1.Expanding Cards
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
flexproperty in the flexbox layout: Let all the child elements of the flexbox model object have the same length, and ignore their internal content. - JavaScript: Use the
[].filter.call()method to quickly realize simple tab switching. Such as the above sample source code:
const panelItems = document.querySelectorAll(".container > .panel");
panelItems.forEach(item => {
item.addEventListener('click',() => {
[].filter.call(item.parentElement.children,el => el !== item).forEach(el => el.classList.remove('active'));
item.classList.add('active')
});
});
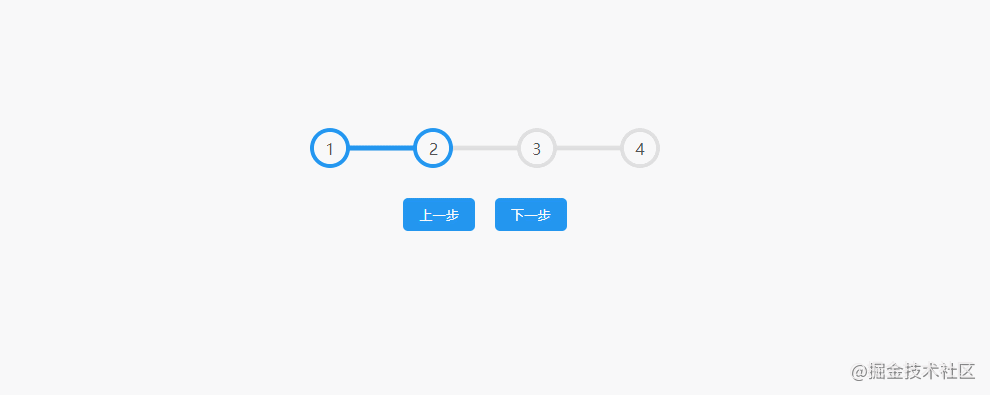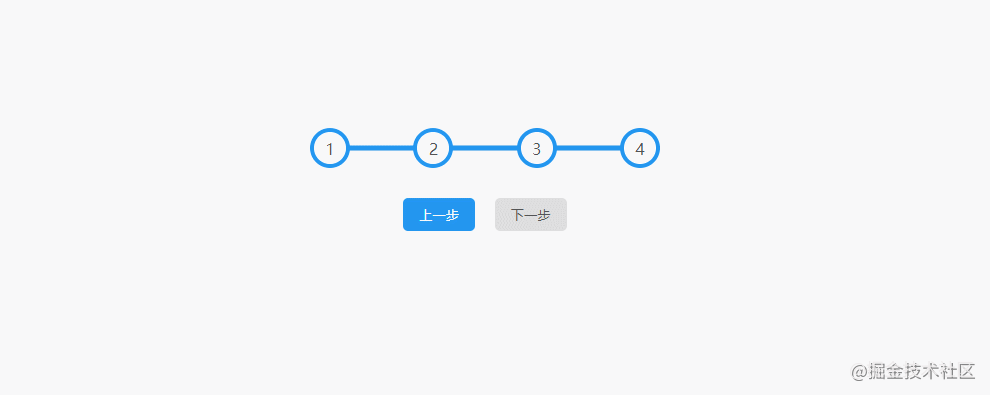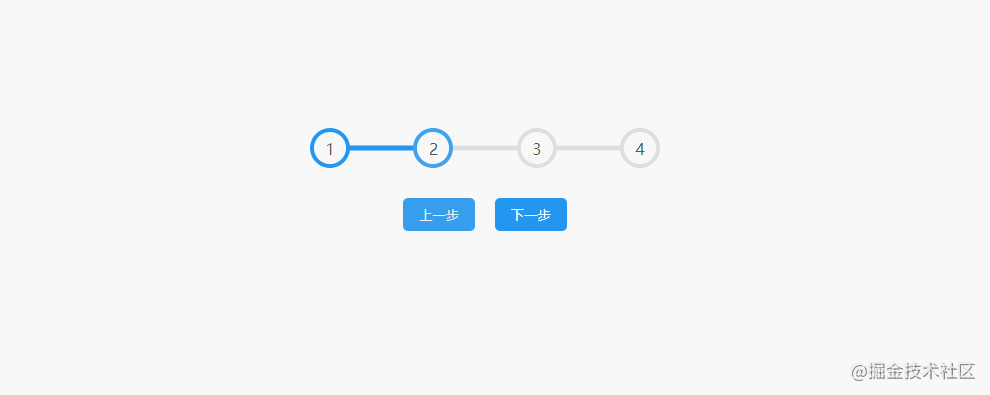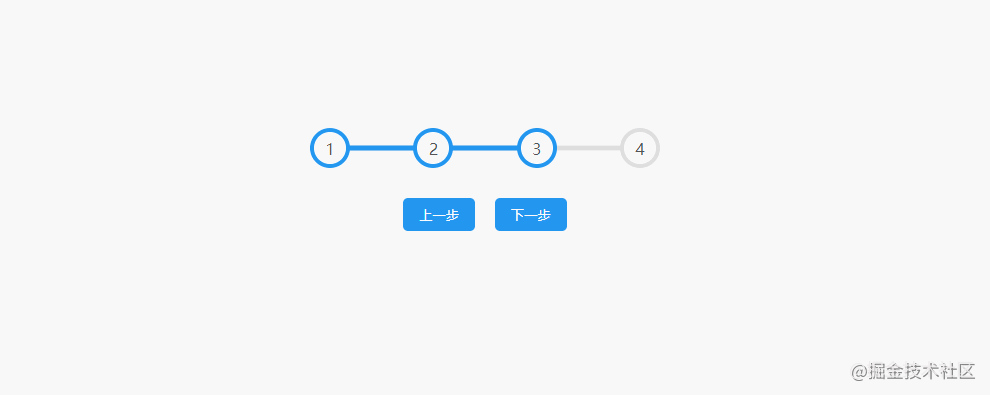
2.Progress Steps
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSvariable usage and flexible box vertical and horizontal centering plus pseudo-element usage. - JavaScript: Calculate the width of the progress bar, the operation of the class name. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function handleClass(el){
let methods = {
addClass,
removeClass
};
function addClass(c){
el.classList.add(c);
return methods;
};
function removeClass(c){
el.classList.remove(c);
return methods;
}
return methods
}3.Rotating Navigation Animation
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: CSS flexible box layout plus
rotateanimation. - JavaScript: The operation of adding and removing class names. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const addClass = (el,className) => el.classList.add(className);
const removeClass = (el,className) => el.classList.remove(className);4.hidden-search-widget
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: CSS to change the width of the transition animation + +
inputofplaceholderstyle. - JavaScript: The operation of adding and removing class names. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
.search.active > .input {
width: 240px;
}
.search.active > .search-btn {
transform: translateX(238px);
}
.search > .search-btn,.search > .input {
border: none;
width: 45px;
height: 45px;
outline: none;
transition: all .3s cubic-bezier(0.25, 0.46, 0.45, 0.94);
border-radius: 8px;
}searchBtn.addEventListener('click',() => {
searchContainer.classList.toggle('active');
searchInput.focus();
})5.Blurry Loading
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSS filterproperty usage;. - JavaScript: Timer plus dynamic setting style. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
let load = 0;
let timer = null;
let blurryLoadingHandler = function(){
load++;
if(load > 99){
clearTimeout(timer)
}else{
timer = setTimeout(blurryLoadingHandler,20);
}
text.textContent = `页面加载${ load }%`;
text.style.opacity = scale(load,0,100,1,0);
bg.style.filter = `blur(${scale(load,0,100,20,0)}px)`;
}
blurryLoadingHandler();Here is a very important utility function (the utility function is used in several subsequent examples), as shown below:
const scale = (n,inMin,inMax,outerMin,outerMax) => (n - inMin) * (outerMax - outerMin) / (inMax - inMin) + outerMin;The purpose of this utility function is to map a range of numbers to another range of numbers. For example, 1 ~ 100 the number range of 0 ~ 1 to 06110fc9051ec0.
details .
6.Scroll Animation
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSdisplacement animation. - JavaScript: Dynamic creation of elements + element scroll event monitoring + judgment of the visible area of the view + anti-shake function. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function debounce(fn,time = 100){
let timer = null;
return function(){
if(timer)clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(fn,time);
}
}
let triggerBottom = window.innerHeight / 5 * 4;
boxElements.forEach((box,index) => {
const top = box.getBoundingClientRect().top;
if(top <= triggerBottom){
box.classList.add('show');
}else{
box.classList.remove('show');
}
})7. Split Landing Page
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSStransition effects + flexible box vertical and horizontal centering +CSSpositioning + width change. - JavaScript: Mouse hover event + operation of class name. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
HTMLElement.prototype.addClass = function(className) {
this.classList.add(className);
};
HTMLElement.prototype.removeClass = function(className){
this.classList.remove(className);
}
const on = (el,type,handler,useCapture = false) => {
if(el && type && handler) {
el.addEventListener(type,handler,useCapture);
}
}
on(leftSplit,'mouseenter',() => container.addClass('hover-left'));
on(leftSplit,'mouseleave',() => container.removeClass('hover-left'));
on(rightSplit,'mouseenter',() => container.addClass('hover-right'));
on(rightSplit,'mouseleave',() => container.removeClass('hover-right'));From this example, I also know the mouseenter、mouseleave and mouseover、mouseout , summarized as follows:
- Enter is only triggered once, and it will continue to be triggered only after the mouse leaves the target element before entering. The same is true for leave. And over and out are constant triggers.
- Enter enters the child element, and it is impossible to distinguish whether it is moved in/out of the child element or the parent element through e.target, while over and out can be distinguished.
8.Form Wave
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSgradient + flexible box vertical and horizontal centering +CSStransition animation +CSSdisplacement transformation + focus on the usage of the focus pseudo-class selector and the same level element selector. - JavaScript: Replace strings with tags + dynamically create elements. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const createLetter = v => v.split("").map((letter,idx) => `<span style="transition-delay:${ idx * 50 }ms">${ letter }</span>`).join("");9.Sound Board
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSgradient + flexible box vertical and horizontal centering + basic style. - JavaScript: Dynamically create elements + play audio (
audiotag). For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
sounds.forEach(sound => {
const btn = create('button');
btn.textContent = sound;
btn.type = "button";
const audio = create('audio');
audio.src = "./audio/" + sound + '.mp3';
audio.id = sound;
btn.addEventListener('click',() => {
stopSounds();
$('#' + sound).play();
});
buttonContainer.appendChild(btn);
buttonContainer.insertAdjacentElement('beforebegin',audio);
});10. Dad Jokes
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSgradient + flexible box vertical and horizontal centering + basic style. - JavaScript: Event monitoring +
fetch APIrequest interface. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const api = 'https://icanhazdadjoke.com';
const on = (el,type,handler,useCapture = false) => {
if(el && type && handler){
el.addEventListener(type,handler,useCapture);
}
}
on(getJokeBtn,'click',request);
request();
async function request(){
const res = await fetch(api,headerConfig);
const data = await res.json();
content.innerHTML = data.joke;
}11. Event Keycodes
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSgradient + flexible box vertical and horizontal centering + basic style. - JavaScript: keyboard event monitoring + properties of the event object. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const container = document.querySelector('#container');
window.addEventListener("keydown",event => {
createKeyCodeTemplate(event);
});
function createKeyCodeTemplate(e){
const { key,keyCode,code } = e;
let template = "";
[
{
title:"event.key",
content:key === " " ? "Space" : key
},
{
title:"event.keyCode",
content:keyCode
},
{
title:"event.code",
content:code
}
].forEach(value => {
template += `<div class="key"><small>${ value.title }</small>${ value.content }</div>`;
});
container.innerHTML = template;
}12. Faq Collapse
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
font-awesomefont library + pseudo element selector + positioning +CSSgradient + basic style. - JavaScript: dynamic creation of elements + switching of class names + event proxy. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const faqs = document.querySelectorAll('.faq-container > .faq');
container.addEventListener('click',e => {
if(e.target.className.indexOf('faq-icon') > -1){
faqs[[].indexOf.call(faqs,e.target.parentElement)].classList.toggle('active');
}
});13. Random Choice Picker
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style.
- JavaScript: dynamic creation of elements + switching of class names + usage of delay timer + random numbers + monitoring of keyboard events. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function createTags(value,splitSymbol){
if(!value || !value.length)return;
const words = value.split(splitSymbol).map(v => v.trim()).filter(v => v);
tags.innerHTML = '';
words.forEach(word => {
const tag = document.createElement('span');
tag.classList.add('tag');
tag.innerText = word;
tags.appendChild(tag);
})
}
function randomTag(){
const time = 50;
let timer = null;
let randomHighLight = () => {
const randomTagElement = pickerRandomTag();
highLightTag(randomTagElement);
timer = setTimeout(randomHighLight,100);
setTimeout(() => {
unHighLightTag(randomTagElement);
},100);
}
randomHighLight();
setTimeout(() => {
clearTimeout(timer);
setTimeout(() => {
const randomTagElement = pickerRandomTag();
highLightTag(randomTagElement);
},100);
},time * 100);
}
function pickerRandomTag(){
const tagElements = document.querySelectorAll('#tags .tag');
return tagElements[Math.floor(Math.random() * tagElements.length)];
}14. Animated Navigation
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style + positioning + displacement transformation and angle rotation.
- JavaScript: Switching of class names. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
toggle.addEventListener('click',() => nav.classList.toggle('active'));15. Incrementing Counter
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient +font-awesomefont library use. - JavaScript: Dynamically create elements + timers to achieve incremental addition. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function updateCounterHandler() {
const counters_elements = document.querySelectorAll('.counter');
counters_elements.forEach(element => {
element.textContent = '0';
const updateCounter = () => {
const value = +element.getAttribute('data-count');
const textContent = +element.textContent;
const increment = value / 100;
if (textContent < value) {
element.textContent = `${Math.ceil(increment + textContent)}`;
setTimeout(updateCounter, 10);
} else {
element.textContent = value;
}
}
updateCounter();
});
}16. Drink Water
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient +CSStransition effects. - JavaScript: regular expression + loop + style and content settings. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
if (actives.length === l) {
setHeightVisible('0', 'hidden', '350px', 'visible');
setTextContent("100%", "0L");
} else if (actives.length === 0) {
setHeightVisible('350px', 'visible', '0', 'hidden');
setTextContent("12.5%", "2L");
} else {
const h1 = unitHei * (l - actives.length) + 'px';
const h2 = unitHei * actives.length + 'px';
setHeightVisible(h1, 'visible', h2, 'visible');
const t1 = (unitHei * actives.length / 350) * 100 + "%";
const t2 = (cups[i].textContent.replace(/ml/, "").replace(/\s+/, "") - 0) * (l - actives.length) / 1000 + 'L';
setTextContent(t1, t2);
}17. movie-app
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient +CSStransition effects + clear floating. - JavaScript: interface request + keyboard event monitoring. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
search.addEventListener('keydown',e => {
if(e.keyCode === 13){
let value = e.target.value.replace(/\s+/,"");
if(value){
getMovies(SEARCH_API + value);
setTimeout(() => {
e.target.value = "";
},1000);
}else{
window.location.reload(true);
}
}
})PS: This example effect requires access over the wall due to limited interface access.
