简言
作为Java程序员, HashMap是一个必知必会的数据类型。无论是从开发中的使用频率还是在面试中考察的频率都足以证明这一点。
HashMap的前世今生
HashMap诞生于JDK1.2, 随着JDK版本的更新以及为了解决JDK1.7中HashMap中hash碰撞问题,
Oracle团队于JEP 180:使用平衡树(Balanced Trees, 即我们所知的红黑树)处理频繁的HashMap冲突。官方文档如下:
- JEP 180: Handle Frequent HashMap Collisions with Balanced Trees
- JDK-8023463 : Improvements to HashMap/LinkedHashMap use of bins/buckets and trees (red/black)
HashMap优化前后的数据结构对比
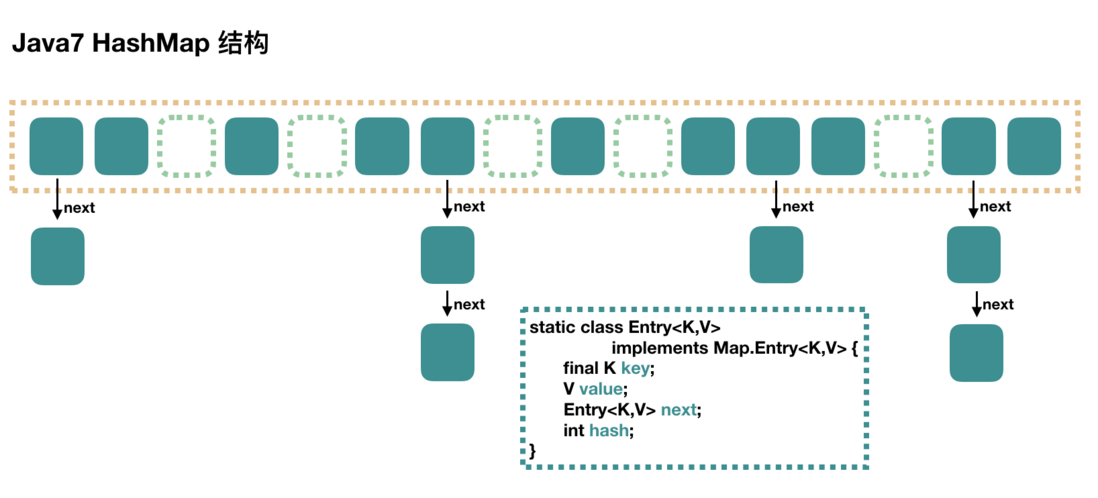
- JDK 1.7中的HashMap
大方向上,HashMap 里面是一个数组,然后数组中每个元素是一个单向链表。下图中,每个绿色
的实体是嵌套类 Entry 的实例,Entry 包含四个属性:key, value, hash 值和用于单向链表的 next。
- capacity:当前数组容量,始终保持 2^n,可以扩容,扩容后数组大小为当前的 2 倍。
- loadFactor:负载因子,默认为 0.75。
- threshold:扩容的阈值,等于 capacity * loadFactor
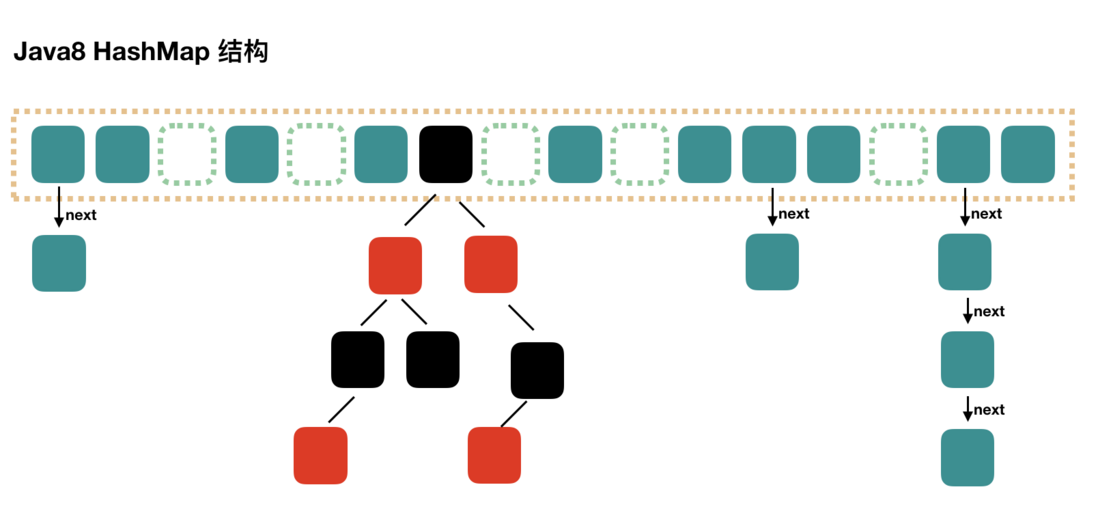
- JDK 1.8中的HashMap
Java8 对 HashMap 进行了一些修改,最大的不同就是利用了红黑树,所以其由 数组+链表+红黑树 组成。
根据 Java7 HashMap 的介绍,我们知道,查找的时候,根据 hash 值我们能够快速定位到数组的
具体下标,但是之后的话,需要顺着链表一个个比较下去才能找到我们需要的,时间复杂度取决
于链表的长度,为 O(n)。为了降低这部分的开销,在 Java8 中,当链表中的元素超过了 8 个以后,
会将链表转换为红黑树,在这些位置进行查找的时候可以降低时间复杂度为 O(logN)。
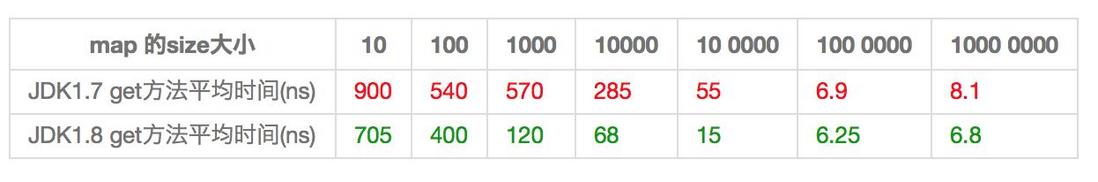
HashMap优化前后的性能对比
Talk is cheap. Show me the code: 手写HashMap
HashMap.java
/**
* @Auther: Noseparte
* @Date: 2019/10/18 11:07
* @Description:
*
* <p>深入剖析 HashMap</p>
*/
public class HashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
// 默认 初始容量
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4;
// 容器的最大值
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
// 默认 负载因子
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
// 链表转红黑树的阈值
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
transient int modCount;
// Node 哈希桶
transient Node[] table;
// 负载因子
final float loadFactor;
// HashMap 所能存储键值对的**极限**
int threshold;
// HashMap 现有键值对的数量
transient int size;
public HashMap(float loadFactor) {
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity){
this(initialCapacity, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if(initialCapacity < 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if(loadFactor <= 0){
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = tableSizeFor(initialCapacity);
}
private static int tableSizeFor(int cap) {
int n = cap - 1;
n |= n >>> 1;
