Physical Storage Media
Access time
$$ Access\ time = Seek\ time + Rotational\ latency + (Transfer\ time) $$
Disk Block
Features
- A contiguous sequence of sectors from a single track
- Data is transferred between disk and main memory in blocks
- The operating system stipulates that a disk block can only contain one file, so the space occupied by the file can only be an integer multiple of the disk block
Block Size
Compare
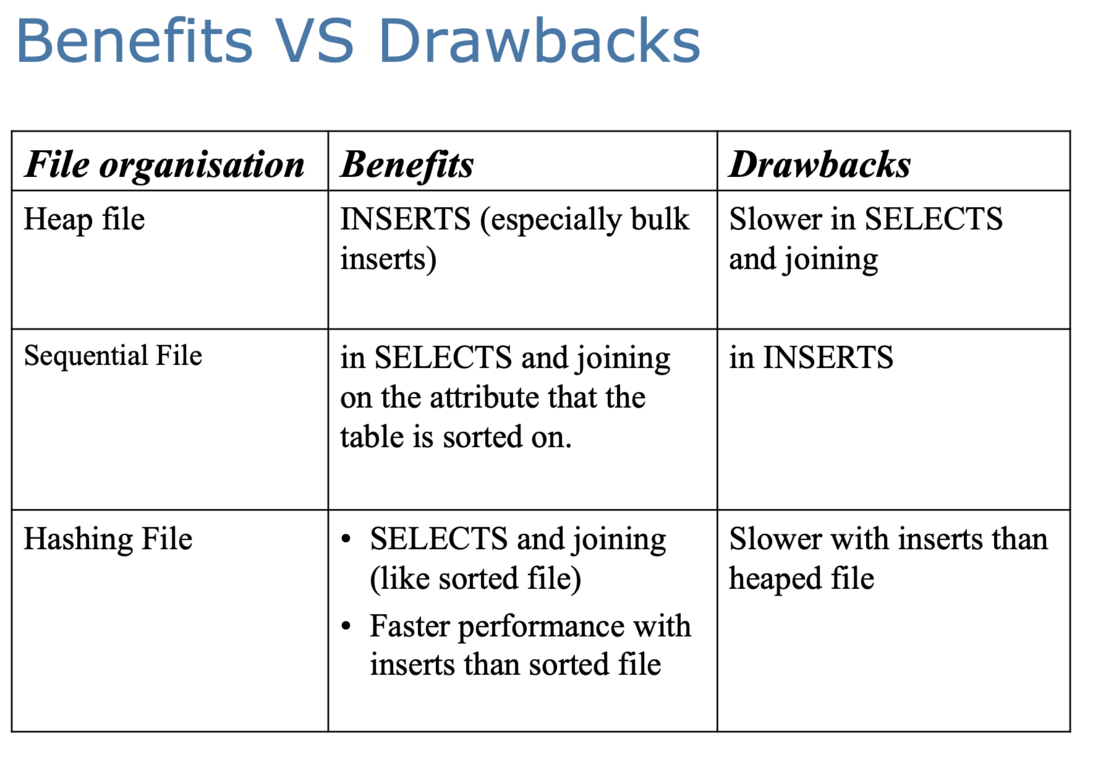
- Smaller blocks: more transfers from disk
- Larger blocks: more space wasted due to partially filled blocks
Therefore, Lareger block sizes may mean space wasted, smaller may lead to more IO times.
Typical block sizes today range from 4 to 16 kilobytes
Access Optimisation
The elevator algorithm:
File Organisation
Definition
Optimise block access time by organising the blocks to correspond to how data will be accessed
- Fixed-length records
- Variable-length records
Fixed-length records
- Allocate only as many records to a block as would fit entirely in the block
- Undesirable to delete records (requires additional block accesses)
Free List
Reference: https://songlee24.github.io/2...
Delete
When delete a record, the record's pointer is inserted in the free list. It will not be deleted immediately.
Insert
We change the header pointer to point to the next available record in the free list.
If no space is available, we add the new record to the end of the file.
Variable-length Records
Variable-length attributes are represented in the initial part of the record by a pair (offset, length)
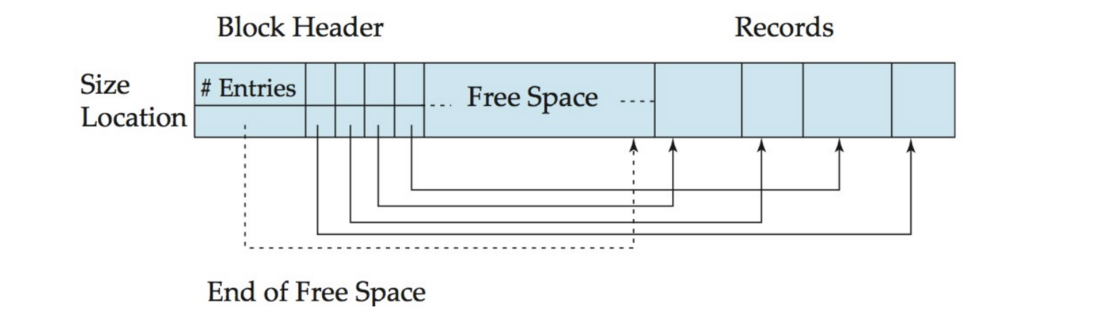
slotted-page structure
- The actual records are allocated contiguously in the block, starting from the end of the block.
- The free space in the block is contiguous, between the final entry in the header array, and the first record
The header stores the information of each records.
Insert
If a record is inserted, space is allocated for it at the end of free space.
Delete
Free the space that it occupies and the records in the block before the deleted record are moved.
Organisation
- Heap
- Sequential
- Hashing
- Multitable clustering file organisation
Sequential File Organisation
It is applied in many databases, such as Rocksdb
Insert
locate the position where the record is to be inserted
- If there is free space insert there
- If no free space, insert the record in an overflow block
- In either case, pointer chain must be updated
Delete
use pointer chains
Multitable Clustering File Organisation
Example
Features
- good for queries involving join
- bad for queries involving only one table
- results in variable size records
- can add pointer chains to link records of a particular relation



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。