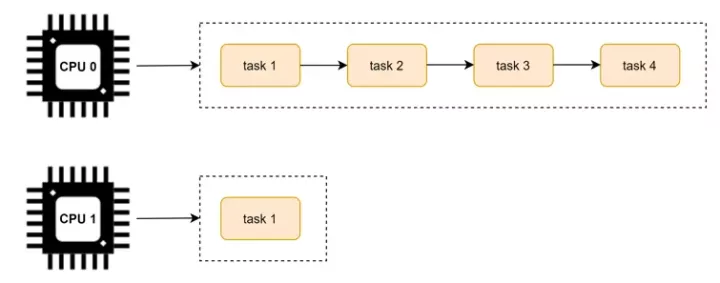
前面的调度学习都是默认在单个 CPU 上的调度策略。我们知道为了 CPU 之间减少“干扰”,每个 CPU 上都有一个任务队列。运行的过程种可能会出现有的 CPU 很忙,有的 CPU 很闲,如下图所示:
为了避免这个问题的出现,Linux 内核实现了 CPU 可运行进程队列之间的负载均衡。
因为负载均衡是在多个核上的均衡,所以在讲解负载均衡之前,我们先看下多核的架构。
将 task 从负载较重的 CPU 上转移到负载相对较轻的 CPU 上执行,这个过程就是负载均衡的过程。
多核架构
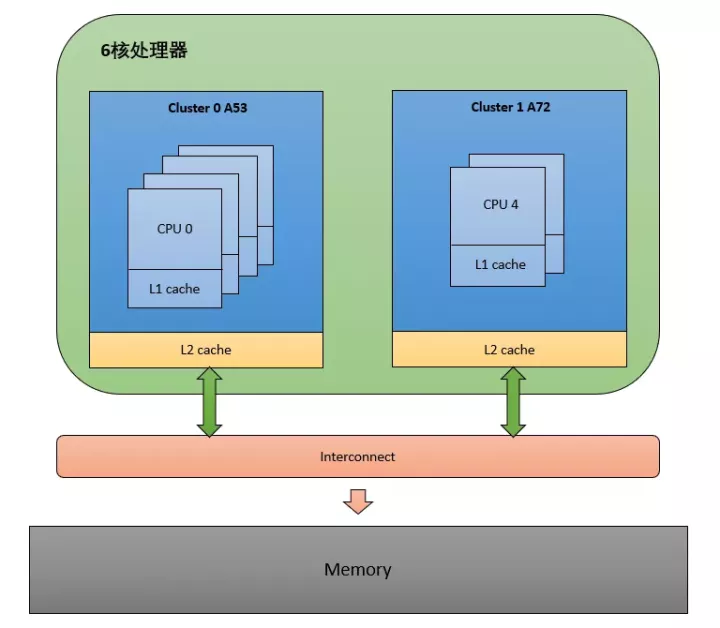
这里以 Arm64 的 NUMA(Non Uniform Memory Access) 架构为例,看下多核架构的组成。
从图中可以看出,这是非一致性内存访问。每个 CPU 访问 local memory,速度更快,延迟更小。因为 Interconnect 模块的存在,整体的内存会构成一个内存池,所以 CPU 也能访问 remote memory,但是相对 local memory 来说速度更慢,延迟更大。
我们知道一个多核心的 SOC 片上系统,内部结构是很复杂的。内核采用 CPU 拓扑结构来描述一个 SOC 的架构,使用调度域和调度组来描述 CPU 之间的层次关系。
LinuxC++后台服务器开发架构师免费学习地址
【文章福利】:小编整理了一些个人觉得比较好的学习书籍、视频资料共享在群文件里面,有需要的可以自行添加哦!~点击加入(需要自取)
CPU 拓扑
每一个 CPU 都会维护这么一个结构体实例,用来描述 CPU 拓扑。
struct cpu_topology {
int thread_id;
int core_id;
int cluster_id;
cpumask_t thread_sibling;
cpumask_t core_sibling;
};
thread_id: 从 mpidr_el1 寄存器中获取
core_id:从 mpidr_el1 寄存器中获取
cluster_id:从mpidr_el1寄存器中获取
thread_sibling:当前 CPU 的兄弟 thread。
core_sibling:当前 CPU 的兄弟Core,即在同一个 Cluster 中的 CPU。
可以通过 /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpuX/topology 查看 cpu topology 的信息。
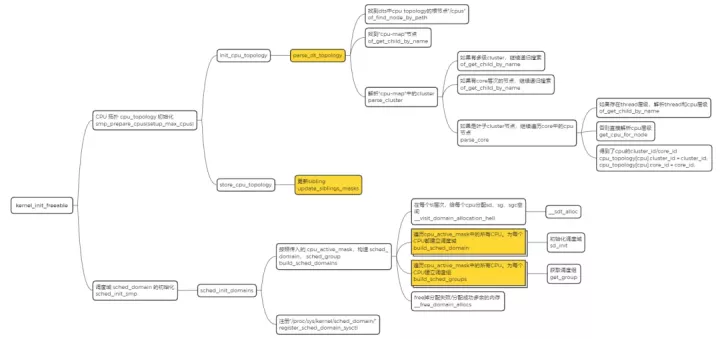
cpu_topology 结构体是通过函数 parse_dt_topology() 解析 DTS 中的信息建立的:
kernel_init() -> kernel_init_freeable() -> smp_prepare_cpus() -> init_cpu_topology() -> parse_dt_topology()
static int __init parse_dt_topology(void)
{
struct device_node *cn, *map;
int ret = 0;
int cpu;
cn = of_find_node_by_path("/cpus"); ------(1)
if (!cn) {
pr_err("No CPU information found in DT\n");
return 0;
}
/*
* When topology is provided cpu-map is essentially a root
* cluster with restricted subnodes.
*/
map = of_get_child_by_name(cn, "cpu-map"); ------(2)
if (!map)
goto out;
ret = parse_cluster(map, 0); ------(3)
if (ret != 0)
goto out_map;
topology_normalize_cpu_scale();
/*
* Check that all cores are in the topology; the SMP code will
* only mark cores described in the DT as possible.
*/
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu)
if (cpu_topology[cpu].cluster_id == -1)
ret = -EINVAL;
out_map:
of_node_put(map);
out:
of_node_put(cn);
return ret;
}找到 dts 中 cpu topology 的根节点 "/cpus"
找到 "cpu-map" 节点
解析 "cpu-map" 中的 cluster
以 i.mx8qm 为例,topology 为:”4A53 + 2A72”,dts中定义如下:
# imx8qm.dtsi
cpus: cpus {
#address-cells = <2>;
#size-cells = <0>;
