背景
前段时间向测试部门提交了一个接口测试的需求,测试在调试接口的过程中时不时的就出现查询不到数据的情况,但是测试流程很明显都还没测到我提交的接口,测试本人也知道,但是他也是纳闷了半天不知道什么情况,没办法测试我的接口只能来向我求助,然后我放下手头工作大致看了下发现只要是请求条件不变异常必先。报错信息也很清晰:java.lang.ClassCastException。
问题定位
从上面的分析,可以看出错误并非必现,但是有着明显的规律:查询条件不变就能必现。这样看来很明显是命中缓存就会有问题。根据异常堆栈信息定位到报错的代码行,有两点重大发现:
- 获取数据的方法使用了spring-cache的注解:
@Cacheable - 被强转的数据是从Redis缓存中获取
这么也看不出个所以然,只能本地跑起来看能不能复现debug看看吧,然后就发现在没命中缓存的时候被强转的类的类加载器是org.springframework.boot.devtools.restart.classloader,而命中缓存后的类加载器就变成sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader。这么看来问题的矛头指向了热部署插件springboot devtools, 那就先Bing一下,搜索一下关键字:springboot devtools 类型转换异常:
看来有不少人都遇到过了,随便点了几个进去,一色的提供的解决方案都是将被转换的类所在的jar包,从springboot devtools热部署中排除掉,这显然不是解决问题正确思路呀,首先如果该类并不是在独立的jar内呢,难道为了这么个问题我要单独搞了jar吗?然后如果真的是这样是不是意味着springboot devtools是有debug的呢?多年的开发经验带给我的直觉是没有正确的使用spring-cache,带着疑惑的角度我准备翻翻springboot-devtools和spring-cache的源码一探究竟!
问题排查
之前也没有阅读过这两个工具的源码,在不知如何下手的情况下,只能猜测摸索着前进。那就从SpringApplication.run()方法入手吧,至少之前看过springboot的源码,还算熟悉。
来看看run方法:
//跟本次问题无关的代码都去除了
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 关键点就在这里, 看类名就能知道该类是干什么的,监听Spring程序启动的
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
allRunners(context, applicationArguments);
return context;
}沿着SpringApplicationRunListeners.starting一路向下找到org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener#starting,
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args));
}一眼扫去就知道这是在广播应用程序启动事件:ApplicationStartingEvent,既然这里有广播那肯定就有监听这个事件的,继续往下找经过SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster.multicastEvent->invokeListener->doInvokeListener这一路调用下来来到listener.onApplicationEvent(event);,这个熟悉spring事件模型的应该比较清楚了吧。
private void doInvokeListener(ApplicationListener listener, ApplicationEvent event) {
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);
}进onApplicationEvent看下,哎吆吓一跳,实现那么多:
这怎么找,刚才不是有个RestartClassLoader吗,搜下:restart试试
效果很明显还真有,肯定就是RestartApplicationListener了,进去看看:
这里面一共监听了四种事件,还记得刚才我们广播的是什么事件吧?第一个就是
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
// 这个就是我们今天的主角
if (event instanceof ApplicationStartingEvent) {
onApplicationStartingEvent((ApplicationStartingEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent((ApplicationPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationReadyEvent || event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
Restarter.getInstance().finish();
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationFailedEvent) {
onApplicationFailedEvent((ApplicationFailedEvent) event);
}
}在onApplicationStartingEvent()方法中调用Restarter.initialize()后我们就进入到springboot-devtools偷天换日的核心地带了,先说下大致流程:
- 启动一个新线程:restartMain,并创建一个RestartClassLoader绑定到线程上下文中
- 在新线程中重新调用springboot应用程序的main方法
- 丢弃Main线程
部分关键源码贴下:
private Throwable doStart() throws Exception {
// 创建restartClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = new RestartClassLoader(this.applicationClassLoader, urls, updatedFiles, this.logger);
return relaunch(classLoader);
}
protected Throwable relaunch(ClassLoader classLoader) throws Exception {
// 创建新线程:restartedMain
RestartLauncher launcher = new RestartLauncher(classLoader,this.mainClassName, this.args,this.exceptionHandler);
launcher.start();
launcher.join();
return launcher.getError();
}RestartLauncher源码:
RestartLauncher(ClassLoader classLoader, String mainClassName, String[] args,
UncaughtExceptionHandler exceptionHandler) {
this.mainClassName = mainClassName;
this.args = args;
