一、前言
前面已经说过,可以通过[]运算符修改或者添加键值对,在这里就不说这种用法了。
二、方法
1、insert
insert方法是专门用来向 map 容器中插入新的键值对的。这里的"插入"指的是 insert() 方法可以将新的键值对插入到 map 容器中的指定位置。如果破坏了map容器的有序性,map容器会对新键值对的位置进行调整,也就是说,虽然insert可以将键值对插入指定的位置,但是插入之后map容器会检查插入的键值对是否符合有序性,不符合的话insert指定的位置就不是插入键值对真正的位置了。
1)不指定位置,直接插入
| 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pair<iterator,bool> insert (const value_type& val); | 引用传递一个键值对 |
| template <class P> pair<iterator,bool> insert (P&& val); | 以右值引用的方式传递键值对 |
区别:传递参数的方式不同。无论是局部定义的键值对变量还是全局定义的键值对变量,都采用普通引用传递的方式;而对于临时的键值对变量,则以右值引用的方式传参。
std::map<int, string> mapInfo{ {1,"test"},{2,"lin"},{3,"wei"} };
//格式1
std::pair<int, string> mapData = { 4, "wu" };
std::pair<std::map<int, string>::iterator, bool> ret;
ret = mapInfo.insert(mapData);
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
//格式2
ret = mapInfo.insert({ 5,"ouyang" });
//等价于
//ret = mapInfo.insert(pair<int, string>{5, "ouyang"});
//ret = mapInfo.insert(make_pair(5, "ouyang"));
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
//插入失败
ret = mapInfo.insert({ 1,"lu" });
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}
结果如下:
由结果可知:
①返回值是一个 pair 对象,其中 pair.first 表示一个迭代器,pair.second 为一个 bool 类型变量:
如果成功插入 val,则该迭代器指向新插入的 val,bool 值为 true;
如果插入 val 失败,则表明当前 map 容器中存有和 val 的键相同的键值对(用 p 表示),此时返回的迭代器指向 p,bool 值为 false。
2)指定位置插入
| 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| iterator insert (const_iterator position, const value_type& val); | 以普通引用的方式传递 val 参数 |
| template <class P> iterator insert (const_iterator position, P&& val); | 以右值引用的方式传递 val 键值对参数 |
std::map<int, string> mapInfo{ {1,"test"},{2,"lin"},{3,"wei"} };
//格式1
std::pair<int, string> mapData = { 4, "wu" };
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
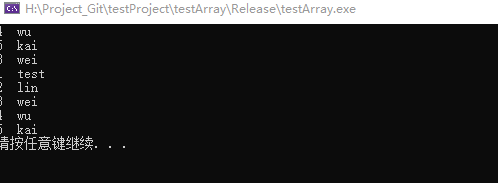
std::map<int, string>::iterator insertIter = mapInfo.insert(++mapIter, mapData);
std::cout << insertIter->first << " " << insertIter->second << std::endl;
//格式2
insertIter = mapInfo.insert(++mapIter, std::pair<int, string>(5, "kai"));
std::cout << insertIter->first << " " << insertIter->second << std::endl;
//插入失败
insertIter = mapInfo.insert(++mapIter, std::pair<int,string>(3,"ouyang"));
std::cout << insertIter->first << " " << insertIter->second << std::endl;
mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}结果如下:
由结果可知:
①和不指定位置的插入的方法的区别,这里返回的是迭代器
如果插入成功,insert() 方法会返回一个指向 map 容器中已插入键值对的迭代器;
如果插入失败,insert() 方法同样会返回一个迭代器,该迭代器指向 map 容器中和 val 具有相同键的那个键值对。
3)向当前 map 容器中插入其它 map 容器指定区域内的所有键值对
| 格式 |
|---|
| template <class InputIterator> void insert (InputIterator first, InputIterator last); |
std::map<int, string> mapInfo{ {1,"test"},{2,"lin"},{3,"wei"} };
std::map<int, string> mapInfo2;
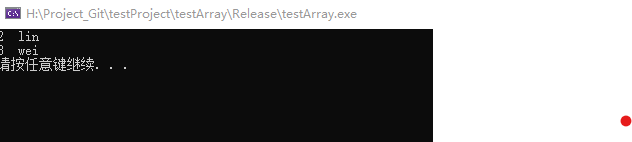
std::map<int, string>::iterator first = ++mapInfo.begin();
std::map<int, string>::iterator last = mapInfo.end();
mapInfo2.insert(first, last);
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo2.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo2.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}
结果如下:
由结果可知:
①需要其他map容器的开始和结束的迭代器,组成一个指定区域
4)一次向 map 容器中插入多个键值对
| 表列 A |
|---|
| void insert ({val1, val2, ...}); |
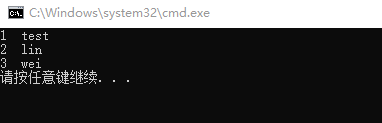
std::map<int, string> mapInfo;
mapInfo.insert({ {1,"test"},{2,"lin"},{3,"wei"} });
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}结果如下:
insert的介绍就到这里,接下来讲讲比insert高效的方法
2、emplace
| 表列 A |
| ----- |
| template <class... Args> pair<iterator,bool> emplace (Args&&... args); |
std::map<int, string> mapInfo;
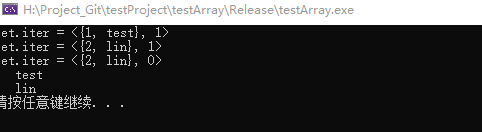
pair<map<int, string>::iterator, bool> ret = mapInfo.emplace(1, "test");
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
ret = mapInfo.emplace(2, "lin");
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
ret = mapInfo.emplace(2, "kai");
std::cout << "ret.iter = <{" << ret.first->first << ", " << ret.first->second << "}, " << ret.second << ">" << std::endl;
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}结果如下:
由结果可知:
①使用emplace方法时,将创建新键值对所需的数据作为参数直接传入即可,返回值是一个pair对象,和不指定位置的insert方法的返回值一样
3、emplace_hint
| 格式 |
|---|
| template <class... Args> iterator emplace_hint (const_iterator position, Args&&... args); |
该方法不仅要传入创建键值对所需要的数据,还需要传入一个迭代器作为第一个参数,指明要插入的位置。
std::map<int, string> mapInfo;
map<int, string>::iterator iter = mapInfo.emplace_hint(mapInfo.begin(), 1, "test");
std::cout << iter->first << " " << iter->second << std::endl;
iter = mapInfo.emplace_hint(mapInfo.begin(), 2, "lin");
cout << iter->first << " " << iter->second << endl;
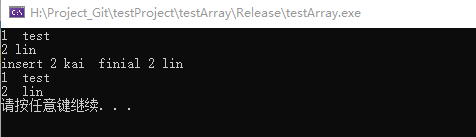
iter = mapInfo.emplace_hint(mapInfo.begin(), 2, "kai");
cout << "insert 2 kai finial " << iter->first << " " << iter->second << endl;
std::map<int, string>::iterator mapIter = mapInfo.begin();
for (; mapIter != mapInfo.end(); mapIter++)
{
std::cout << mapIter->first << " " << mapIter->second << std::endl;
}结果如下:
①返回值是一个迭代器。当成功插入新键值对时,返回的迭代器指向新插入的键值对;反之,如果插入失败,则表明 map 容器中存有相同键的键值对,返回的迭代器就指向这个键值对


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。