18. background-slider
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient + shadow effect + positioning + pseudo element selector. - JavaScript: Operation of background setting and class name. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
let currentActive = 0;
function setBackgroundImage(){
const url = slideItems[currentActive].style.backgroundImage;
background.style.backgroundImage = url;
}
function setSlideItem(){
const currentSlide = slideItems[currentActive];
const siblings = [].filter.call(slideItems,slide => slide !== currentSlide);
currentSlide.classList.add('active');
siblings.forEach(slide => slide.classList.remove('active'));
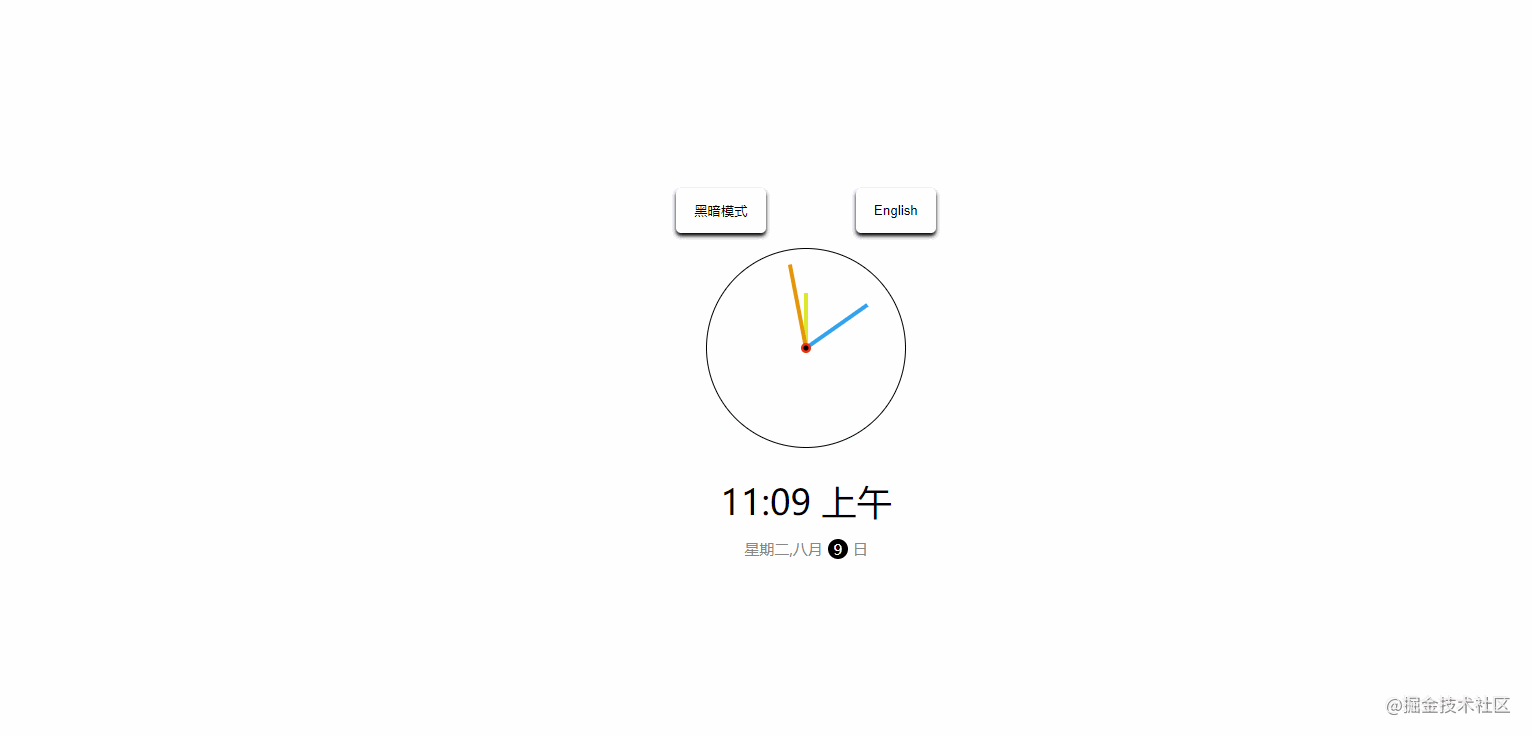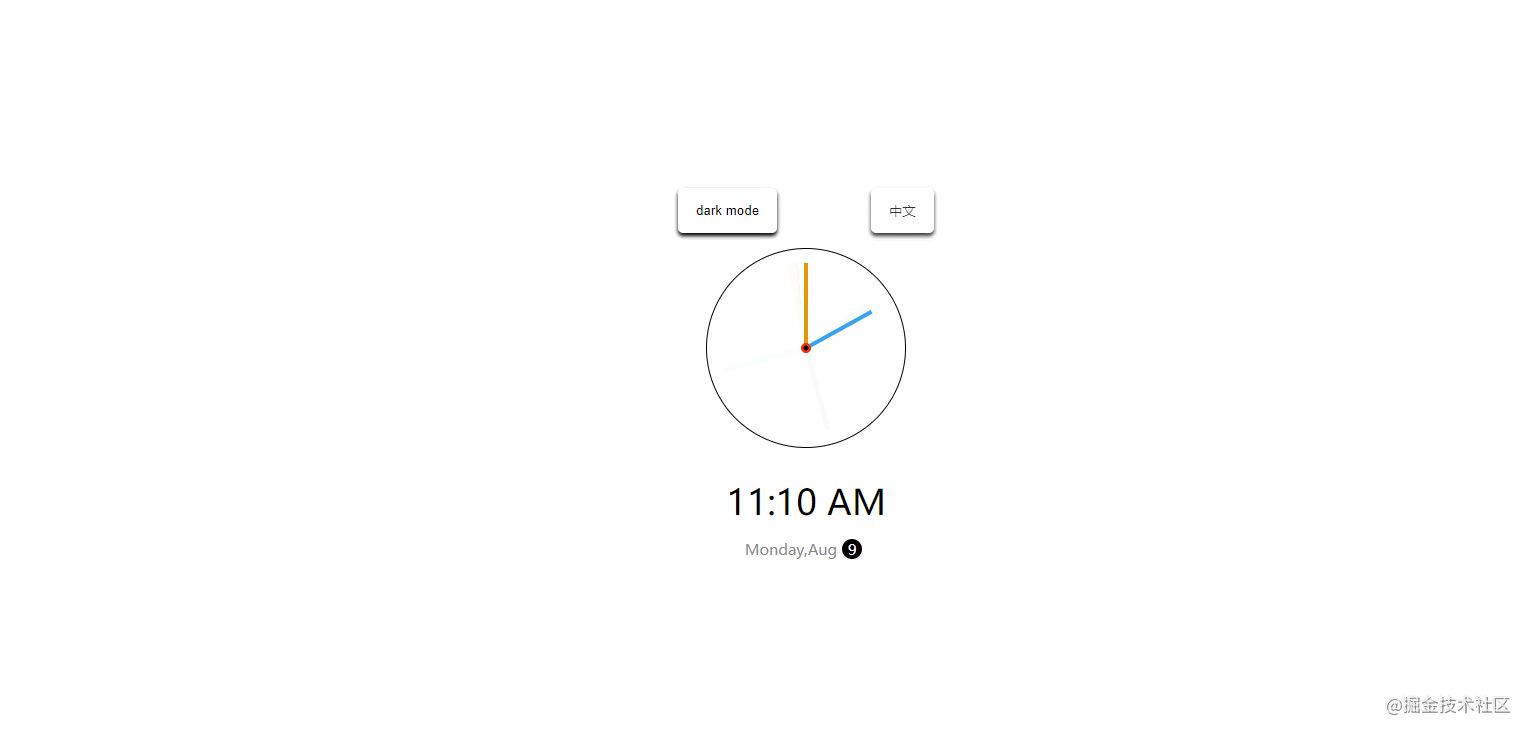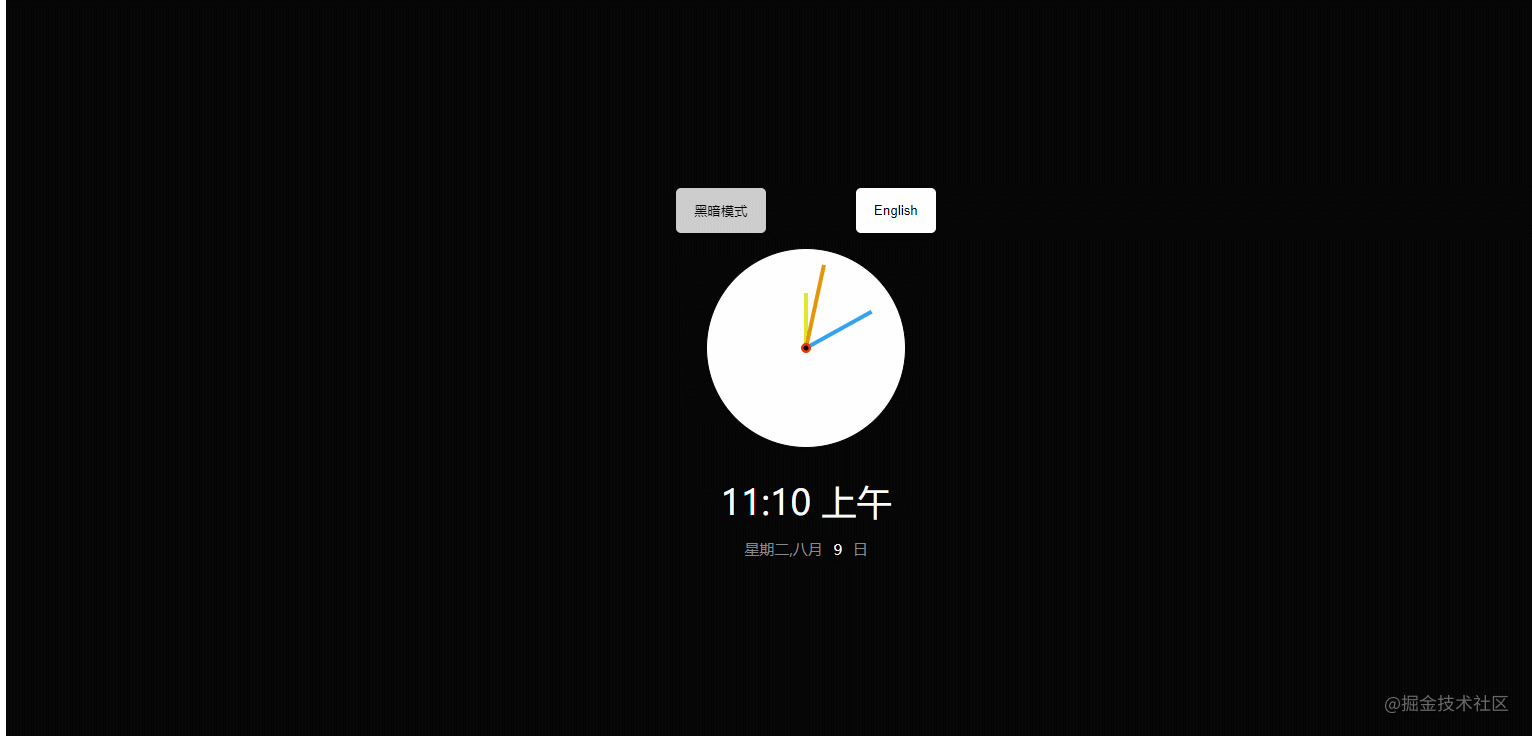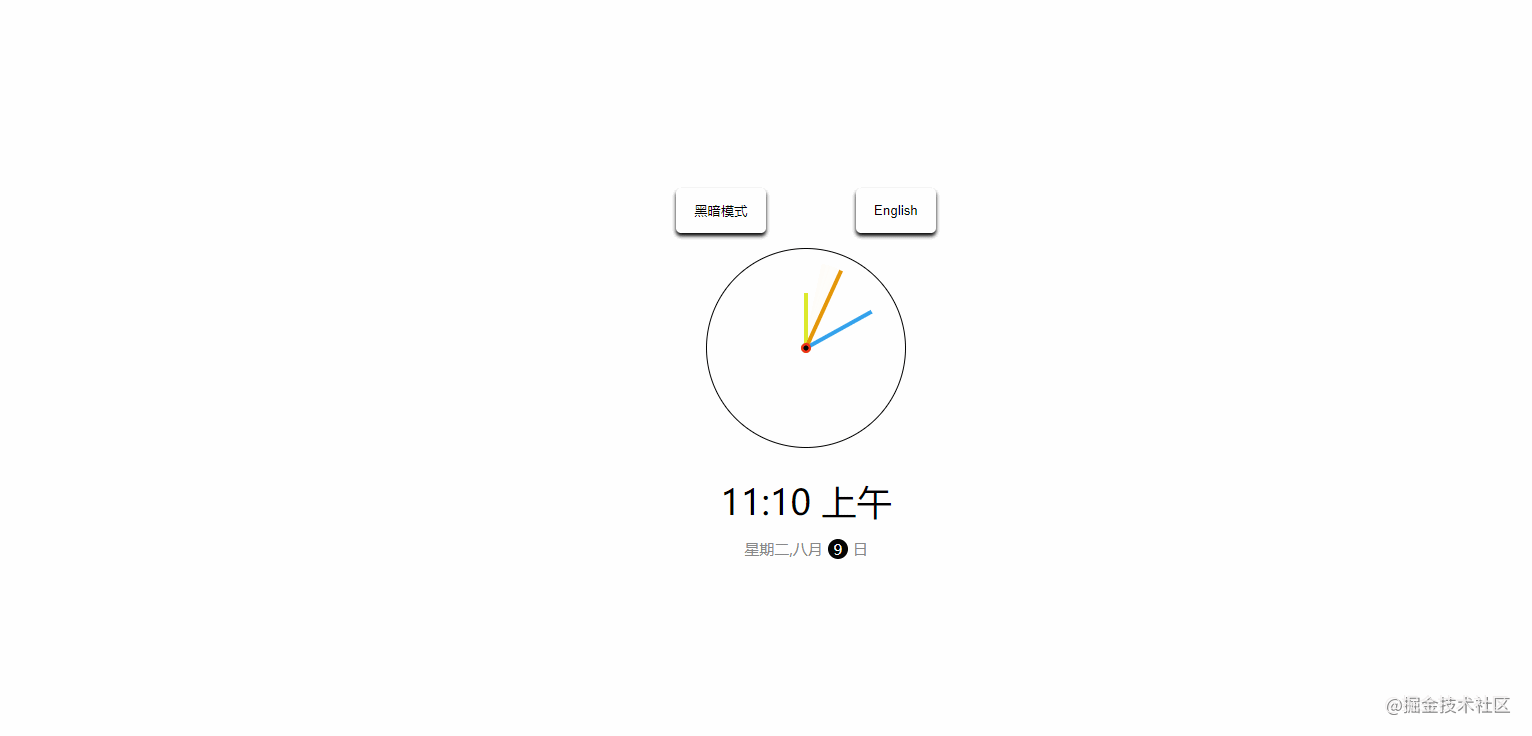
}19. theme-clock
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSvariable + shadow effect + positioning. - JavaScript: Switch between Chinese and English, switch themes, and handle date objects. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function setCurrentDate(){
const date = new Date();
const month = date.getMonth();
const day = date.getDay();
const time = date.getDate();
const hour = date.getHours();
const hourForClock = hour % 12;
const minute = date.getMinutes();
const second = date.getSeconds();
const amPm = hour >= 12 ? langText[currentLang]['time-after-text'] : langText[currentLang]['time-before-text'];
const w = currentLang === 'zh' ? dayZHs : days;
const m = currentLang === 'zh' ? monthZHs : months;
const values = [
`translate(-50%,-100%) rotate(${ scale(hourForClock,0,11,0,360) }deg)`,
`translate(-50%,-100%) rotate(${ scale(minute,0,59,0,360) }deg)`,
`translate(-50%,-100%) rotate(${ scale(second,0,59,0,360) }deg)`
];
[hourEl,minuteEl,secondEl].forEach((item,index) => setTransForm(item,values[index]));
timeEl.innerHTML = `${ hour }:${ minute >= 10 ? minute : '0' + minute } ${ amPm }`;
dateEl.innerHTML = `${w[day]},${ m[month]}<span class="circle">${ time }</span>${ langText[currentLang]['date-day-text'] }`;
timer = setTimeout(setCurrentDate,1000);
}PS: This example also uses the same tool function scale20. button-ripple-effect
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style +
CSSgradient +CSSanimation. - JavaScript: calculation of coordinates + offset + timer. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const x = e.clientX;
const y = e.clientY;
const left = this.offsetLeft;
const top = this.offsetTop;
const circleX = x - left;
const circleY = y - top;
const span = document.createElement('span');
span.classList.add('circle');
span.style.left = circleX + 'px';
span.style.top = circleY + 'px';
this.appendChild(span);
setTimeout(() => span.remove(),1000);21. drawing-app
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style.
- JavaScript:
canvas API+mouseevents and the usage of calculating the coordinates ofxandyewColorPickerFor example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function mouseDownHandler(e){
isPressed = true;
x = e.offsetX;
y = e.offsetY;
}
function throttle(fn,wait = 100){
let done = false;
return (...args) => {
if(!done){
fn.call(this,args);
done = true;
}
setTimeout(() => {
done = false;
},wait);
}
}22. drag-n-drop
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient +CSSflexible box layout. - JavaScript:
drag event API+ Randomly generate pictures. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function onDragStart(){
this.classList.add('drag-move');
setTimeout(() => this.className = "invisible",200);
}
function onDragEnd(){
this.classList.add("drag-fill");
}
function onDragOver(e){
e.preventDefault();
}
function onDragEnter(e){
e.preventDefault();
this.classList.add('drag-active');
}
function onDragLeave(){
this.className = "drag-item";
}
function onDrop(){
this.className = "drag-item";
this.appendChild(dragFill);
}23. content-placholder
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient +CSScard style. - JavaScript: Skeleton screen loading effect. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
animated_bgs.forEach(bg => bg.classList.remove("animated-bg"));
animated_bgs_texts.forEach(text => text.classList.remove("animated-bg-text"));24. sticky-navbar
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient + fixed positioning navigation. - JavaScript: scroll event. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
window.addEventListener("scroll",e => {
if(window.scrollY > nav.offsetHeight + 100) {
nav.classList.add("active");
}else{
nav.classList.remove("active");
}
})PS: The layout of the mobile terminal is also done here.
25. double-slider
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style +
CSSgradient + displacement transformation. - JavaScript: The realization idea of the carousel diagram is mainly to use
transformYmobile terminal to usetransformX. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function setTransform(){
let translate = isHorizontal() ? "translateX" : "translateY";
leftSlide.style.transform = `${ translate }(${position * currentIndex}px)`;
rightSlide.style.transform = `${ translate }(${-(position * currentIndex)}px)`;
}26. toast-notification
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style + basic style of the message prompt box.
