系列文章目录
@TOC
前言
前面一章讲了微服务的一些优点和缺点,那如何做到
一、目标
二、使用步骤
1. 安装 consul
我们可以直接使用官方提供的二进制文件来进行安装部署,其官网地址为 https://www.consul.io/downloads
下载后为可执行文件,在我们开发试验过程中,可以直接使用 consul agent -dev 命令来启动一个单节点的 consul
在启动的打印日志中可以看到 agent: Started HTTP server on 127.0.0.1:8500 (tcp), 我们可以在浏览器直接访问 127.0.0.1:8500 即可看到如下
这里我们的 consul 就启动成功了
2. 服务注册
在网络编程中,一般会提供项目的 IP、PORT、PROTOCOL,在服务治理中,我们还需要知道对应的服务名、实例名以及一些自定义的扩展信息
在这里使用 ServiceInstance 接口来规定注册服务时必须的一些信息,同时用 DefaultServiceInstance 实现
type ServiceInstance interface {
// return The unique instance ID as registered.
GetInstanceId() string
// return The service ID as registered.
GetServiceId() string
// return The hostname of the registered service instance.
GetHost() string
// return The port of the registered service instance.
GetPort() int
// return Whether the port of the registered service instance uses HTTPS.
IsSecure() bool
// return The key / value pair metadata associated with the service instance.
GetMetadata() map[string]string
}
type DefaultServiceInstance struct {
InstanceId string
ServiceId string
Host string
Port int
Secure bool
Metadata map[string]string
}
func NewDefaultServiceInstance(serviceId string, host string, port int, secure bool,
metadata map[string]string, instanceId string) (*DefaultServiceInstance, error) {
// 如果没有传入 IP 则获取一下,这个方法在多网卡的情况下,并不好用
if len(host) == 0 {
localIP, err := util.GetLocalIP()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
host = localIP
}
if len(instanceId) == 0 {
instanceId = serviceId + "-" + strconv.FormatInt(time.Now().Unix(), 10) + "-" + strconv.Itoa(rand.Intn(9000)+1000)
}
return &DefaultServiceInstance{InstanceId: instanceId, ServiceId: serviceId, Host: host, Port: port, Secure: secure, Metadata: metadata}, nil
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) GetInstanceId() string {
return serviceInstance.InstanceId
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) GetServiceId() string {
return serviceInstance.ServiceId
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) GetHost() string {
return serviceInstance.Host
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) GetPort() int {
return serviceInstance.Port
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) IsSecure() bool {
return serviceInstance.Secure
}
func (serviceInstance DefaultServiceInstance) GetMetadata() map[string]string {
return serviceInstance.Metadata
}定义接口
在上面规定了需要注册的服务的必要信息,下面定义下服务注册和剔除的方法
type ServiceRegistry interface {
Register(serviceInstance cloud.ServiceInstance) bool
Deregister()
}具体实现
因为 consul 提供了 http 接口来对consul 进行操作,我们也可以使用 http 请求方式进行注册和剔除操作,具体 http 接口文档见 https://www.consul.io/api-docs, consul 默认提供了go 语言的实现,这里直接使用 github.com/hashicorp/consul/api
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/hashicorp/consul/api"
"strconv"
"unsafe"
)
type consulServiceRegistry struct {
serviceInstances map[string]map[string]cloud.ServiceInstance
client api.Client
localServiceInstance cloud.ServiceInstance
}
func (c consulServiceRegistry) Register(serviceInstance cloud.ServiceInstance) bool {