A53_0: cpu@0 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a53", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x0>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A53 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A53_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a53_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A53_1: cpu@1 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a53", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x1>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A53 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A53_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a53_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A53_2: cpu@2 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a53", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x2>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A53 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A53_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a53_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A53_3: cpu@3 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a53", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x3>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A53 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A53_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a53_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A72_0: cpu@100 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a72", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x100>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A72 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A72_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a72_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A72_1: cpu@101 {
device_type = "cpu";
compatible = "arm,cortex-a72", "arm,armv8";
reg = <0x0 0x101>;
clocks = <&clk IMX_SC_R_A72 IMX_SC_PM_CLK_CPU>;
enable-method = "psci";
next-level-cache = <&A72_L2>;
operating-points-v2 = <&a72_opp_table>;
#cooling-cells = <2>;
};
A53_L2: l2-cache0 {
compatible = "cache";
};
A72_L2: l2-cache1 {
compatible = "cache";
};
cpu-map {
cluster0 {
core0 {
cpu = <&A53_0>;
};
core1 {
cpu = <&A53_1>;
};
core2 {
cpu = <&A53_2>;
};
core3 {
cpu = <&A53_3>;
};
};
cluster1 {
core0 {
cpu = <&A72_0>;
};
core1 {
cpu = <&A72_1>;
};
};
};
};
经过 parse_dt_topology(),update_siblings_masks() 解析后得到 cpu_topology 的值为:
CPU0: cluster_id = 0, core_id = 0
CPU1: cluster_id = 0, core_id = 1
CPU2: cluster_id = 0, core_id = 2
CPU3: cluster_id = 0, core_id = 3
CPU4: cluster_id = 1, core_id = 0
CPU5: cluster_id = 1, core_id = 1
调度域和调度组
在 Linux 内核中,调度域使用 sched_domain 结构表示,调度组使用 sched_group 结构表示。
调度域 sched_domain
struct sched_domain {
struct sched_domain *parent;
struct sched_domain *child;
struct sched_group *groups;
unsigned long min_interval;
unsigned long max_interval;
...