- JavaScript: Encapsulate a randomly created message prompt box. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function createNotification({message = null,type = null,auto = false,autoTime = 1000,left = 0,top = 0}){
const toastItem = createEle("div");
let closeItem = null;
if(!auto){
closeItem = createEle("span");
closeItem.innerHTML = "×";
closeItem.className = "toast-close-btn";
}
toastItem.className = `toast toast-${type}`;
toastItem.textContent = message;
if(closeItem)toastItem.appendChild(closeItem);
container.appendChild(toastItem);
const leftValue = (left - toastItem.clientWidth) <= 0 ? 0 : left - toastItem.clientWidth - 30;
const topValue = (top - toastItem.clientHeight) <= 0 ? 0 : top - toastItem.clientHeight - 30;
toastItem.style.left = leftValue + 'px';
toastItem.style.top = topValue + 'px';
if(auto){
setTimeout(() => {
toastItem.remove();
},autoTime);
}else{
closeItem.addEventListener("click",() => {
toastItem.remove();
});
}
}Message box can refer to the realization of ideas this article .
27. github-profiles
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style.
- JavaScript:
try-catchhandles abnormal syntax +axios APIrequestgithub API+async-awaitsyntax. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
async function getRepoList(username){
try {
const { data } = await axios(githubAPI + username + '/repos?sort=created');
addRepoList(data);
} catch (error) {
if(error.response.status == 404){
createErrorCard("查找仓库出错!");
}
}
}28. double-click-heart
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style +
CSSdraw love. - JavaScript: Calculation of the number of events. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function clickHandler(e){
if(clickTime === 0){
clickTime = Date.now();
}else{
if(Date.now() - clickTime < 400){
createHeart(e);
clickTime = 0;
}else{
clickTime = Date.now();
}
}
}29. auto-text-effect
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style.
- JavaScript: Timer + timer time calculation. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
let time = 300 / speed.value;
writeText();
function writeText(){
text.innerHTML = string.slice(0,idx);
idx++;
if(idx > string.length){
idx = 1;
}
setTimeout(writeText,time);
}
speed.addEventListener("input",e => time = 300 / e.target.value);30. password generator
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout.
- JavaScript: Chinese and English switching + selection box event monitoring + random number +
copy API. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function getRandomLower(){
// a ~ z 的code为 97 ~ 122
// 可根据charCodeAt()方法获取
return String.fromCharCode(Math.floor(Math.random() * 26) + 97);
}
function getRandomUpper(){
// A ~ Z 的code为 65 ~ 90
// 可根据charCodeAt()方法获取
return String.fromCharCode(Math.floor(Math.random() * 26) + 65);
}
function getRandomNumber(){
// 0 ~ 9的code为48 ~ 57
// 可根据charCodeAt()方法获取
return String.fromCharCode(Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 48);
}31. good-cheap-fast
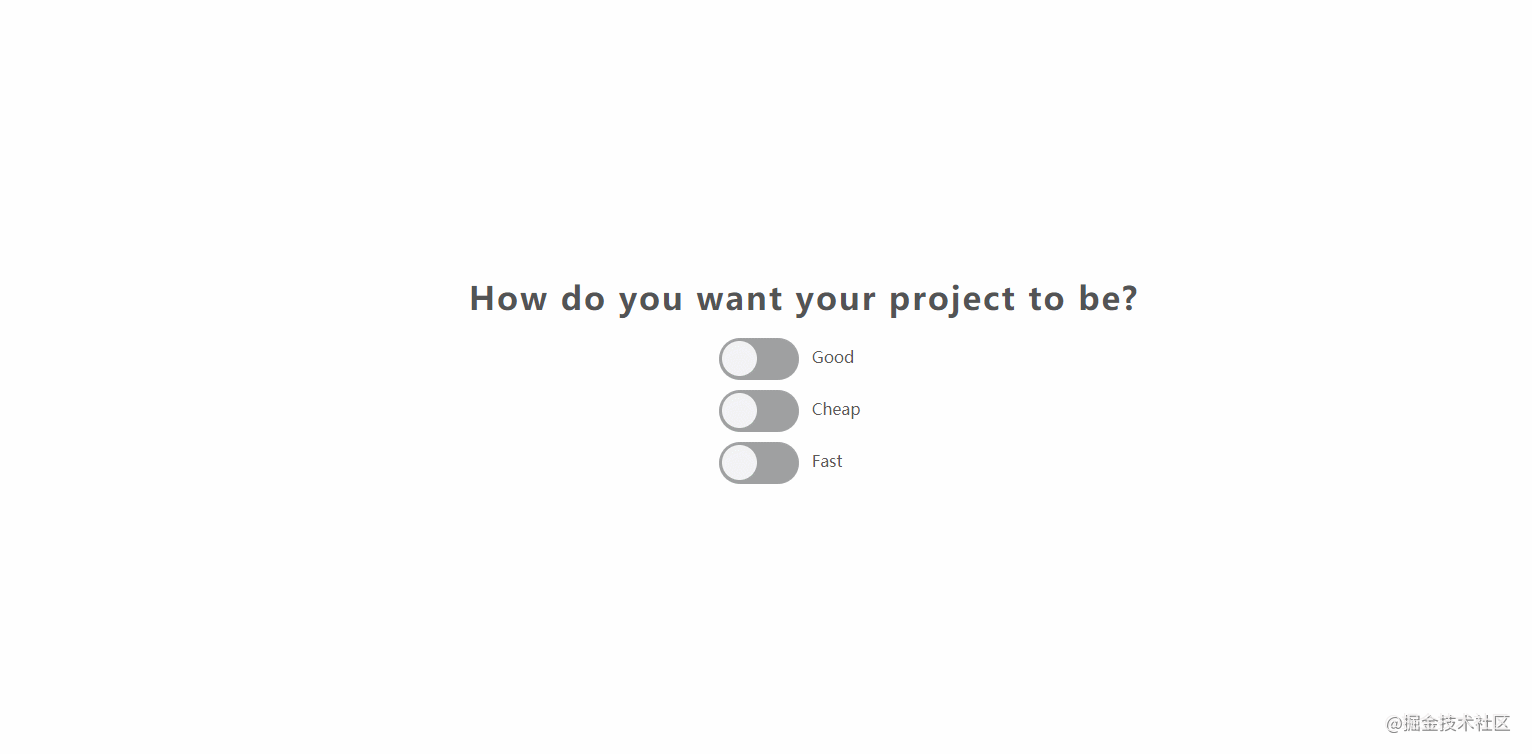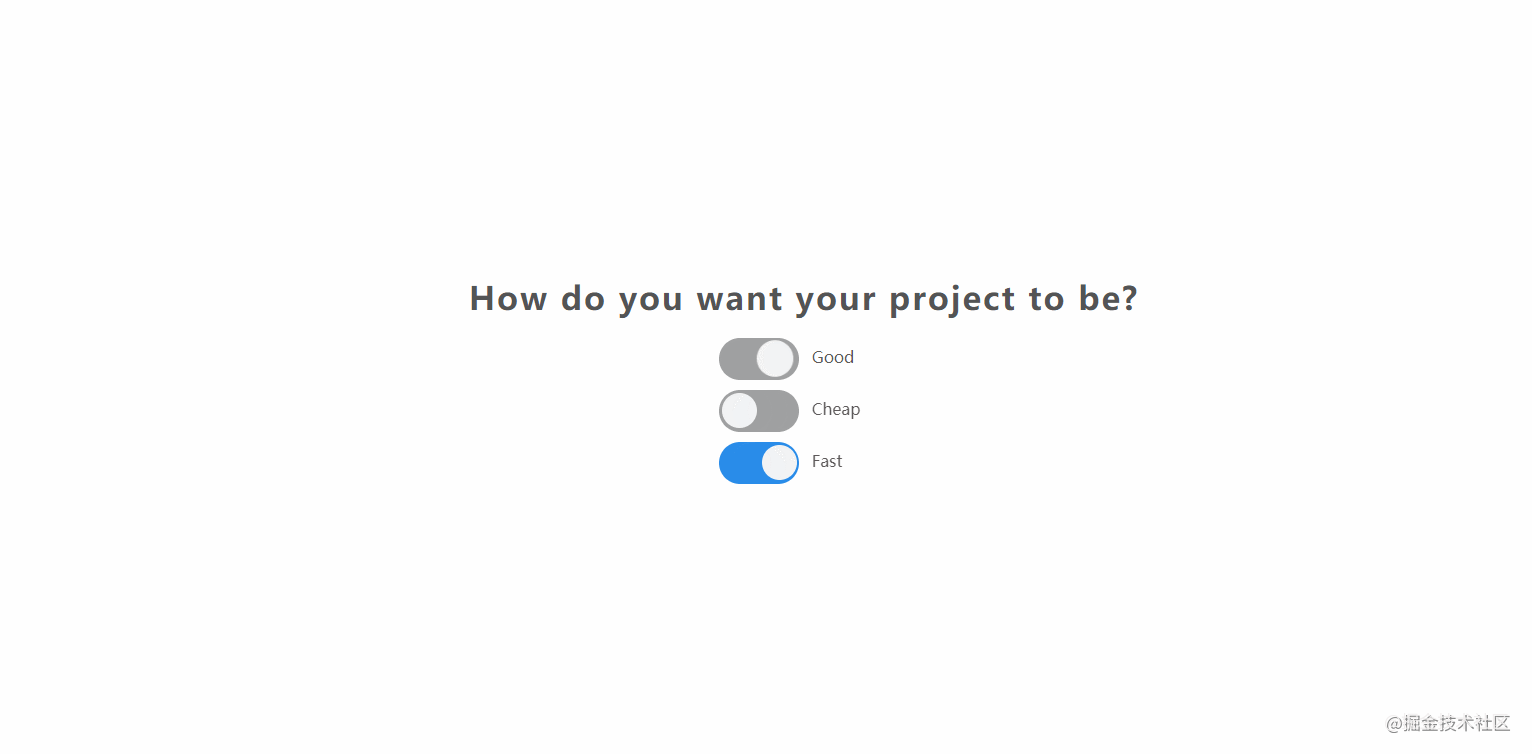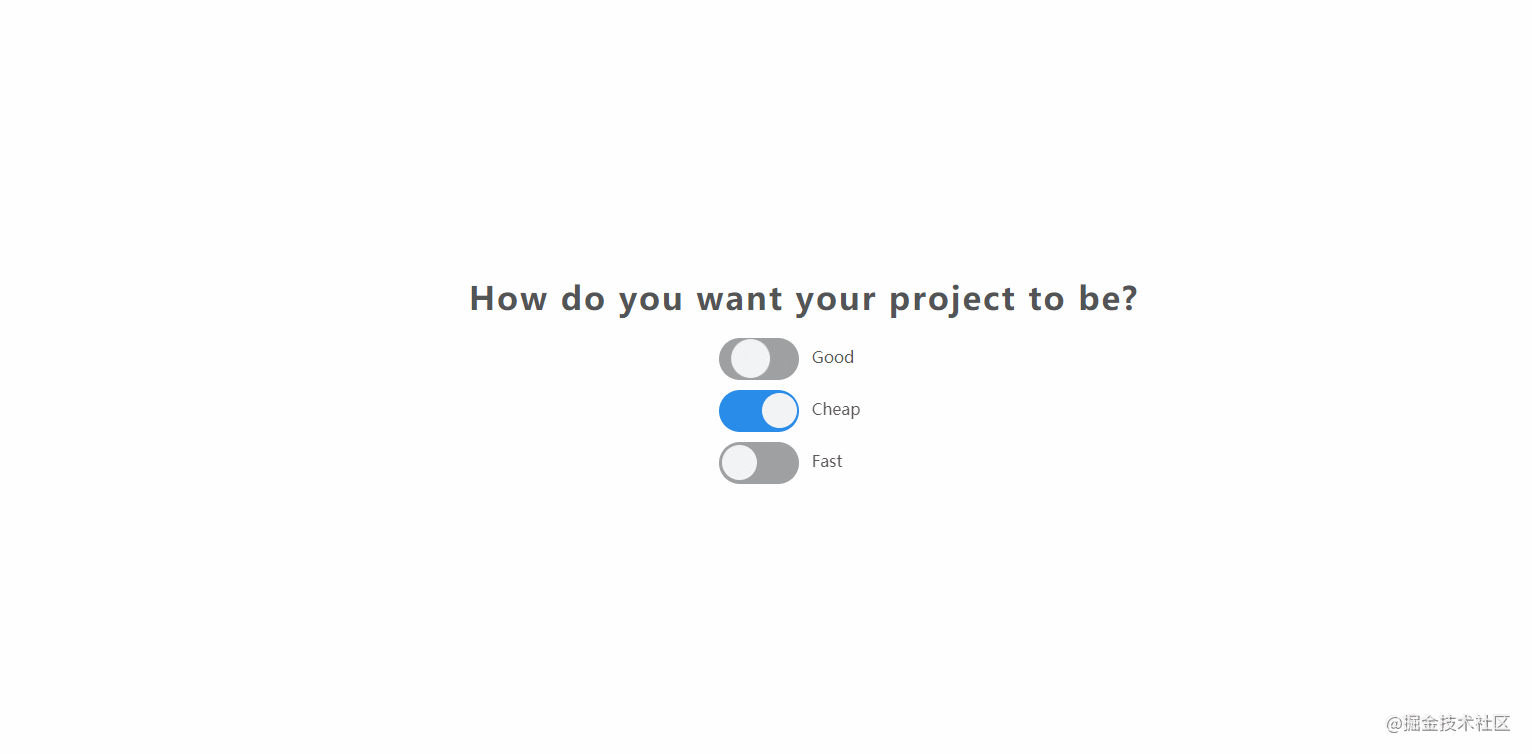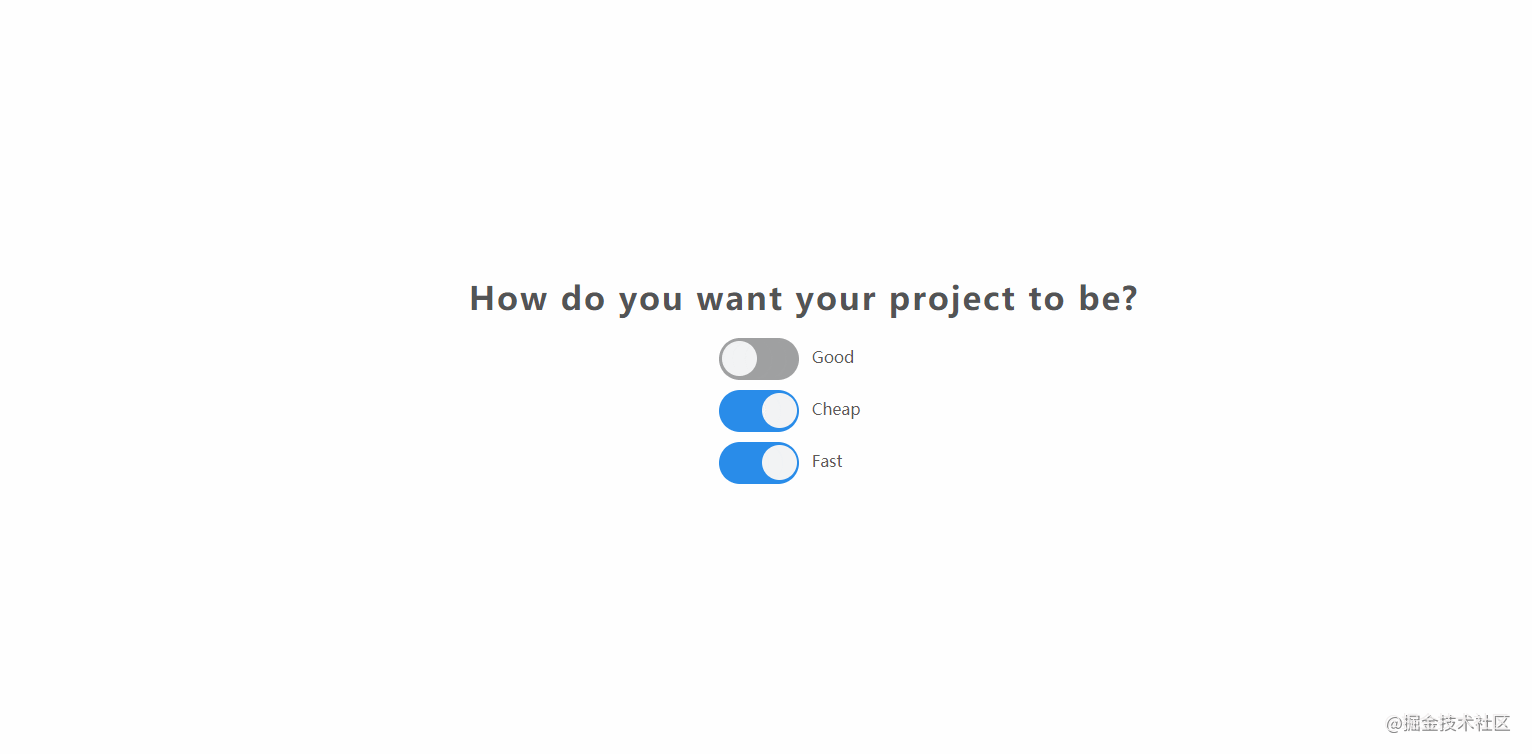
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSimplements switch widget style + basic layout style. - JavaScript:
inputof thechangeevent of 06110fc906755e. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
const checkBoxElements = document.querySelectorAll(".switch-container input[type='checkbox']");
checkBoxElements.forEach(item => item.addEventListener("change",e => {
const index = Array.from(checkBoxElements).indexOf(e.target);
if(Array.from(checkBoxElements).every(v => v.checked)){
if(index === 0){
checkBoxElements[2].checked = false;
}else if(index === 1){
checkBoxElements[0].checked = false;
}else{
checkBoxElements[1].checked = false;
}
}
}));32. notes-app
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style + card layout.