// 创建注册到consul的服务到
registration := new(api.AgentServiceRegistration)
registration.ID = serviceInstance.GetInstanceId()
registration.Name = serviceInstance.GetServiceId()
registration.Port = serviceInstance.GetPort()
var tags []string
if serviceInstance.IsSecure() {
tags = append(tags, "secure=true")
} else {
tags = append(tags, "secure=false")
}
if serviceInstance.GetMetadata() != nil {
var tags []string
for key, value := range serviceInstance.GetMetadata() {
tags = append(tags, key+"="+value)
}
registration.Tags = tags
}
registration.Tags = tags
registration.Address = serviceInstance.GetHost()
// 增加consul健康检查回调函数
check := new(api.AgentServiceCheck)
schema := "http"
if serviceInstance.IsSecure() {
schema = "https"
}
check.HTTP = fmt.Sprintf("%s://%s:%d/actuator/health", schema, registration.Address, registration.Port)
check.Timeout = "5s"
check.Interval = "5s"
check.DeregisterCriticalServiceAfter = "20s" // 故障检查失败30s后 consul自动将注册服务删除
registration.Check = check
// 注册服务到consul
err := c.client.Agent().ServiceRegister(registration)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return false
}
if c.serviceInstances == nil {
c.serviceInstances = map[string]map[string]cloud.ServiceInstance{}
}
services := c.serviceInstances[serviceInstance.GetServiceId()]
if services == nil {
services = map[string]cloud.ServiceInstance{}
}
services[serviceInstance.GetInstanceId()] = serviceInstance
c.serviceInstances[serviceInstance.GetServiceId()] = services
c.localServiceInstance = serviceInstance
return true
}
// deregister a service
func (c consulServiceRegistry) Deregister() {
if c.serviceInstances == nil {
return
}
services := c.serviceInstances[c.localServiceInstance.GetServiceId()]
if services == nil {
return
}
delete(services, c.localServiceInstance.GetInstanceId())
if len(services) == 0 {
delete(c.serviceInstances, c.localServiceInstance.GetServiceId())
}
_ = c.client.Agent().ServiceDeregister(c.localServiceInstance.GetInstanceId())
c.localServiceInstance = nil
}
// new a consulServiceRegistry instance
// token is optional
func NewConsulServiceRegistry(host string, port int, token string) (*consulServiceRegistry, error) {
if len(host) < 3 {
return nil, errors.New("check host")
}
if port <= 0 || port > 65535 {
return nil, errors.New("check port, port should between 1 and 65535")
}
config := api.DefaultConfig()
config.Address = host + ":" + strconv.Itoa(port)
config.Token = token
client, err := api.NewClient(config)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &consulServiceRegistry{client: *client}, nil
}
测试用例
注册服务的代码基本完成,来测试一下
func TestConsulServiceRegistry(t *testing.T) {
host := "127.0.0.1"
port := 8500
registryDiscoveryClient, _ := extension.NewConsulServiceRegistry(host, port, "")
ip, err := util.GetLocalIP()
if err != nil {
t.Error(err)
}
serviceInstanceInfo, _ := cloud.NewDefaultServiceInstance("go-user-server", "", 8090,
false, map[string]string{"user":"zyn"}, "")
registryDiscoveryClient.Register(serviceInstanceInfo)
