对 A2 中每条记录,寻找 A3 中第 1 个成立的条件,并追加到对应的组中
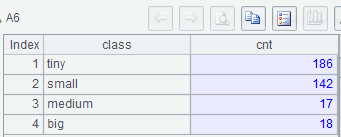
示例 2:列出华东地区大型城市数量、其它地区大型城市数量、非大型城市数量
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN')
select 'East&Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
and district in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu', 'Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Other&Big', count(*)
from t
where population>=2000000
and district not in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu','Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Not Big', count(*)
from t
where population<2000000;
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN')
select 'East&Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
and district in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu', 'Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Other&Big', count(*)
from t
where population>=2000000
and district not in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu','Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Not Big', count(*)
from t
where population<2000000; 集算器 SPL:
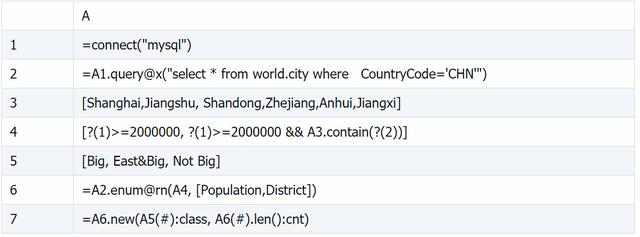
A5: enum@n 将不满足 A4 中所有条件的记录存放到追加的最后一组中

示例 3:列出所有地区大型城市数量、华东地区大型城市数量、非大型城市数量
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN')
select 'Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
union all
select 'East&Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
and district in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu','Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Not Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population<2000000;
MySQL8:
with t as (select * from world.city where CountryCode='CHN')
select 'Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
union all
select 'East&Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population>=2000000
and district in ('Shanghai','Jiangshu','Shandong','Zhejiang','Anhui','Jiangxi')
union all
select 'Not Big' class, count(*) cnt
from t
where population<2000000; 集算器 SPL:
A6: 若 A2 中记录满足 A4 中多个条件时,enum@r 会将其追加到对应的每个组中

优势总结
- 有库写 SQL,没库写 SPL
用 Java 程序直接汇总计算数据,还是比较累的,代码很长,并且不可复用,很多情况数据也不在数据库里,有了 SPL,就能像在 Java 中用 SQL 一样了,十分方便。 - 常用无忧,不花钱就能取得终身使用权的入门版
如果要分析的数据是一次性或临时性的,润乾集算器每个月都提供免费试用授权,可以循环免费使用。但要和 Java 应用程序集成起来部署到服务器上长期使用,定期更换试用授权还是比较麻烦,润乾提供了有终身使用权的入门版,解决了这个后顾之忧,获得方式参考 如何免费使用润乾集算器? - 技术文档和社区支持
官方提供的集算器技术文档本身就有很多现成的例子,常规问题从文档里都能找到解决方法。如果获得了入门版,不仅能够使用 SPL 的常规功能,碰到任何问题都可以去乾学院上去咨询,官方通过该社区对入门版用户提供免费的技术支持。


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。