- The JavaScript:
marked.jsuse +localStorage APIstoring data calculation + mouse cursor position. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
on($(".edit", note), "click", e => {
const isFocus = textarea.getAttribute("data-focus");
if (isFocus === "false") {
textarea.setAttribute("data-focus","true");
if(textarea.classList.contains("hidden")){
textarea.classList.remove("hidden");
}
if(!focusStatus){
textarea.value = notes[index].text;
}
const text = textarea.value.trim();
// console.log(text);
if (textarea.setSelectionRange) {
textarea.focus();
textarea.setSelectionRange(text.length, text.length);
}else if (textarea.createTextRange) {
const range = textarea.createTextRange();
range.collapse(true);
range.moveEnd('character', text.length);
range.moveStart('character', text.length);
range.select();
}
} else {
textarea.setAttribute("data-focus","false");
notes[index].text = textarea.value;
main.innerHTML = marked(notes[index].text);
setData("notes", notes);
}
});33. animated-countdown
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style + displacement, rotation, zoom animation.
- JavaScript: Animation event + animation creation and reset. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function runAnimation(){
const numArr = $$("span",numGroup);
const nextToLast = numArr.length - 1;
numArr[0].classList.add("in");
numArr.forEach((num,index) => {
num.addEventListener("animationend",e => {
const {animationName} = e;
if(animationName === "goIn" && index !== nextToLast){
num.classList.remove("in");
num.classList.add("out");
}else if(animationName === "goOut" && num.nextElementSibling){
num.nextElementSibling.classList.add("in");
}else{
counter.classList.add("hide");
final.classList.add("show");
}
})
})
}
function resetAnimation(){
counter.classList.remove("hide");
final.classList.remove("show");
const numArr = $$("span",numGroup);
if(numArr){
numArr.forEach(num => num.classList.value = '');
numArr[0].classList.add("in");
}
}34. image-carousel
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout.
- JavaScript: Timer implements carousel. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function changeCarouselItem(){
if(currentIndex > carouselItems.length - 1){
currentIndex = 0;
}else if(currentIndex < 0){
currentIndex = carouselItems.length - 1;
}
carousel.style.transform = `translateX(-${ currentIndex * carouselContainer.offsetWidth }px)`;
}PS: Here is an extra timer pit, that is to say, for example, if we use setTimeout to simulate the setInterval method, there will be problems here. I added a comment in the js code.
// let interval = mySetInterval(run,1000);
// Why use this method can't achieve the desired effect?