};parent:由于调度域是分层的,上层调度域是下层的调度域的父亲,所以这个字段指向的是当前调度域的上层调度域。
child:如上所述,这个字段用来指向当前调度域的下层调度域。
groups:每个调度域都拥有一批调度组,所以这个字段指向的是属于当前调度域的调度组列表。
min_interval/max_interval:做均衡也是需要开销的,不能时刻去检查调度域的均衡状态,这两个参数定义了检查该 sched domain 均衡状态的时间间隔的范围
sched_domain 是分成两个 level,base domain 称为 MC domain(multi core domain),顶层 domain 称为 DIE domain。
调度组 sched_group
struct sched_group {
struct sched_group *next;
unsigned int group_weight;
...
struct sched_group_capacity *sgc;
unsigned long cpumask[0];};
next:指向属于同一个调度域的下一个调度组。
group_weight:该调度组中有多少个cpu。
sgc:该调度组的算力信息。
cpumask:用于标记属于当前调度组的 CPU 列表(每个位表示一个 CPU)。
为了减少锁的竞争,每一个 CPU 都有自己的 MC domain、DIE domain 以及 sched_group,并且形成了 sched_domain 之间的层级结构,sched_group 的环形链表结构。CPU 对应的调度域和调度组可通过在设备模型文件 /proc/sys/kernel/sched_domain 里查看。
具体的 sched_domain 的初始化代码分析如下:
kernel_init() -> kernel_init_freeable() -> sched_init_smp() -> init_sched_domains(cpu_active_mask) -> build_sched_domains(doms_cur[0], NULL)
static int
build_sched_domains(const struct cpumask *cpu_map, struct sched_domain_attr *attr)
{
enum s_alloc alloc_state;
struct sched_domain *sd;
struct s_data d;
int i, ret = -ENOMEM;
alloc_state = __visit_domain_allocation_hell(&d, cpu_map); ------(1)
if (alloc_state != sa_rootdomain)
goto error;
/* Set up domains for CPUs specified by the cpu_map: */
for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) {
struct sched_domain_topology_level *tl;
sd = NULL;
for_each_sd_topology(tl) {
sd = build_sched_domain(tl, cpu_map, attr, sd, i); ------(2)
if (tl == sched_domain_topology)
*per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i) = sd;
if (tl->flags & SDTL_OVERLAP)
sd->flags |= SD_OVERLAP;
}
}
/* Build the groups for the domains */
for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) {
for (sd = *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i); sd; sd = sd->parent) {
sd->span_weight = cpumask_weight(sched_domain_span(sd));
if (sd->flags & SD_OVERLAP) {
if (build_overlap_sched_groups(sd, i))
goto error;
} else {
if (build_sched_groups(sd, i)) ------(3)
goto error;
}
}
}
......