n |= n >>> 2;
n |= n >>> 4;
n |= n >>> 8;
n |= n >>> 16;
return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1;
}
public Set<Entry<K, V>> entrySet() {
return null;
}
private void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) {
}
private void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) {
}
private void treeifyBin(Node<K,V>[] newTable, int hash) {
}
/**
* Hash算法 取key的hashCode值、高位运算、取模运算。
*
* @param key key键
* @return
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
// Create a regular (non-tree) node
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
return new Node<K, V>(hash, key, value, next);
}
}
Node节点
/**
* @Auther: Noseparte
* @Date: 2019/10/18 11:13
* @Description:
*
* <p>Node 维护一个链表</p>
*/
static class Node<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K, V>{
final int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Node<K, V> next;
public Node(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K, V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
public final K getKey() {
return key;
}
public final V getValue() {
return value;
}
public final V setValue(V newValue) {
V oldValue = this.value;
value = newValue;
return oldValue;
}
}TreeNode.java 红黑树
/**
* @Auther: Noseparte
* @Date: 2019/10/18 15:53
* @Description:
*
* <p>红黑树 Red-black tree</p>
*/
static final class TreeNode<K, V> extends Node{
TreeNode<K, V> parent;
TreeNode<K, V> left;
TreeNode<K, V> right;
TreeNode<K, V> prev;
boolean red;
TreeNode(int hash, K key, V value, HashMap.Node<K, V> next) {
super(hash, key, value, next);
}
final void split(HashMap<K,V> kvHashMap, Node[] newTable, int index, int oldCapacity) {
}
/**
* 得到树节点
*
* @param hash key的hash值
* @param key key键
* @return
*/
TreeNode<K, V> getTreeNode(int hash, Object key) {
return ((parent != null) ? root() : this).find(hash, key, null);
}
final TreeNode<K,V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) {
// 略 感兴趣请查看源码
return null;
}
final TreeNode<K,V> root() {
for (TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) {
if ((p = r.parent) == null)
return r;
r = p;
}
}