// Use this method as follow to replace window.setInterval,clicked the prev button more to get the stranger effect.
// Maybe this method does not conform to the specification,So make sure to use window.setInterval.
// function mySetInterval(handler,time = 1000){
// let timer = null;
// const interval = () => {
// handler();
// timer = setTimeout(interval,time);
// }
// interval();
// return {
// clearMyInterval(){
// clearTimeout(timer);
// }
// }
// }This is because we use setTimeout achieve timer does not meet specifications, setInterval default will 10ms delayed execution.
refers to the specification .
35. hover board
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style +
CSSgradient. - JavaScript: Dynamically create elements + floating events. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function setColor(element){
element.style.background = `linear-gradient(135deg, ${ randomColor() } 10%, ${ randomColor() } 100%)`;
element.style.boxShadow = `0 0 2px ${ randomColor() },0 0 10px ${ randomColor() }`;
}
function removeColor(element){
element.style.background = `linear-gradient(135deg, #1d064e 10%, #10031a 100%)`;
element.style.boxShadow = `0 0 2px #736a85`;
}36. pokedex
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout +
CSSgradient. - JavaScript:
fetch APIinterface request + create card. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function createPokemon(pokemon){
const pokemonItem = document.createElement("div");
pokemonItem.classList.add("pokedex");
const name = pokemon.name[0].toUpperCase() + pokemon.name.slice(1).toLowerCase();
const id = pokemon.id.toString().padStart(3,"0");
const poke_types = pokemon.types.map(type => type.type.name);
const type = main_types.find(type => poke_types.indexOf(type) > -1);
const color = colors[type];
pokemonItem.style.background = `linear-gradient(135deg, ${ color } 10%, ${ randomColor() } 100%)`;
pokemonItem.innerHTML = `
<div class="pokedex-avatar">
<img src="https://pokeres.bastionbot.org/images/pokemon/${pokemon.id}.png" alt="the pokemon">
</div>
<div class="info">
<span class="number">#${ id }</span>
<h3 class="name">${ name }</h3>
<small class="type">Type:<span>${ type }</span></small>
</div>`;
container.appendChild(pokemonItem);
}Special note: The interface does not seem to be stable, maybe because of my network, the picture is not loaded.
37. mobile-tab-navigation
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout +
CSSgradient to achieve mobile phone layout. - JavaScript: It feels like a carousel switch on the mobile terminal, using
opacity, there is nothing to say. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function hideAllElement(nodeList){
nodeList.forEach(item => item.classList.remove("active"));