/* Attach the domains */
rcu_read_lock();
for_each_cpu(i, cpu_map) {
int max_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->max_cap_orig_cpu);
int min_cpu = READ_ONCE(d.rd->min_cap_orig_cpu);
sd = *per_cpu_ptr(d.sd, i);
if ((max_cpu < 0) || (cpu_rq(i)->cpu_capacity_orig >
cpu_rq(max_cpu)->cpu_capacity_orig))
WRITE_ONCE(d.rd->max_cap_orig_cpu, i);
if ((min_cpu < 0) || (cpu_rq(i)->cpu_capacity_orig <
cpu_rq(min_cpu)->cpu_capacity_orig))
WRITE_ONCE(d.rd->min_cap_orig_cpu, i);
cpu_attach_domain(sd, d.rd, i); ------(4)
}
rcu_read_unlock();
if (!cpumask_empty(cpu_map))
update_asym_cpucapacity(cpumask_first(cpu_map));
ret = 0;
error:
__free_domain_allocs(&d, alloc_state, cpu_map); ------(5)
return ret;
}在每个 tl 层次,给每个 CPU 分配 sd、sg、sgc 空间
遍历 cpu_map 里所有 CPU,创建与物理拓扑结构对应的多级调度域
遍历 cpu_map 里所有 CPU, 创建调度组
将每个 CPU 的 rq 与 rd(root_domain) 进行绑定
free 掉分配失败或者分配成功多余的内存
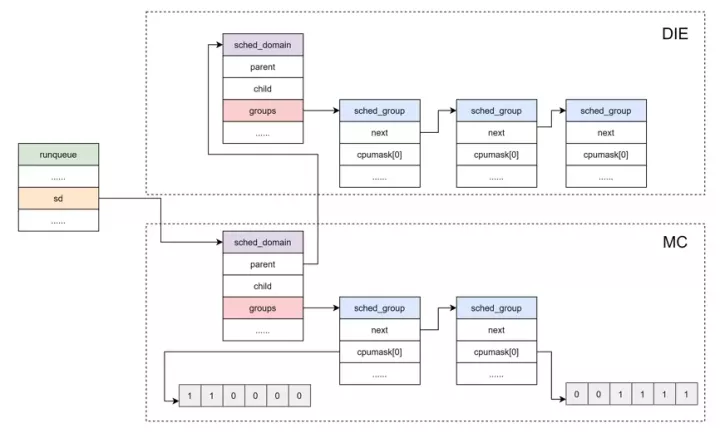
所以,可运行进程队列与调度域和调度组的关系如下图所示:
总结
这里用一张图来总结下 CPU 拓扑,调度域初始化的过程,如下所示:
根据已经生成的 CPU 拓扑,调度域和调度组,最终可以生成如下图所示的关系图。
在上面的结构中,顶层的 DIE domain 覆盖了系统中所有的 CPU,4 个 A53 是 Cluster 0,共享 L2 cache,两外 2 个 A72 是 Cluster 1,共享 L2 cache。那么每个 Cluster 可以认为是一个 MC 调度域,左边的 MC 调度域中有 4 个调度组,右边的 MC 调度域中有 2 个调度组,每个调度组中只有 1 个 CPU。整个 SOC 可以认为是高一级别的 DIE 调度域,其中有两个调度组,Cluster 0 属于一个调度组,Cluster 1 属于另一个调度组。跨 Cluster 的负载均衡是需要清除 L2 cache 的,开销是很大的,因此 SOC 级别的 DIE 调度域进行负载均衡的开销比 MC 调度域更大一些。
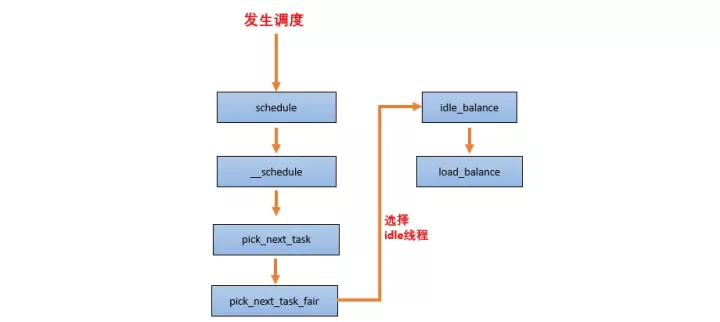
到目前为止,我们已经将内核的调度域构建起来了,CFS 可以利用 sched_domain 来完成多核间的负载均衡了。
何时做负载均衡?