Node<K,V> putTreeVal(HashMap<K, V> kvHashMap, Node<K, V>[] newTable, int hash, K key, V value) {
// 红黑树直接插入键值对
return null;
}
}HashMap中的常用函数解析
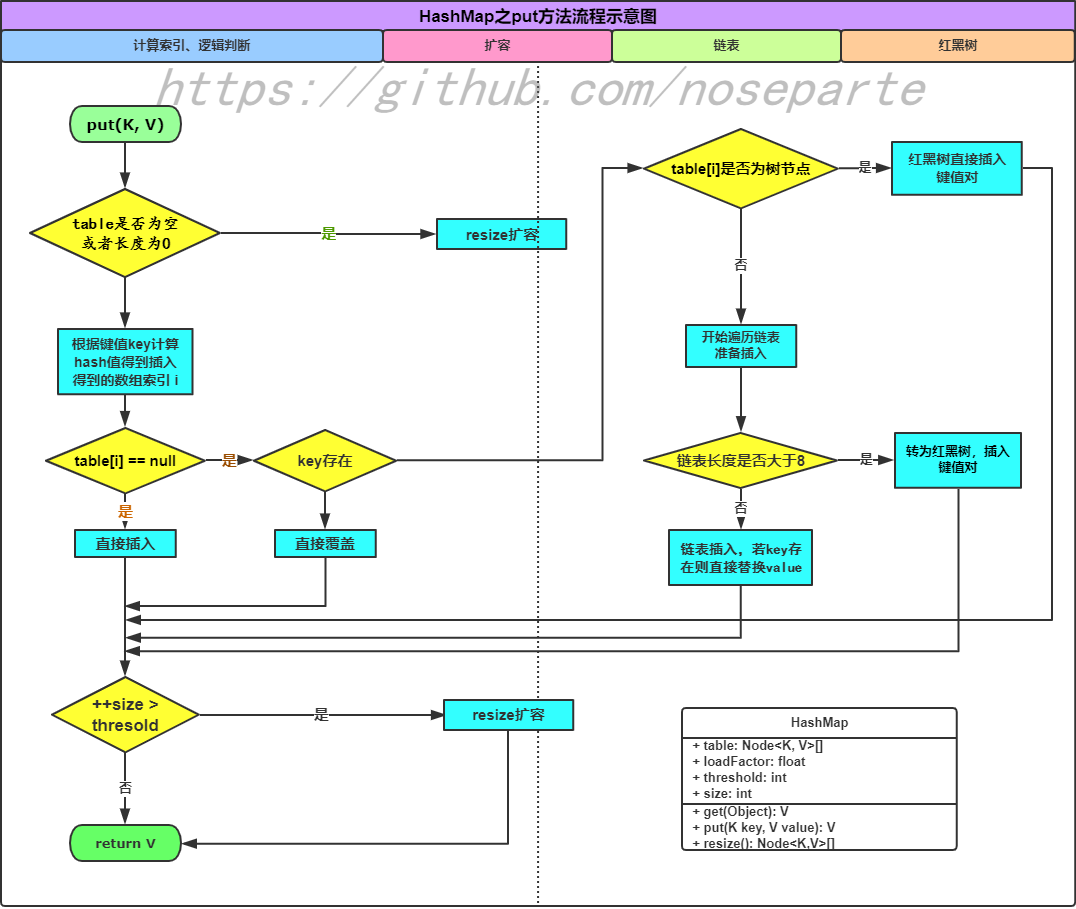
put(K key, V value)
public class HashMap{
/**
* 调用层 HashMap插入k-V键值对
*
* @param key key键
* @param value value值
* @return V
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
/**
* 实现层 HashMap插入k-V键值对的底层实现
*
* @param hash key对应的hash值
* @param key key键
* @param value value值
* @param onlyIfAbsent 如果为true, 不改变现存的值
* @param evict 如果为false,会新创建一个
* @return
*/
final public V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K, V>[] newTable;
Node<K, V> node;
int n, i;
/** table是否为空, 或者长度是否为0 */
if ((newTable = table) == null || (n = newTable.length) == 0)
// 扩容
n = (newTable = resize()).length;
// 根据键值key计算hash值得到插入得到的数组索引 i
if ((node = newTable[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null) {
// 如果为空, 直接插入
newTable[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
} else {
Node<K, V> e;
K k;
// 通过校验key与key的hash值
if (node.hash == hash &&
((k = node.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) {
// 存在则直接插入
e = node;
// table[i]是否为树节点
} else if (node instanceof TreeNode) {
// 红黑树直接插入键值对
e = ((TreeNode<K, V>) node).putTreeVal(this, newTable, hash, key, value);
} else {
// 开始遍历链表准备插入
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = node.next) == null) {
node.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// 链表长度是否大于8
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1)
// 转为红黑树,插入键值对
treeifyBin(newTable, hash);
break;
}
// 链表插入,若key存在则直接替换value
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
node = e;
}
}
if (e != null) {
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null) {
e.value = value;
}
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
}get()
public class HashMap{
/**
* 通过key获取value k-v
* @param key key值
* @return value
*/
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
return (e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null ? null : e.value;
}
/**
* 查找HashMap中的某个K-V的底层实现
* @param hash node#hash值
* @param key node#key值
* @return
*/