}
navItems.forEach((item,index) => {
item.addEventListener("click",() => {
hideAllElement(navItems);
hideAllElement(carouselItems);
item.classList.add("active");
carouselItems[index].classList.add("active");
})
})38. password-strength-background
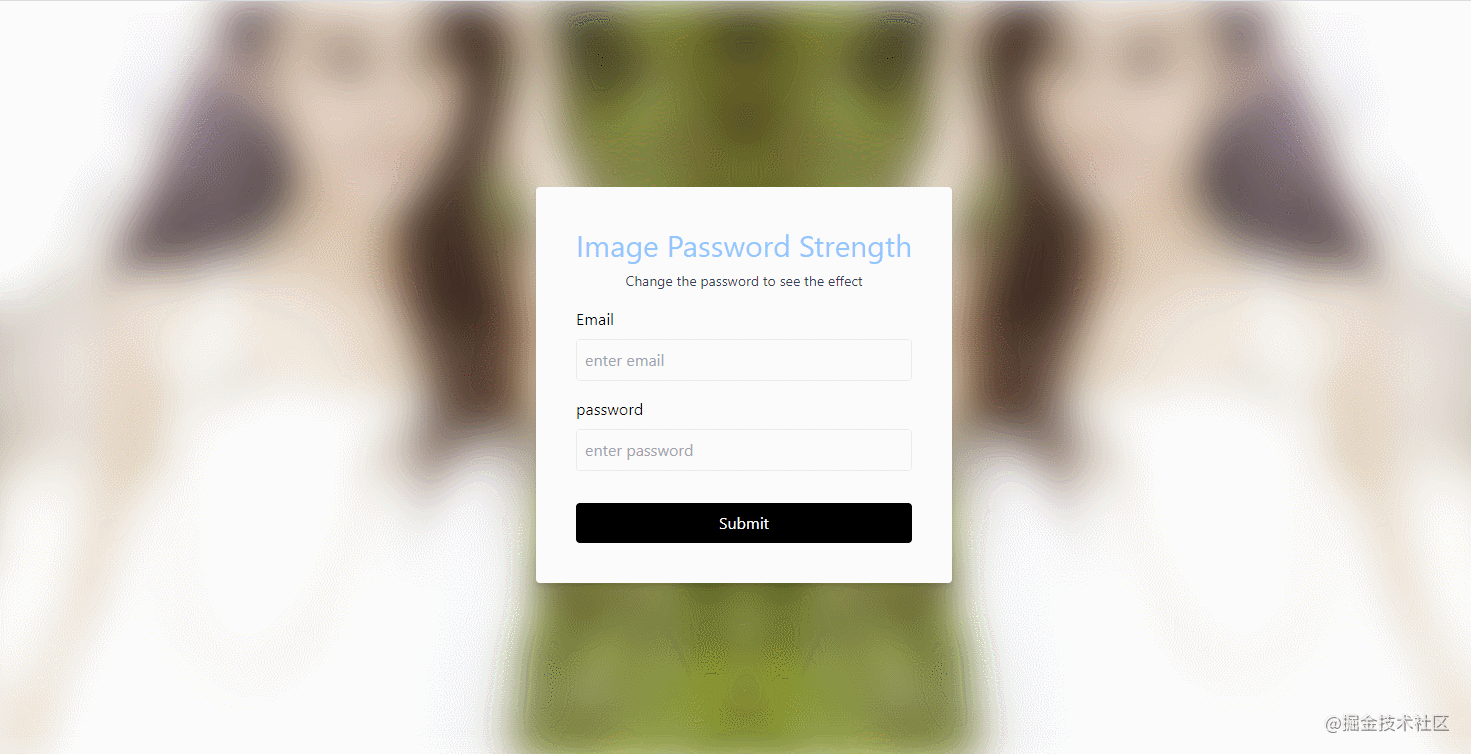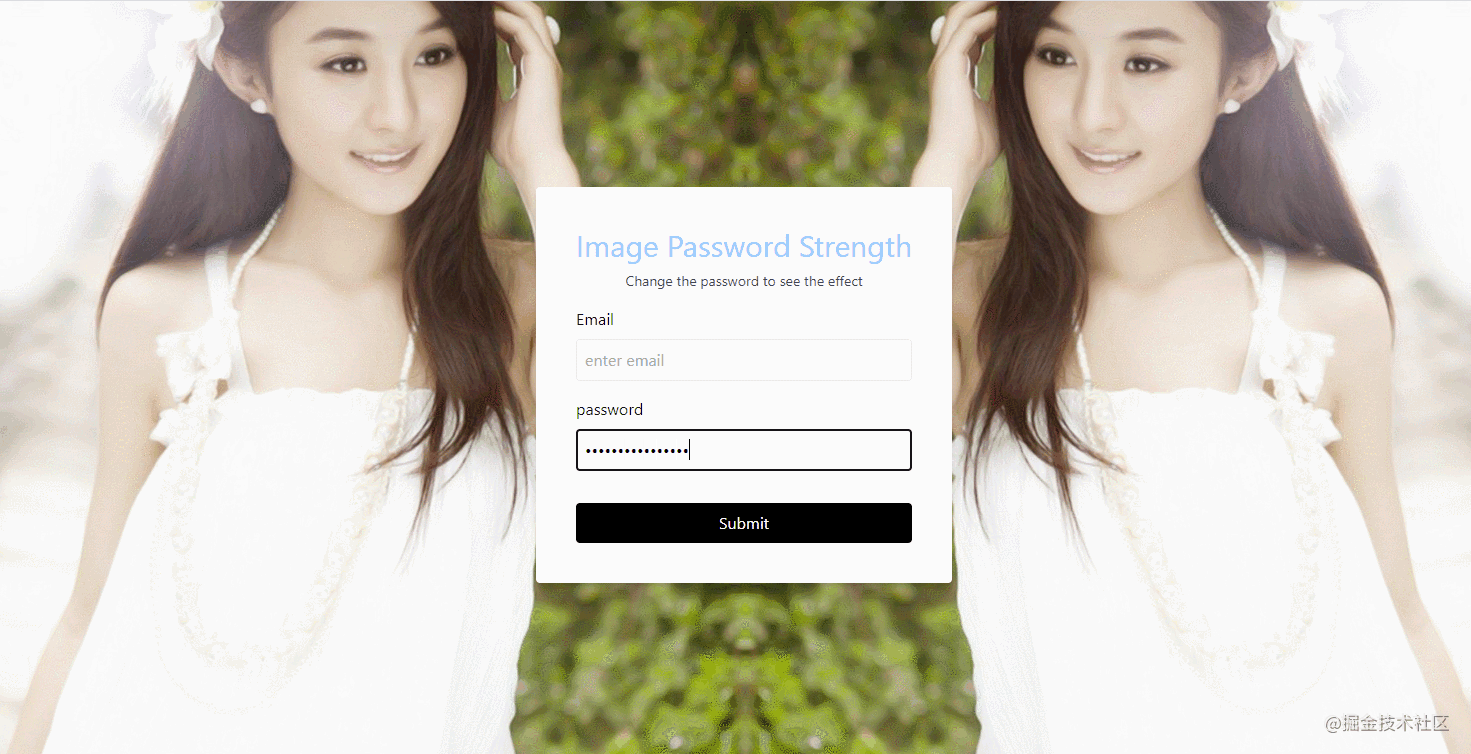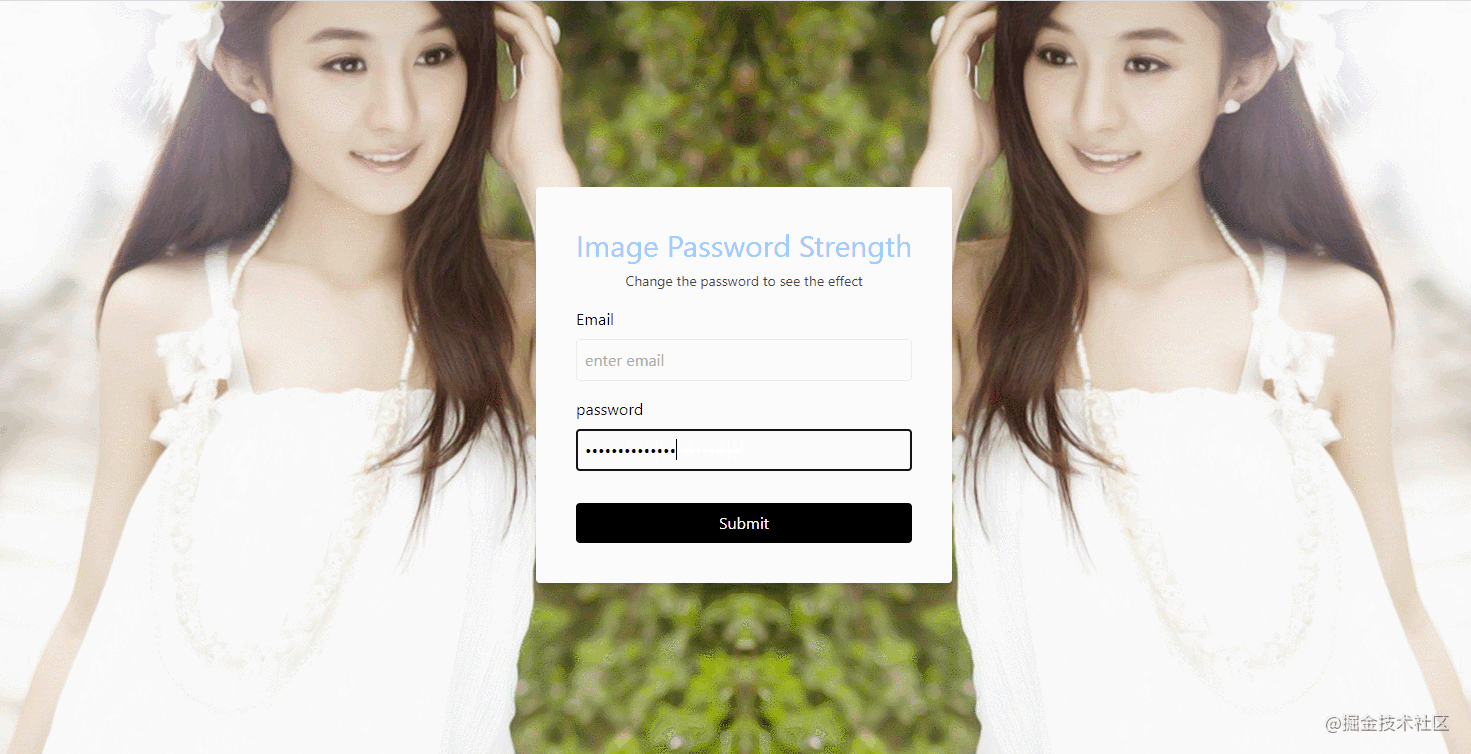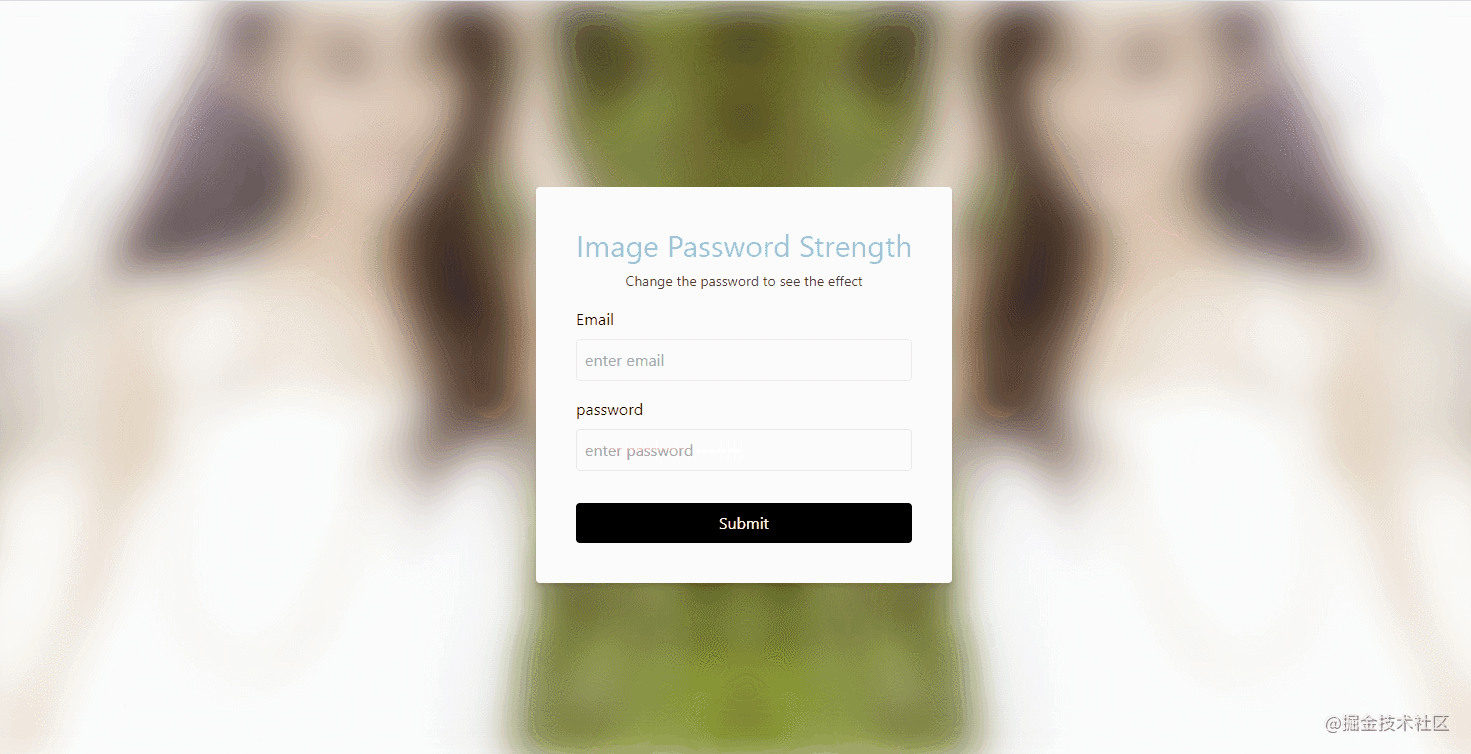
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Actually, it mainly uses
tailwind.css, theCSSframework. - JavaScript: Listen to input box events, and then change the background blur. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
password.addEventListener("input",e => {
const { value } = e.target;
const blur = 20 - value.length * 2;
background.style.filter = `blur(${ blur }px)`;
});39. 3D-background-boxes
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
vw、vhlayout +skewtilt transformation. - JavaScript: Loop + background image positioning settings. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function createBox(){
for(let i = 0;i < 4;i++){
for(let j = 0;j < 4;j++){
const box = document.createElement("div");
box.classList.add("box");
box.style.backgroundPosition = `${ -j * 15 }vw ${ -i * 15 }vh`;
boxContainer.appendChild(box);
}
}
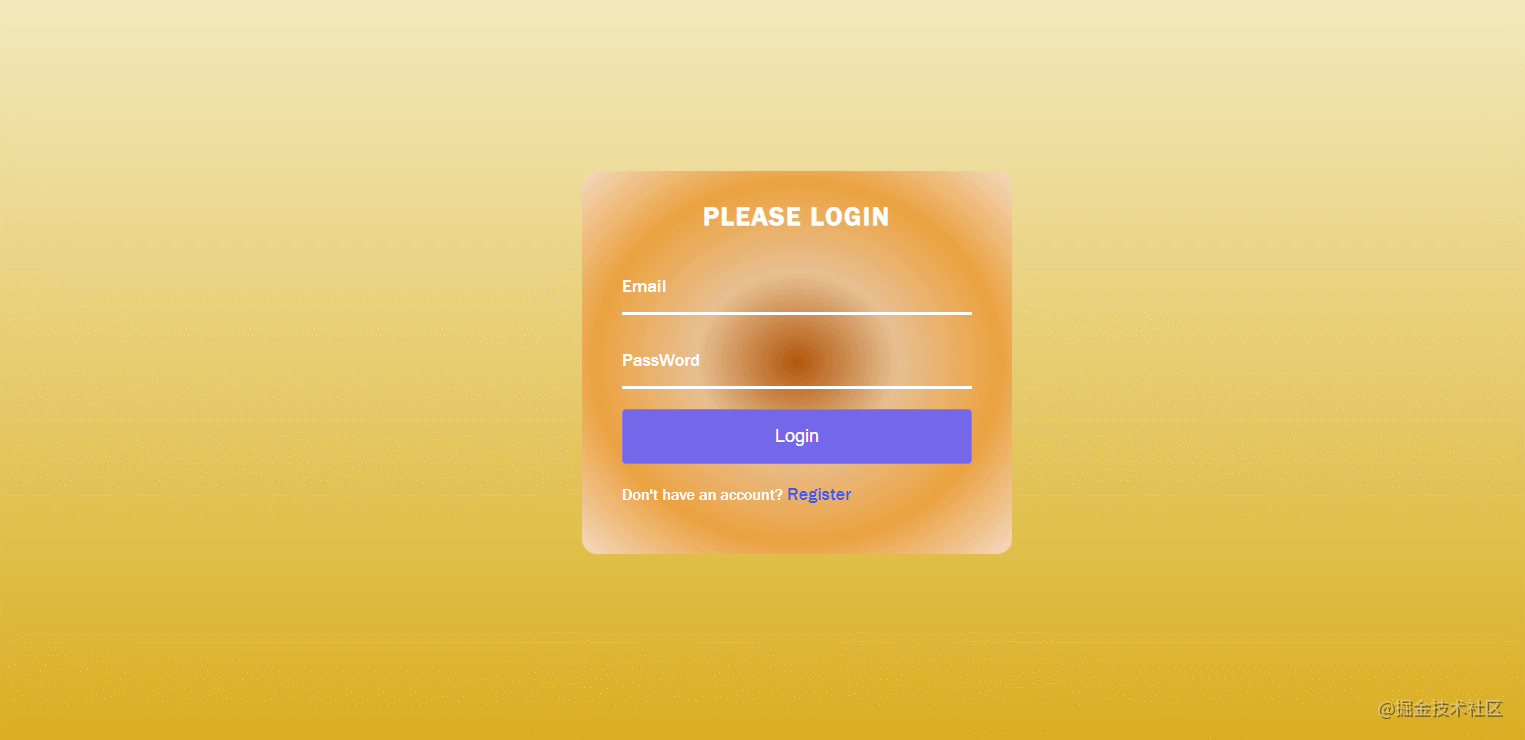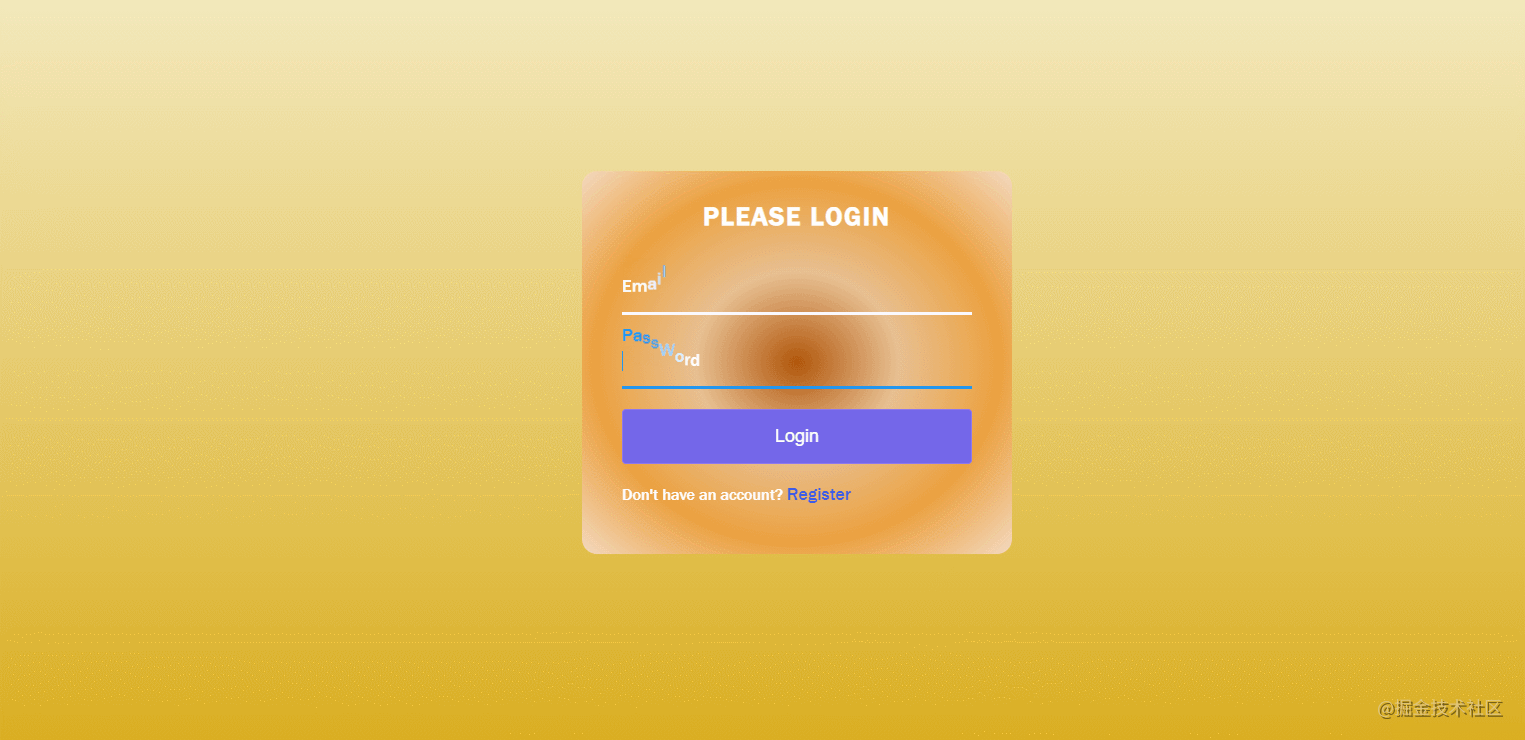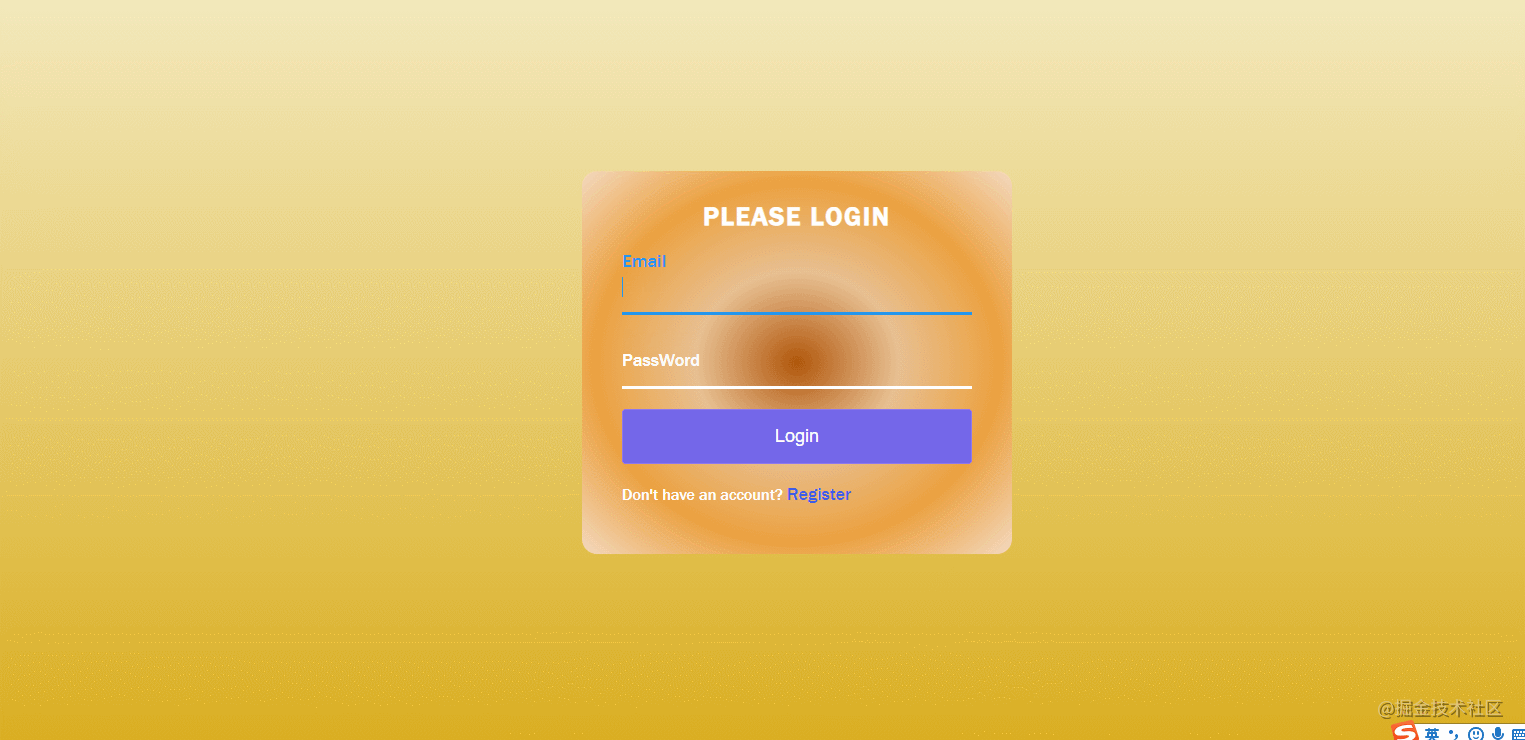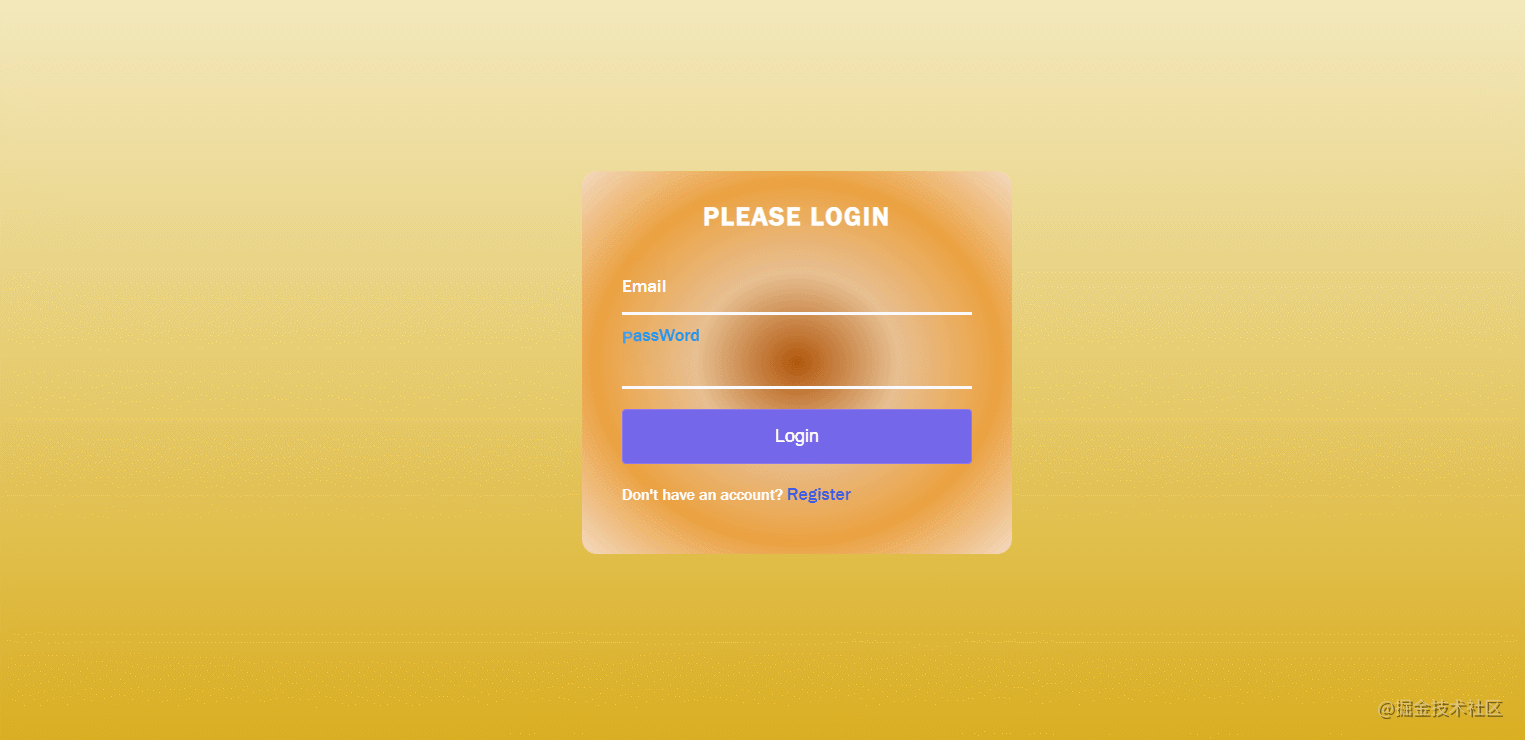
}40. Verify Your Account
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: basic style layout + some special style settings of
input - JavaScript:
JavaScript focusevent. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
.code-container .code:focus {
border-color: #2397ef;
}
.code::-webkit-outer-spin-button,
.code::-webkit-inner-spin-button {
-webkit-appearance: none;
margin: 0;
}
.code:valid {
border-color: #034775;
box-shadow: 0 10px 10px -5px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.25);
}function onFocusHandler(nodeList){
onFocus(nodeList[0]);
nodeList.forEach((node,index) => {
node.addEventListener("keydown",e => {
// console.log(e.key);
if(e.key >= 0 && e.key <= 9){
nodeList[index].value = "";
setTimeout(() => onFocus(nodeList[index + 1]),0);
}else{
setTimeout(() => onFocus(nodeList[index - 1]),0);
}
})
});
}
function onFocus(node){
if(!node)return;
const { nodeName } = node;
return nodeName && nodeName.toLowerCase() === "input" && node.focus();
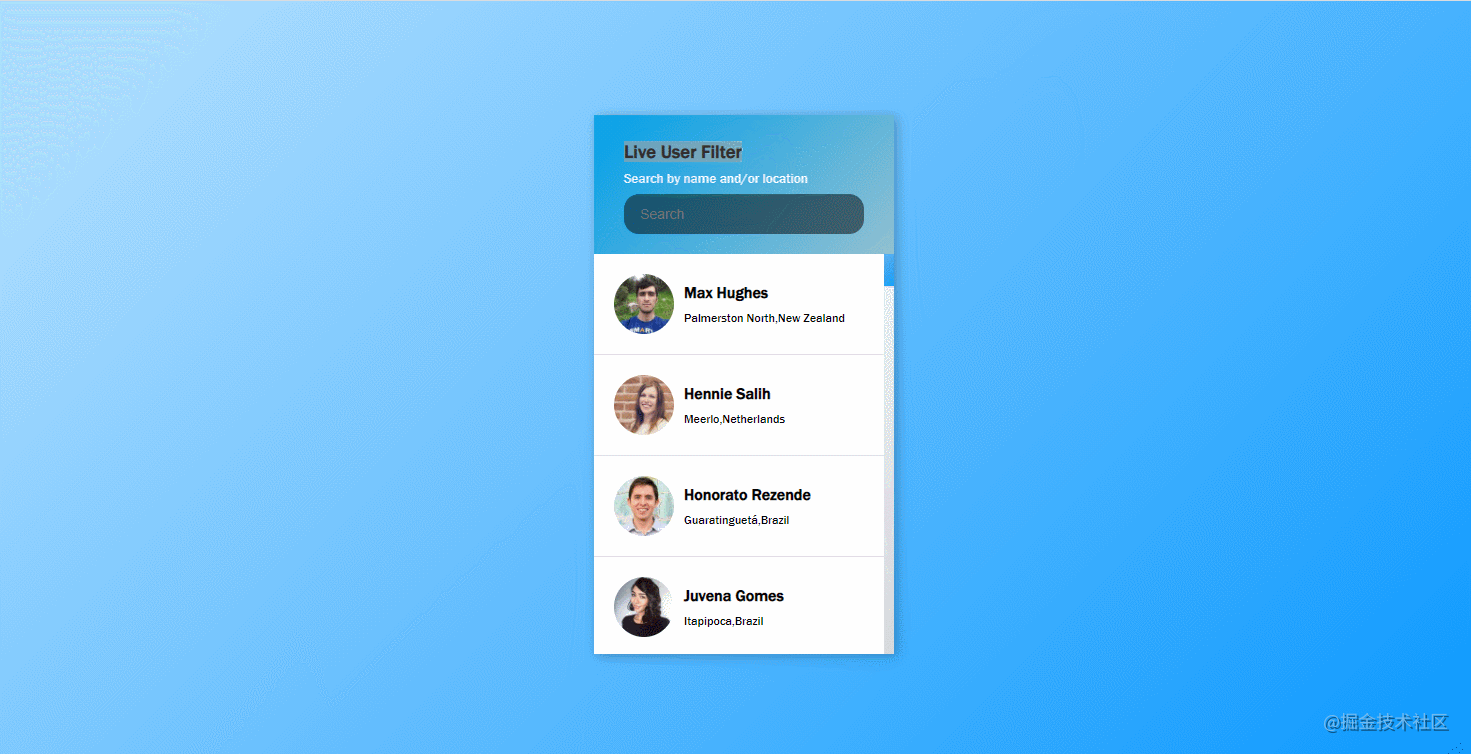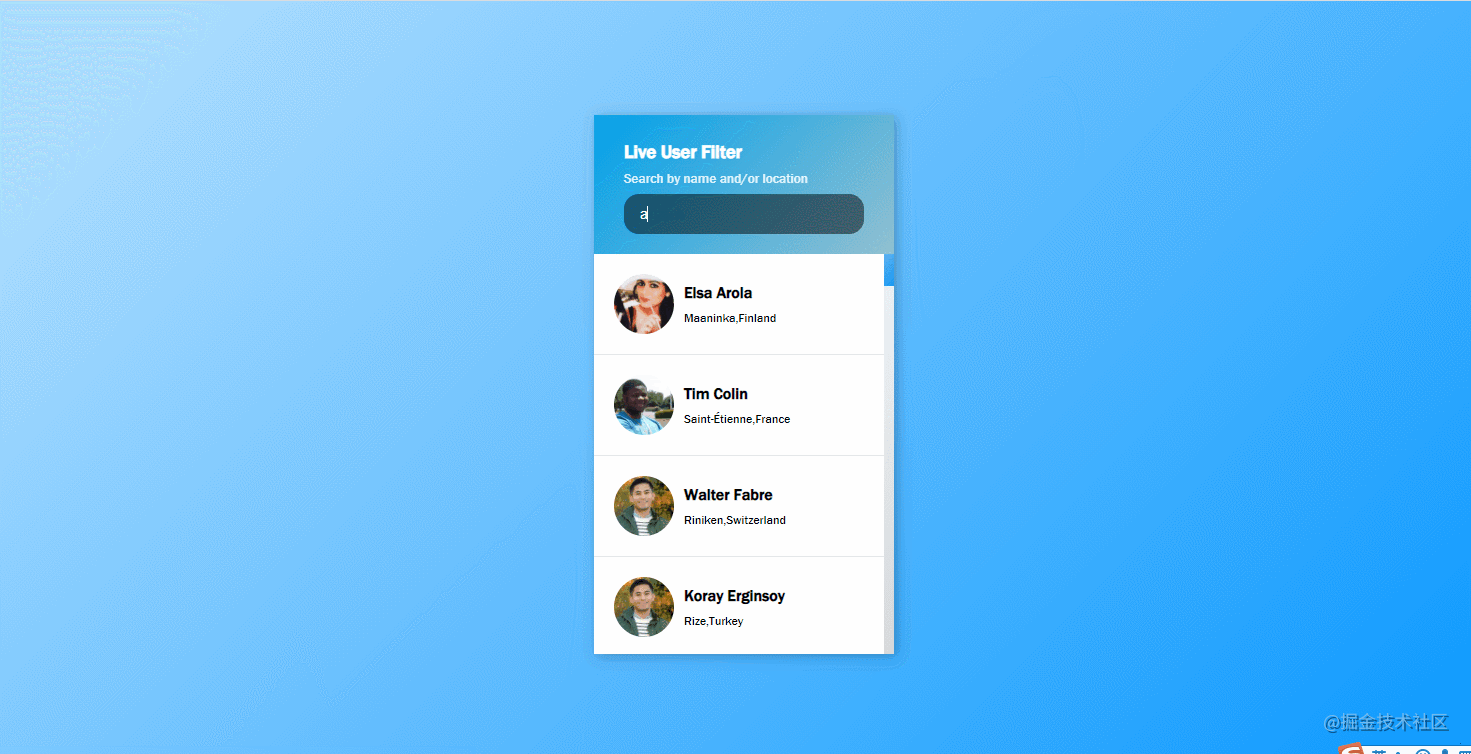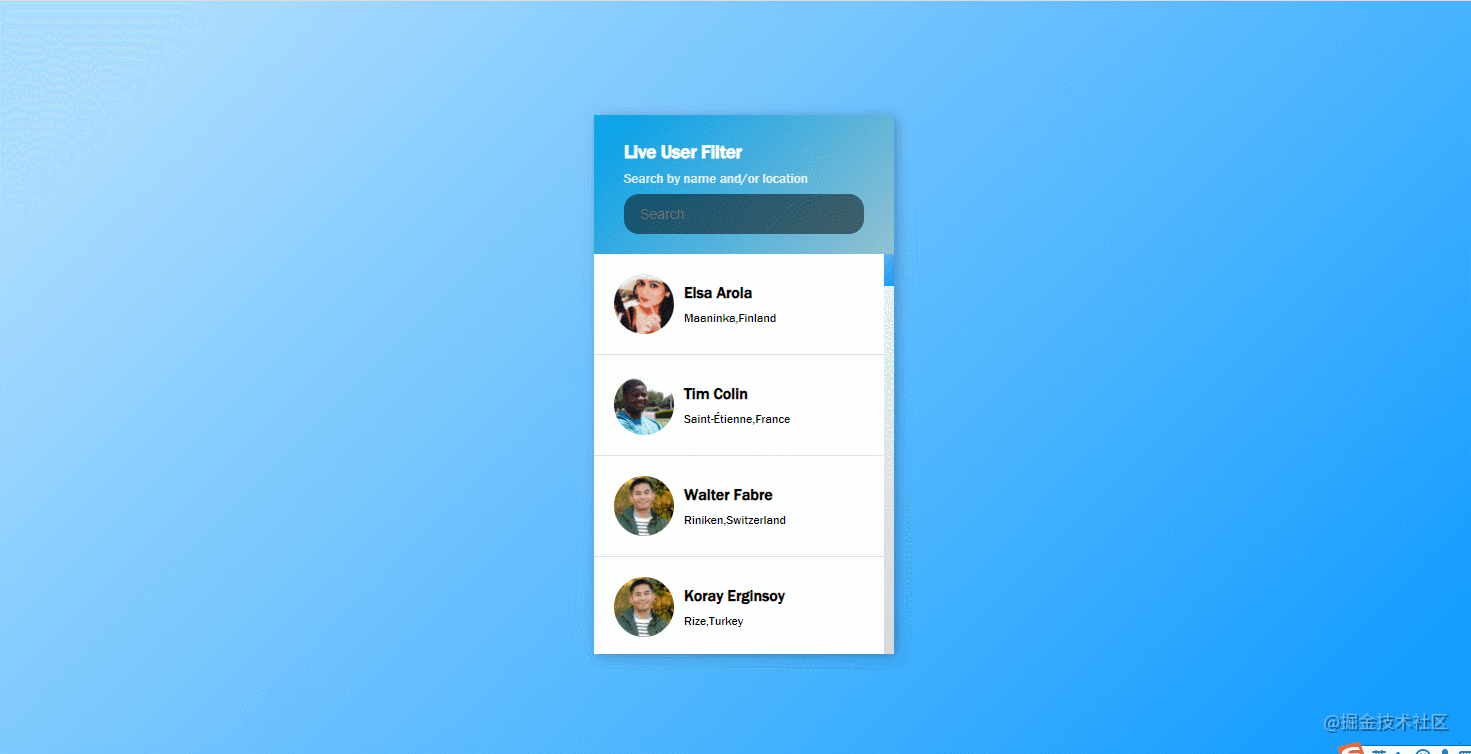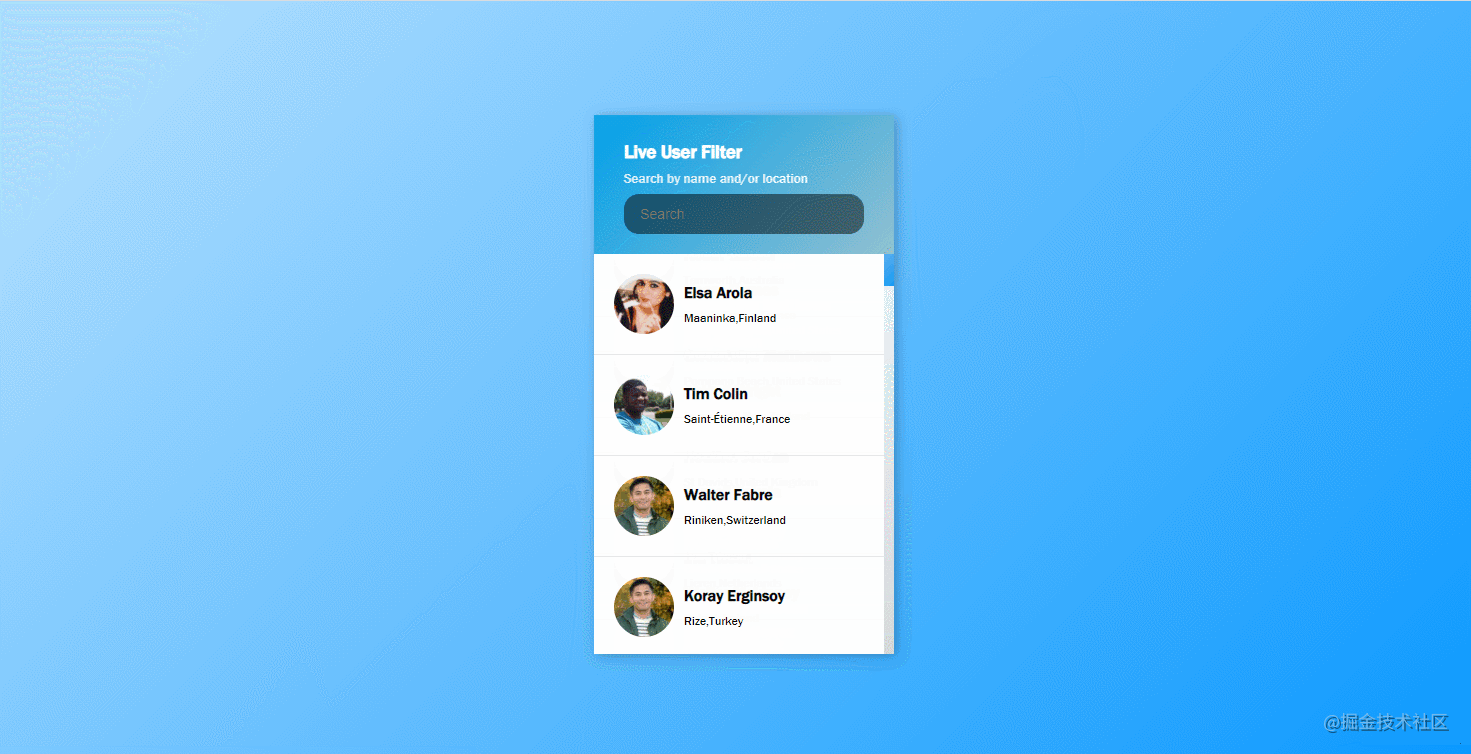
}41. live-user-filter
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout + scroll bar style.