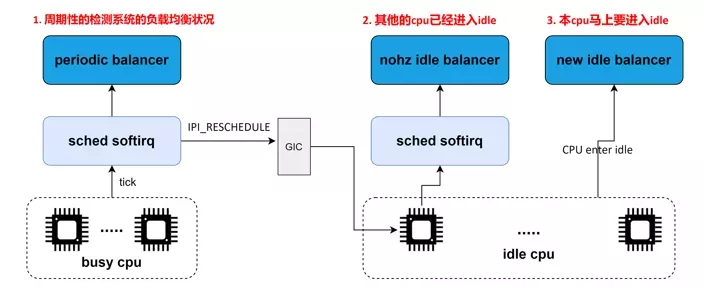
CFS 任务的负载均衡器有两种:
一种是针对 busy CPU 的 periodic balancer,用于进程在 busy CPU 上的均衡
一种是针对 idle CPU 的 idle balancer,用于把 busy CPU 上的进程均衡到 idle CPU 上来。
periodic balancer:周期性负载均衡是在时钟中断 scheduler_tick 中,找到该 domain 中最繁忙的 sched group 和 CPU runqueue,将其上的任务 pull 到本 CPU,以便让系统的负载处于均衡的状态。
nohz idle balancer:当其他的 CPU 已经进入 idle,本 CPU 任务太重,需要通过 IPI 将其他 idle 的 CPU 唤醒来进行负载均衡。
new idle balancer:本 CPU 上没有任务执行,马上要进入 idle 状态的时候,看看其他 CPU 是否需要帮忙,来从 busy cpu 上 pull 任务,让整个系统的负载处于均衡状态。
负载均衡的基本过程
当一个 CPU 上进行负载均衡的时候,总是从 base domain 开始,检查其所属 sched group 之间的负载均衡情况,如果有不均衡情况,那么会在该 CPU 所属 Cluster 之间进行迁移,以便维护 Cluster 内各个CPU 的任务负载均衡。
load_balance 是处理负载均衡的核心函数,它的处理单元是一个调度域,其中会包含对调度组的处理。
static int load_balance(int this_cpu, struct rq *this_rq,
struct sched_domain *sd, enum cpu_idle_type idle,
int *continue_balancing)
{
......
redo:
if (!should_we_balance(&env)) {
*continue_balancing = 0;
goto out_balanced;
}
group = find_busiest_group(&env); ------(1)
if (!group) {
schedstat_inc(sd->lb_nobusyg[idle]);
goto out_balanced;
}
busiest = find_busiest_queue(&env, group); ------(2)
if (!busiest) {
schedstat_inc(sd->lb_nobusyq[idle]);
goto out_balanced;
}
BUG_ON(busiest == env.dst_rq);
schedstat_add(sd->lb_imbalance[idle], env.imbalance);
env.src_cpu = busiest->cpu;
env.src_rq = busiest;
ld_moved = 0;
if (busiest->nr_running > 1) {
env.flags |= LBF_ALL_PINNED;
env.loop_max = min(sysctl_sched_nr_migrate, busiest->nr_running);
more_balance:
rq_lock_irqsave(busiest, &rf);
update_rq_clock(busiest);
cur_ld_moved = detach_tasks(&env); ------(3)
rq_unlock(busiest, &rf);
if (cur_ld_moved) {
attach_tasks(&env); ------(4)
ld_moved += cur_ld_moved;
}
local_irq_restore(rf.flags);
if (env.flags & LBF_NEED_BREAK) {
env.flags &= ~LBF_NEED_BREAK;
goto more_balance;
}
......
}
......
out:
return ld_moved;
}找到该 domain 中最繁忙的 sched group
在这个最繁忙的 group 中挑选最繁忙的 CPU runqueue, 作为 src
从这个队列中选择任务来迁移,然后把被选中的任务从其所在的 runqueue 中移除
从最繁忙的 CPU runqueue 中 pull 一些任务到当前可运行队列 dst




**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。