private final Node<K,V> getNode(int hash, Object key) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first, e; int n; K k;
if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&
(first = tab[(n - 1) & hash]) != null) {
if (first.hash == hash && // always check first node
((k = first.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return first;
if ((e = first.next) != null) {
if (first instanceof TreeNode)
return ((TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key);
do {
/**
* 寻Node
* @param hash Node对应的hash值
* @param key 判断key是否相同
* @return Node
*/
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
return e;
} while ((e = e.next) != null);
}
}
return null;
}
}resize()
public class HashMap{
/**
* 哈系桶数组 扩容
* <p>
* if null: 初始化数组长度[12] DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR * DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY
* else: 2的指数幂扩容 table.length << 1
* <p/>
* <p>
* 位运算 c为自然常数
* c << 1 ==> 2c
* c << 2 ==> 4c
* <p/>
* @return
*/
final Node<K, V>[] resize(){
/// <summary>
/// 哈希桶数组 初始化
/// <summary>
Node<K, V>[] oldTable = this.table;
int oldCapacity = (oldTable == null) ? 0 : oldTable.length;
int oldThreshold = this.threshold;
int newCapacity, newThreshold = 0;
if(oldCapacity > 0){
if(oldCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY){
threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return oldTable;
}
else if ((newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1) < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY &&
oldCapacity >= DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY){
newThreshold = oldThreshold << 1;
}
}
else if (oldThreshold > 0){ // 初始大小为threshold
newCapacity = oldThreshold;
}
else { // 如果threshold为0时, 使用默认值
newCapacity = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY;
newThreshold = (int) (DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY * DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR);
}
if(newThreshold == 0){
float currentThreshold = newCapacity * loadFactor;
newThreshold = newCapacity < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY && currentThreshold < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY ?