- JavaScript:
fetch APIinterface request +inputevent filtering data. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
async function requestData(){
const res = await fetch('https://randomuser.me/api?results=50');
const { results } = await res.json();
result.innerHTML = "";
results.forEach(user => {
const listItem = document.createElement("li");
filterData.push(listItem);
const { picture:{ large },name:{ first,last },location:{ city,country } } = user;
listItem.innerHTML = `
<img src="${ large }" alt="${ first + ' ' + last }" />
<div class="user-info">
<h4>${ first } ${ last }</h4>
<p>${ city },${ country }</p>
</div>
`;
result.appendChild(listItem);
})
}42. feedback-ui-design
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSDraw a heart + basic style layout. - JavaScript: The realization of the tab switching function. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
ratingItem.forEach(item => {
item.addEventListener("click",e => {
siblings(item).forEach(sib => sib.classList.remove("active"));
item.classList.add("active");
selectRating = item.innerText;
})
});
send.addEventListener("click",() => {
selectRatingItem.innerText = selectRating;
sendPage.classList.add("hide");
receivePage.classList.remove("hide");
});
back.addEventListener("click",() => {
selectRating = $(".rating.active").innerText;
selectRatingItem.innerText = $(".rating.active").innerText;
sendPage.classList.remove("hide");
receivePage.classList.add("hide");
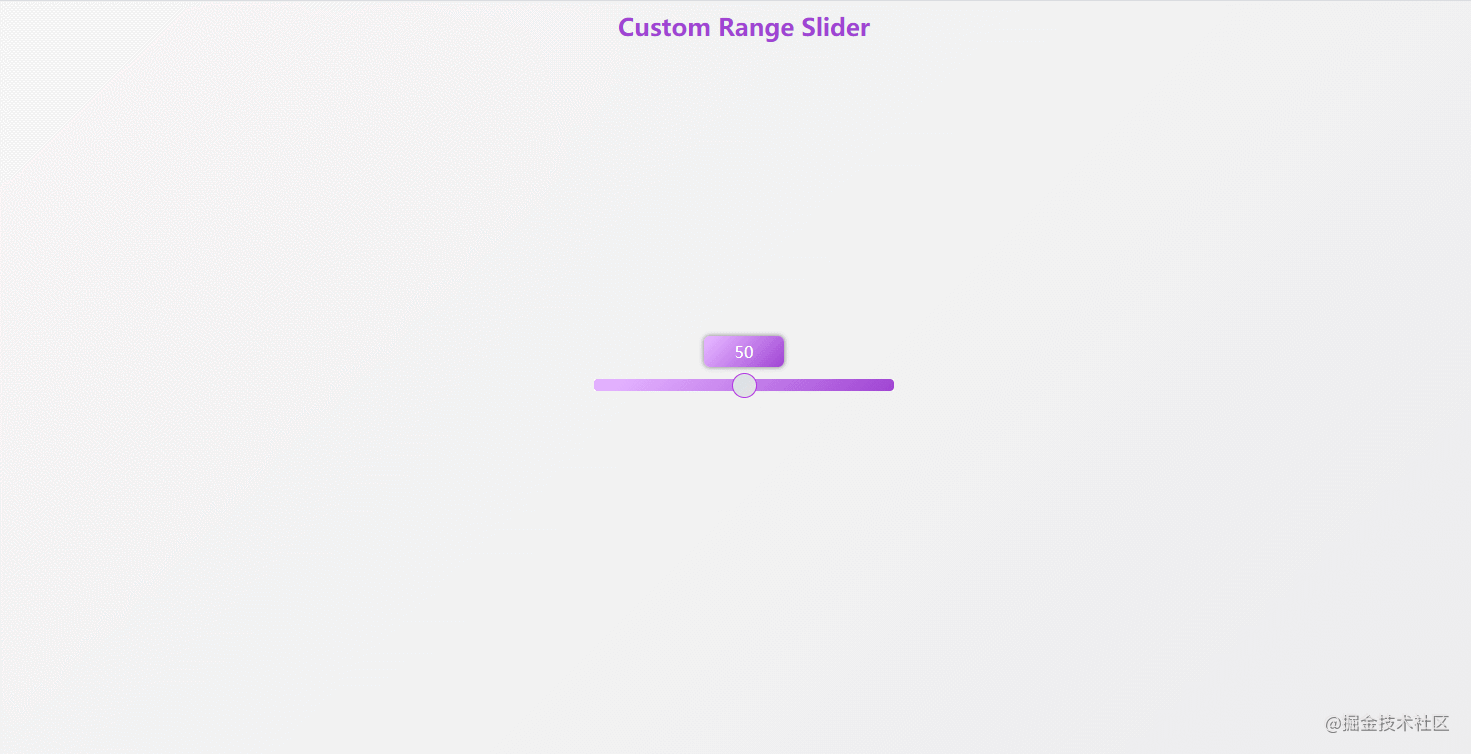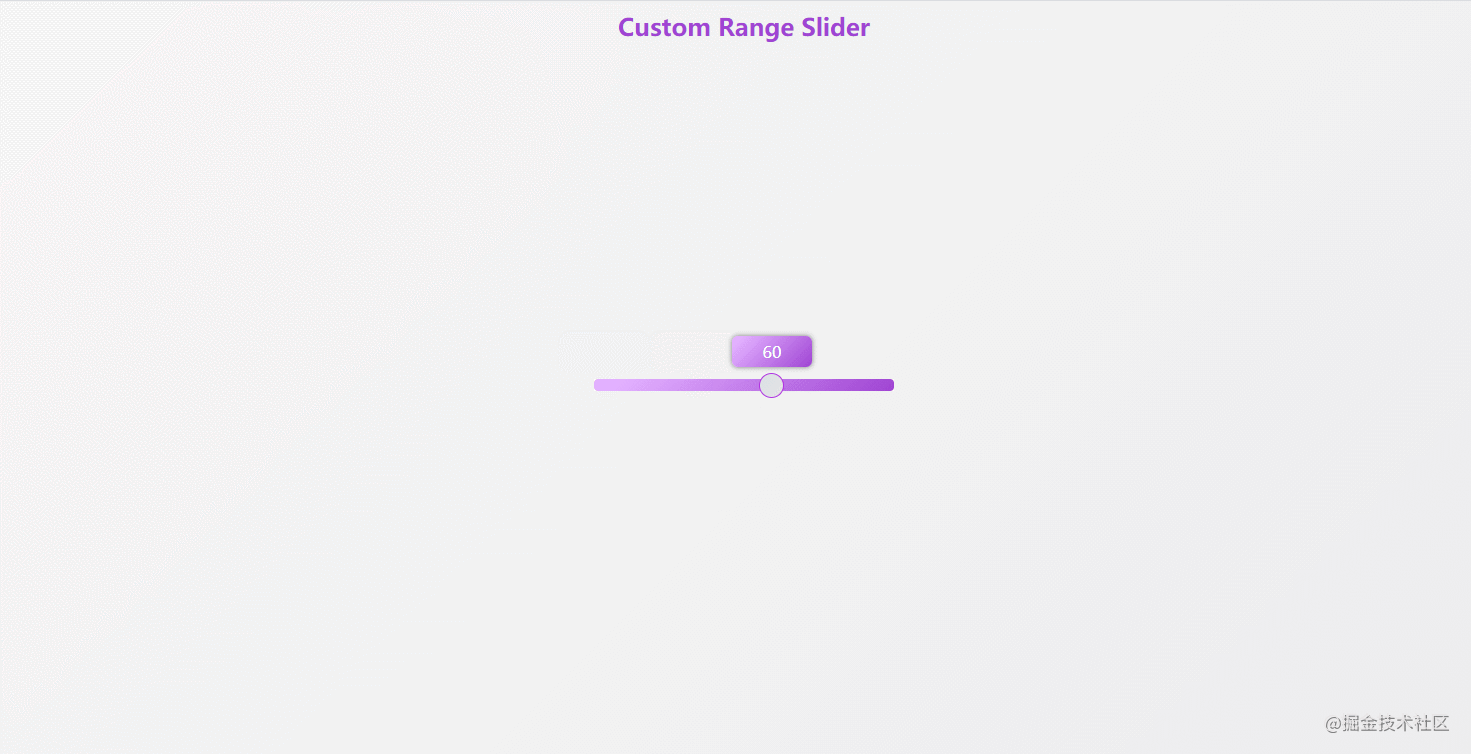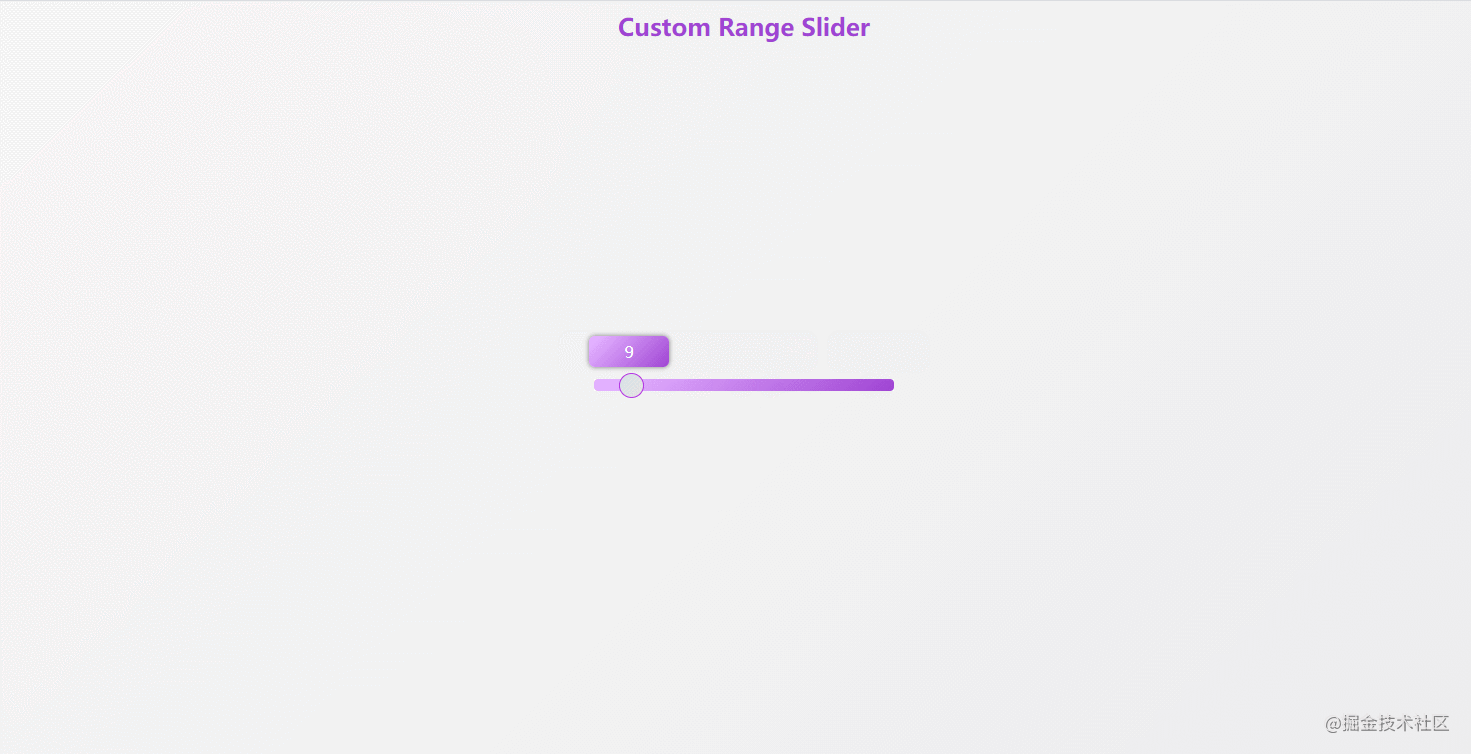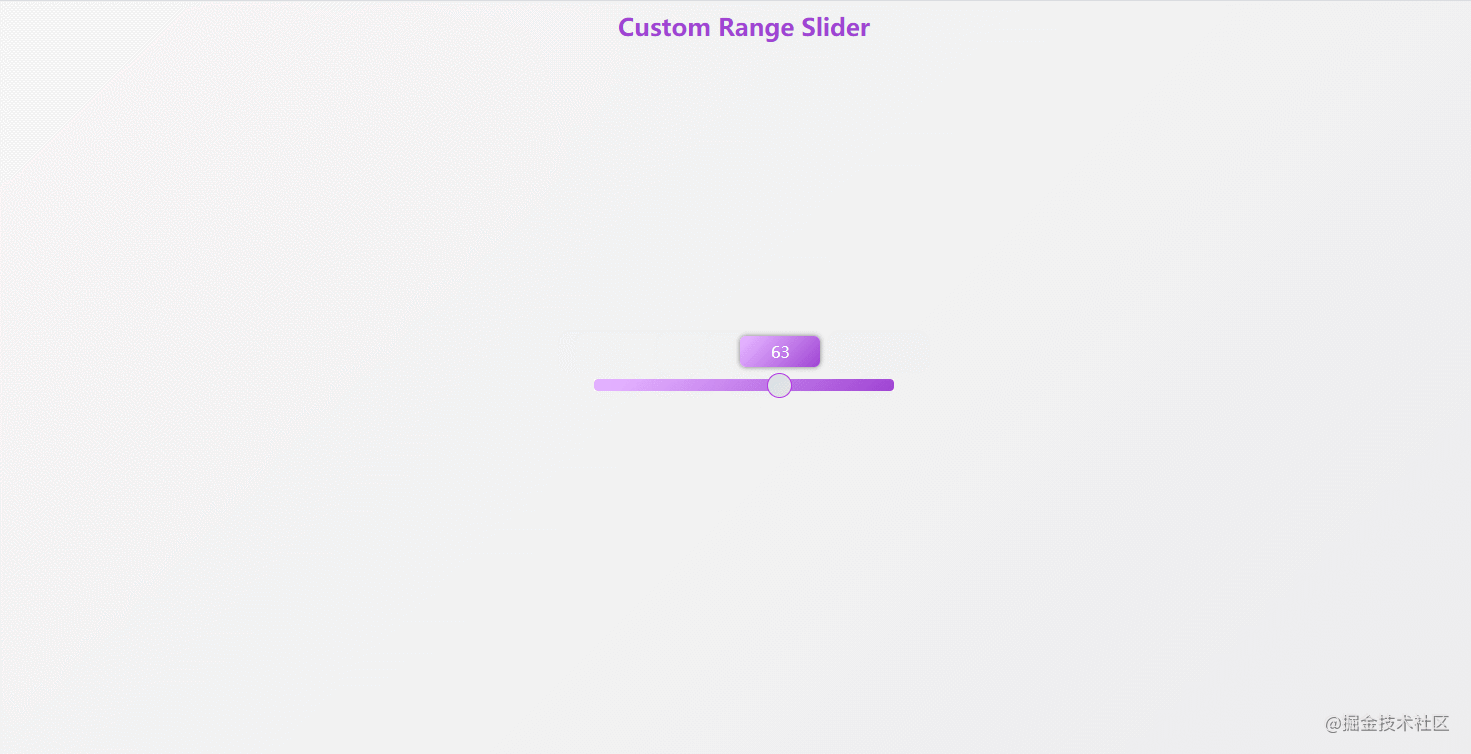
});43. custom-range-slider
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
inputelement style settings (compatible writing) + basic style layout. - JavaScript: The
inputevent listener of theinput rangeFor example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
input[type="range"]::-webkit-slider-runnable-track {
background-image: linear-gradient(135deg, #E2B0FF 10%, #9F44D3 100%);
width: 100%;
height: 12px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
input[type="range"]::-webkit-slider-thumb {
-webkit-appearance: none;
width: 25px;
height: 25px;
border-radius: 50%;
background-image: linear-gradient(135deg, #d9e2e6 10%, #e4e1e4 100%);
border: 1px solid #b233e4;
cursor: pointer;
margin-top: -6px;
}range.addEventListener("input",e => {
// string to the number
const value = +e.target.value;
const label = e.target.nextElementSibling;
const range_width = getStyle(e.target,"width");//XXpx
const label_width = getStyle(label,"width");//XXpx
// Due to contain px,slice the width
const num_width = +range_width.slice(0,range_width.length - 2);
const num_label_width = +label_width.slice(0,label_width.length - 2);
const min = +e.target.min;
const max = +e.target.max;
const left = value * (num_width / max) - num_label_width / 2 + scale(value,min,max,10,-10);
label.style.left = `${left}px`;
label.innerHTML = value;
});44. netflix-mobile-navigation
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: change of navigation width +
CSSgradient + basic style layout. - JavaScript: Click the button to switch the display or hide of the navigation bar. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function changeNav(type){
navList.forEach(nav => nav.classList[type === "open" ? "add" : "remove"]("visible"));
}45. quiz-app
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Card layout + basic style.
- JavaScript: form submission + calculation of multiple choice questions. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
submit.addEventListener("click",() => {
const answer = getSelected();
if(answer){
if(answer === quizData[currentQuestion].correct){
score++;
}
currentQuestion++;
if(currentQuestion > quizData.length - 1){
quizContainer.innerHTML = `
<h2>You answered ${ score } / ${ quizData.length } questions correctly!</h2>
<button type="button" class="btn" onclick="location.reload()">reload</button>
`
}else{
loadQuiz();
}
}
})46. testimonial-box-switcher
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS:
CSSanimation + width change to achieve progress bar +font-awesomefont library use + basic style layout. - JavaScript: The usage of the timer, note that the execution time of the timer is the same as the execution animation time of the set progress bar. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
.progress-bar {
width: 100%;
height: 4px;
background-color: #fff;
animation: grow 10s linear infinite;
transform-origin: left;
}
@keyframes grow {
0% {
transform: scaleX(0);
}
}function updateTestimonial(){
const { text,name,position,photo } = testimonials[currentIndex];
const renderElements = [testimonial,username,role];
userImage.setAttribute("src",photo);
order.innerHTML = currentIndex + 1;
[text,name,position].forEach((item,index) => renderElements[index].innerHTML = item);
currentIndex++;
if(currentIndex > testimonials.length - 1){
currentIndex = 0;
}
}Special note: CSS can also implement a progress bar.