r := gin.Default()
// 健康检测接口,其实只要是 200 就认为成功了
r.GET("/actuator/health", func(c *gin.Context) {
c.JSON(200, gin.H{
"message": "pong",
})
})
err = r.Run(":8090")
if err != nil{
registryDiscoveryClient.Deregister()
}
}
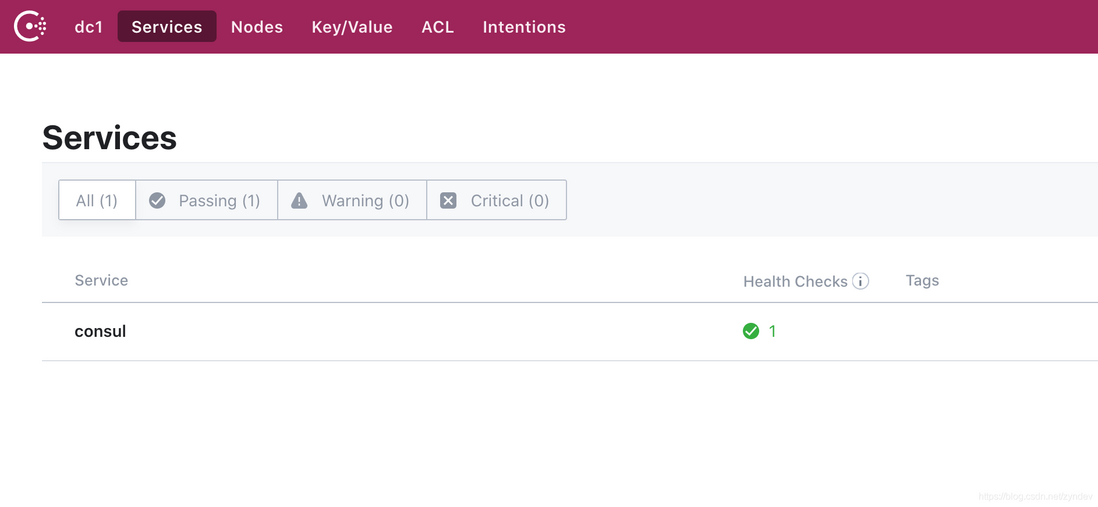
如果成功,则会在 consul 看到 go-user-server 这个服务
3. 服务发现
在服务发现中,一般会需要两个方法
- 获取所有的服务列表
- 获取指定的服务的所有实例信息
接口定义
type DiscoveryClient interface {
/**
* Gets all ServiceInstances associated with a particular serviceId.
* @param serviceId The serviceId to query.
* @return A List of ServiceInstance.
*/
GetInstances(serviceId string) ([]cloud.ServiceInstance, error)
/**
* @return All known service IDs.
*/
GetServices() ([]string, error)
}
具体实现
来实现一下
type consulServiceRegistry struct {
serviceInstances map[string]map[string]cloud.ServiceInstance
client api.Client
localServiceInstance cloud.ServiceInstance
}
func (c consulServiceRegistry) GetInstances(serviceId string) ([]cloud.ServiceInstance, error) {
catalogService, _, _ := c.client.Catalog().Service(serviceId, "", nil)
if len(catalogService) > 0 {
result := make([]cloud.ServiceInstance, len(catalogService))
for index, sever := range catalogService {
s := cloud.DefaultServiceInstance{
InstanceId: sever.ServiceID,
ServiceId: sever.ServiceName,
Host: sever.Address,
Port: sever.ServicePort,
Metadata: sever.ServiceMeta,
}
result[index] = s
}
return result, nil
}
return nil, nil
}
func (c consulServiceRegistry) GetServices() ([]string, error) {
services, _, _ := c.client.Catalog().Services(nil)
result := make([]string, unsafe.Sizeof(services))
index := 0
for serviceName, _ := range services {
result[index] = serviceName
index++
}
return result, nil
}
// new a consulServiceRegistry instance
// token is optional
func NewConsulServiceRegistry(host string, port int, token string) (*consulServiceRegistry, error) {
if len(host) < 3 {
return nil, errors.New("check host")
}
if port <= 0 || port > 65535 {
return nil, errors.New("check port, port should between 1 and 65535")
}
config := api.DefaultConfig()
config.Address = host + ":" + strconv.Itoa(port)
config.Token = token
client, err := api.NewClient(config)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &consulServiceRegistry{client: *client}, nil
}测试用例
func TestConsulServiceDiscovery(t *testing.T) {
host := "127.0.0.1"
port := 8500
token := ""
registryDiscoveryClient, err := extension.NewConsulServiceRegistry(host, port, token)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
t.Log(registryDiscoveryClient.GetServices())
t.Log(registryDiscoveryClient.GetInstances("go-user-server"))
}结果
consul_service_registry_test.go:57: [consul go-user-server ] <nil>
consul_service_registry_test.go:59: [{go-user-server-1602590661-56179 go-user-server 127.0.0.1 8090 false map[user:zyn]}] <nil>总结
通过使用 consul api 我们可以简单的实现基于 consul 的服务发现,在通过结合 http rpc 就可简单的实现服务的调用,下面一章来简单讲下 go 如何发起 http 请求,为我们做 rpc 做个铺垫
具体代码见 https://github.com/zhangyunan...
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。