(int) currentThreshold : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
threshold = newThreshold;
Node[] newTable = new Node[newCapacity];
table = newTable;
if(oldTable != null){
for(int j = 0; j < oldCapacity; ++j){
Node<K, V> eachNode;
if((eachNode = oldTable[j]) != null){
oldTable[j] = null;
if(eachNode.next == null){
newTable[eachNode.hash & (newCapacity - 1)] = eachNode;
}
else if (eachNode instanceof TreeNode){
((TreeNode)eachNode).split(this, newTable, j, oldCapacity);
}
else {
Node<K, V> leftHead = null, leftTail = null;
Node<K, V> rightHead = null, rightTail = null;
Node<K, V> next;
do {
next = eachNode;
if((eachNode.hash & oldCapacity) == 0){
if(leftTail == null){
leftHead = eachNode;
}else {
leftTail.next = eachNode;
}
leftTail = eachNode;
}
else {
if (rightHead == null){
rightHead = eachNode;
}else {
rightTail.next = eachNode;
}
rightTail = eachNode;
}
}while ((eachNode = next) != null);
if (leftTail != null){
leftTail.next = null;
newTable[j] = leftHead;
}
if (rightTail != null){
rightTail.next = null;
newTable[j] = rightHead;
}
}
}
}
}
return newTable;
}
}HashMap中的衍生题
- 为什么HashMap中平衡树使用的是红黑树?
插入效率比平衡二叉树高,查询效率比普通二叉树高。所以选择性能相对折中的红黑树。
- 链表or红黑树?
Hash与红黑树的区别:
权衡三个因素: 查找速度, 数据量, 内存使用,可扩展性,有序性。
红黑树是有序的,Hash是无序的,根据需求来选择。
红黑树占用的内存更小(仅需要为其存在的节点分配内存),而Hash事先应该分配足够的内存存储散列表,即使有些槽可能弃用
红黑树查找和删除的时间复杂度都是O(logn),Hash查找和删除的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
- 何为Hash碰撞? 怎么避免?
所谓哈希(hash),就是将不同的输入映射成独一无二的、固定长度的值(又称"哈希值")。
如果不同的输入得到了同一个哈希值,就发生了"哈希碰撞"(collision)。
防止哈希碰撞的最有效方法,就是扩大哈希值的取值空间。
阮一峰: 哈希碰撞与生日攻击
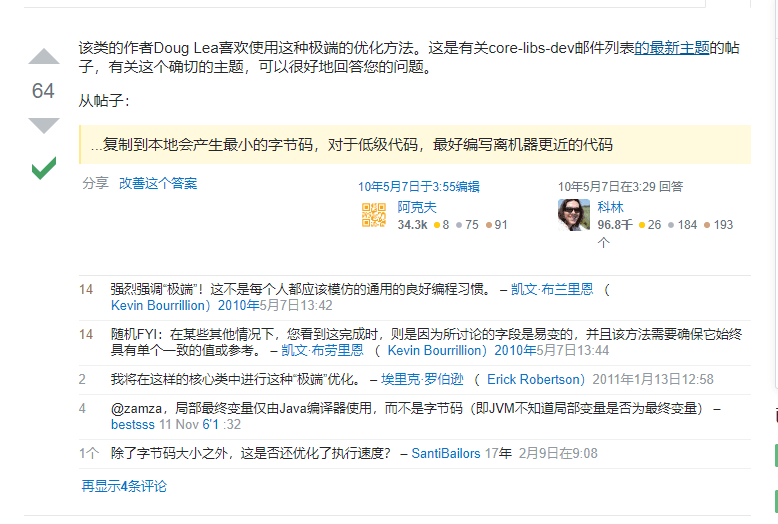
- 看HashMap源码时, 为什么会在函数内部定义一个局部变量?
简而言之,是Doug Lea大神自己的一种优化手段
Stack Overflow原文
Doug Lea大神的原话
finally
- JDK1.8中的HashMap基于JDK1.7中的HashMap(数组+链表), 新增了红黑树, 极大程度的优化了HashMap的性能
- HashMap是线程不安全的,不要在并发的环境中同时操作HashMap,建议使用ConcurrentHashMap。
- 扩容是一个特别耗性能的操作,所以当程序员在使用HashMap的时候,估算map的大小,初始化的时候给一个大致的数值,避免map进行频繁的扩容。
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。