47. random-image-feed
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: picture layout + basic style layout +
CSSprompt box realization (positioning + pseudo-element) +CSSrealization of back to the top effect. - JavaScript: random number + (monitoring of scroll events) to control the display and hide of the button back to the top. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function onLoad(rows = 5) {
container.innerHTML = "";
for (let i = 0; i < rows * 3; i++) {
const imageItem = document.createElement("img");
imageItem.src = `${refreshURL}${getRandomSize()}`;
imageItem.alt = "random image-" + i;
imageItem.loading = "lazy";
container.appendChild(imageItem);
}
}
function getRandomSize() {
return `${getRandomValue()}x${getRandomValue()}`;
}
function getRandomValue() {
return Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) + 300;
}
window.onload = () => {
changeBtn.addEventListener("click", () => onLoad());
window.addEventListener("scroll", () => {
const { scrollTop, scrollHeight } = document.documentElement || document.body;
const { clientHeight } = flexCenter;
back.style.display = scrollTop + clientHeight > scrollHeight ? 'block' : 'none';
})
onLoad();
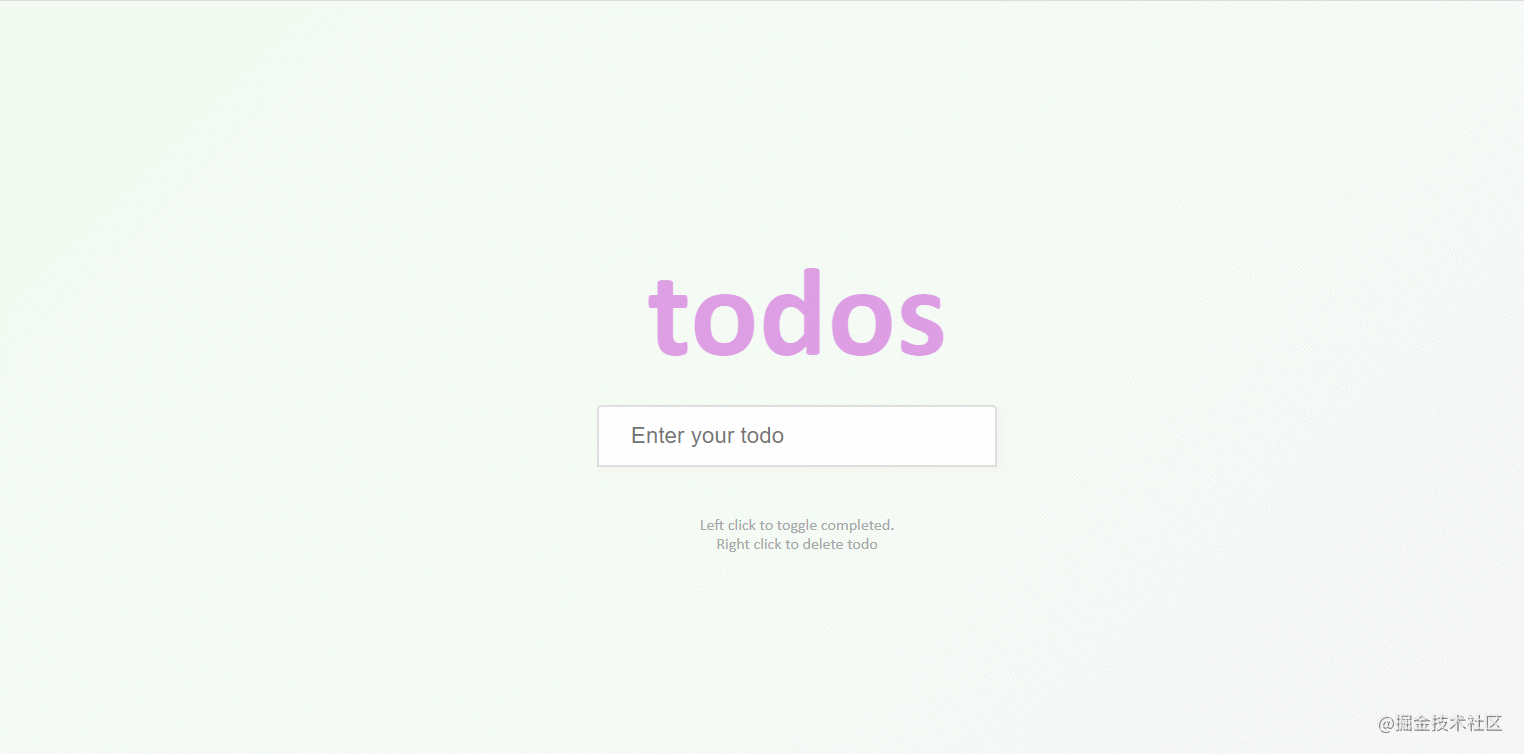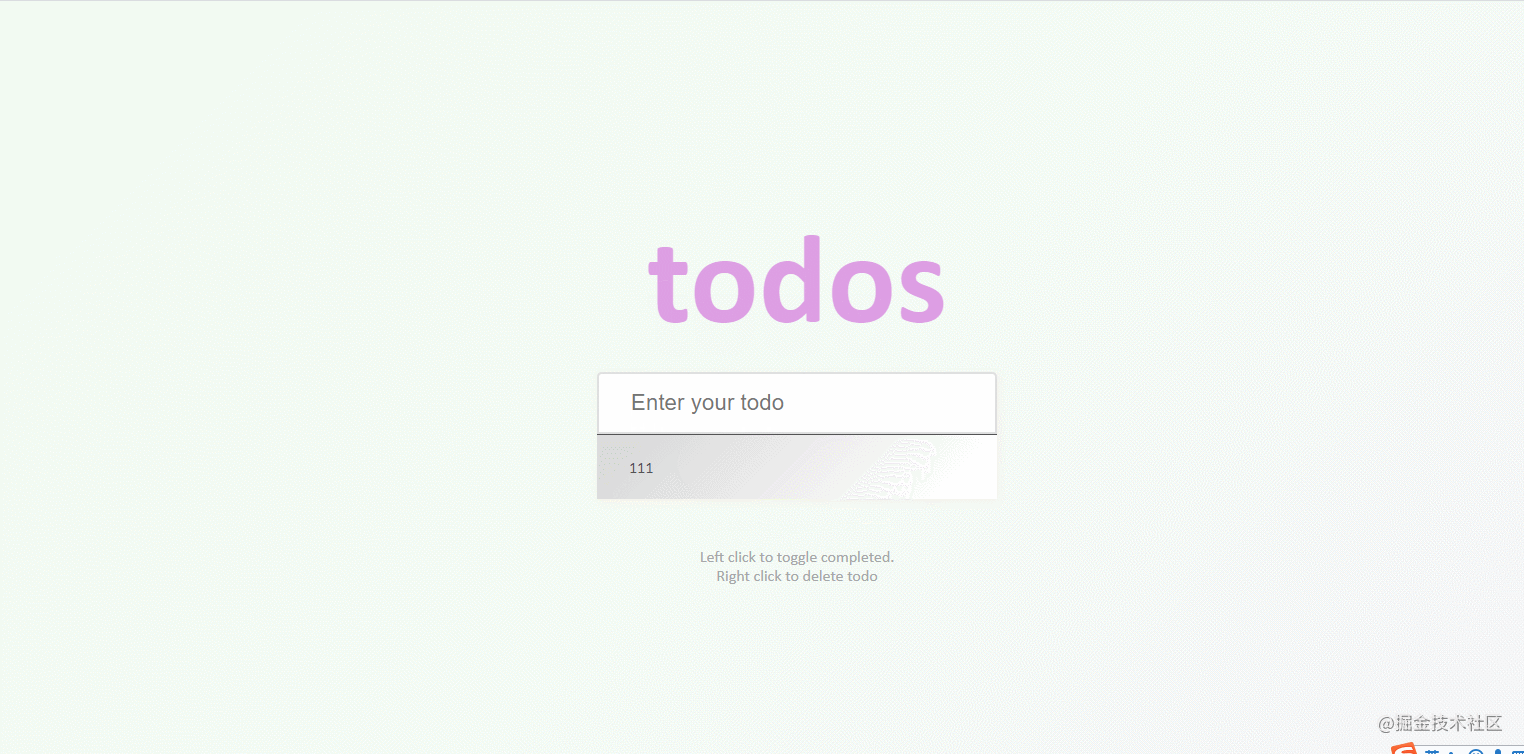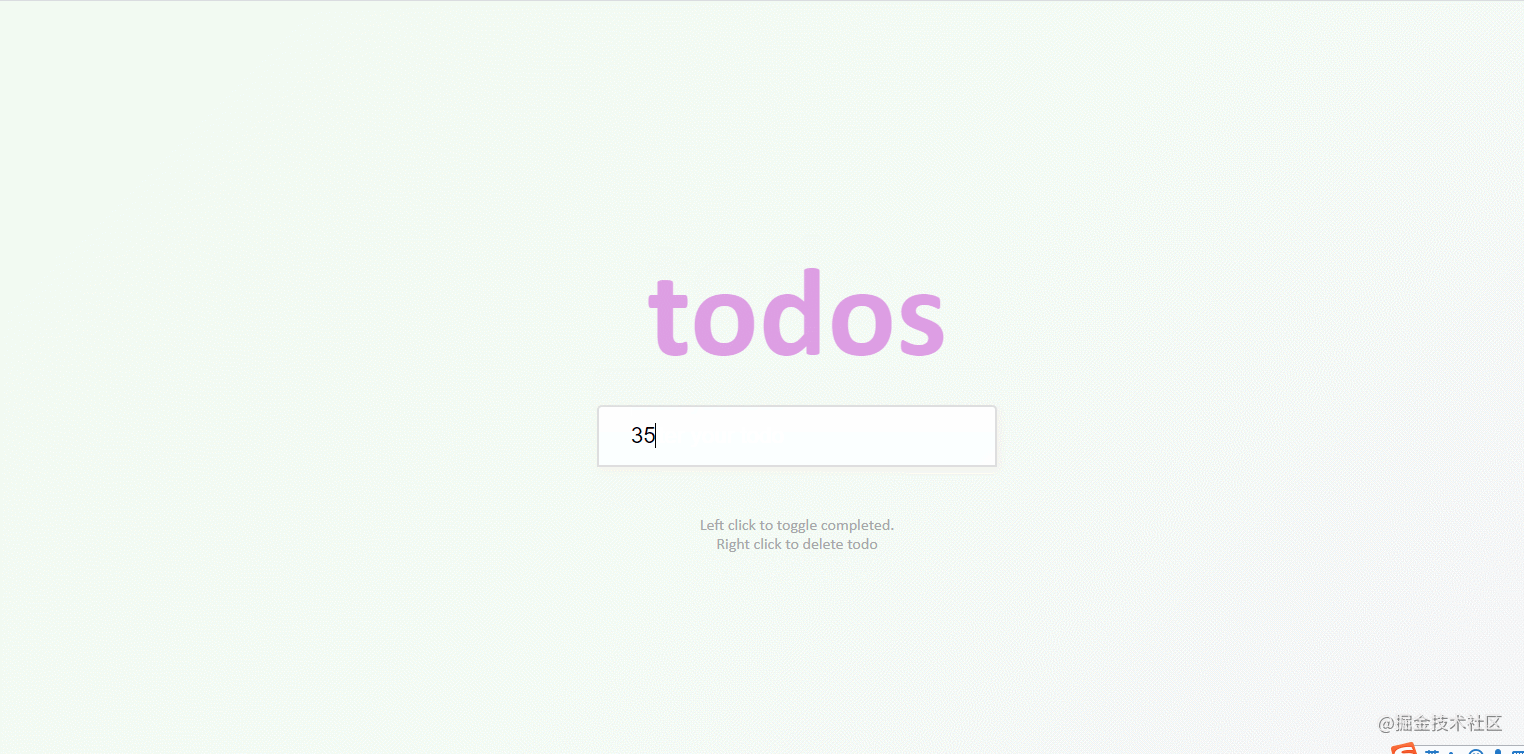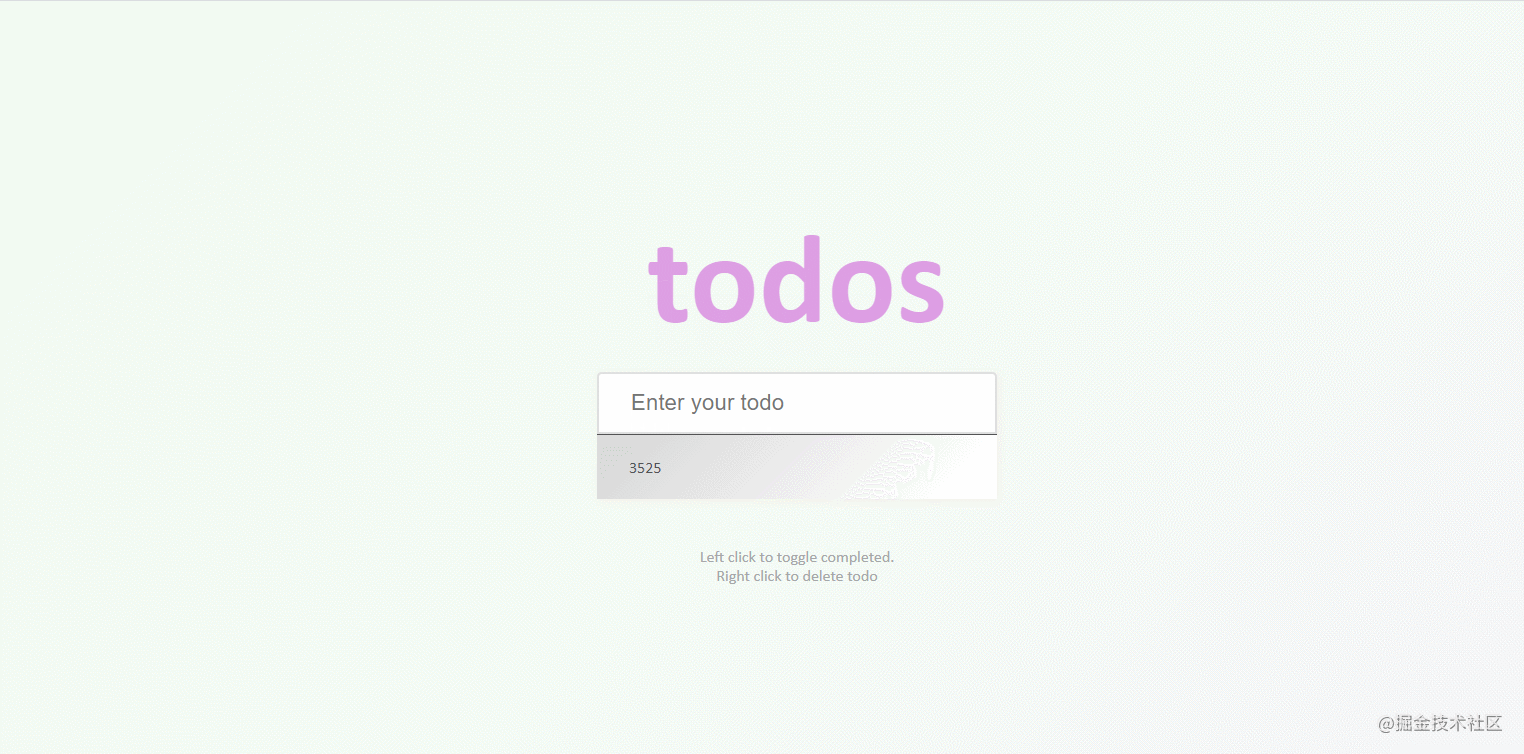
}48. todo-list
The effect is shown in the figure:
- source code
- online example
- [] Summary of knowledge points:
- CSS: Basic style layout +
CSSgradient. - JavaScript:
keydownandcontextmenuevents +localStorage APIstoring data. For example, the source code of the above example is as follows:
function addTodo(todo){
let inputValue = input.value;
if(todo){
inputValue = todo.text;
}
if(inputValue){
const liItem = document.createElement("li");
liItem.innerText = inputValue;
if(todo && todo.complete){
liItem.classList.add("complete");
}
liItem.addEventListener("click",() => {
liItem.classList.toggle("complete");
updateList();
});
liItem.addEventListener("contextmenu",(e) => {
e.preventDefault();
liItem.remove();
updateList();
});
todoList.appendChild(liItem);
input.value = "";
updateList();
}
}
function updateList(){
const listItem = $$("li",todoList);
const saveTodoData = [];
listItem.forEach(item => {
saveTodoData




































**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。