// restartedMain线程名称就是在这类设置的
setName("restartedMain");
setUncaughtExceptionHandler(exceptionHandler);
setDaemon(false);
setContextClassLoader(classLoader);
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 使用restartClassLoader重新加载包含main方法的类
Class<?> mainClass = getContextClassLoader().loadClass(this.mainClassName);
// 找到main方法
Method mainMethod = mainClass.getDeclaredMethod("main", String[].class);
//重新执行main方法
mainMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { this.args });
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
this.error = ex;
getUncaughtExceptionHandler().uncaughtException(this, ex);
}
}回过头来在Restarter类中immediateRestart方法中doStart()方法调用之后,调用SilentExitExceptionHandler.exitCurrentThread()静默丢弃我们的Main线程。
private void immediateRestart() {
try {
// 上文中的doStart方法就是从这里进去的
getLeakSafeThread().callAndWait(() -> {
start(FailureHandler.NONE);
cleanupCaches();
return null;
});
}
catch (Exception ex) {
this.logger.warn("Unable to initialize restarter", ex);
}
SilentExitExceptionHandler.exitCurrentThread();
}SilentExitExceptionHandler源码:
public static void exitCurrentThread() {
throw new SilentExitException();
}
// 运行时异常什么也不做,不知不觉中把Jvm分配给我们的主线程给替换了
private static class SilentExitException extends RuntimeException {
}总结:
到这里我们理清了RestartClassLoader是如何替换AppClassLoader的,那按照正常的逻辑后面应用程序中所有的本地类都应该由RestartClassLoader加载。实时情况确实是,在没有命中缓存的时候报强制类型转换异常的类的classLoader确实是RestartClassLoader,命中缓存的就不是了,那问题是否是出在缓存层了呢。来看下spring-cache是如何使用的:
配置CacheManage:
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){
// 默认的缓存配置
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
Set<String> cacheNames = new HashSet<>();
cacheNames.add("cache_test");
// 对每个缓存空间应用不同的配置
Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> configMap = new HashMap<>();
configMap.put("cache_test", defaultCacheConfig);
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(defaultCacheConfig)
.initialCacheNames(cacheNames)
.withInitialCacheConfigurations(configMap)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}看代码很明显他使用了默认的RedisCacheConfiguration的配置RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()源码
public static RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig() {
return defaultCacheConfig(null);
}
public static RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
registerDefaultConverters(conversionService);
return new RedisCacheConfiguration(Duration.ZERO, true, true, CacheKeyPrefix.simple(),
SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.string()),
SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.java(classLoader)), conversionService);
}从RedisCacheConfiguration#defaultCacheConfig源码可以看出两个点:
- 存在重载方法支持传入ClassLoader
- 默认提供的redis的Value序列化方式是:
RedisSerializer.java(classLoader)->new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader)
到这里稍有经验的程序员应该都知道JDK的序列化是由java.io.ObjectInputStream来完成的。
我这里就不贴JdkSerializationRedisSerializer的源码了,代码比较简单,反正最后做反序列化这个工作的是ObjectInputStream的子类org.springframework.core.ConfigurableObjectInputStream,该类重写了resolveClass()方法,实现上首先判断是否存在ClassLoader,有的话直接用该ClassLoader加载该类。否则就调用父类的同名方法。而ObjectInputStream获取ClassLoader的方式则是调用VM.latestUserDefinedLoader(),不了解latestUserDefinedLoader的可以自己百度下。到这里问题就很清晰了吧
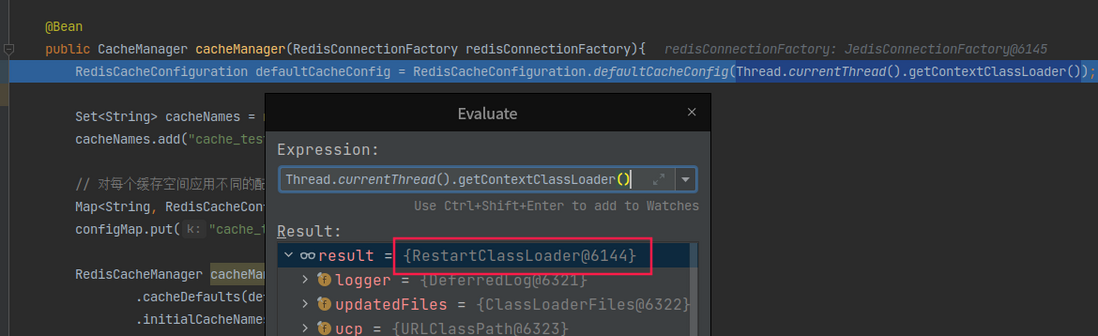
那我们改下代码,传入当前线程的ClassLoader试试,向下面这样:
RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader())果然可以了。这是为什么呢?因为在springboot-devtools中已经替换了主线程,同时更换了与线程绑定的ClassLoader为RestartClassLoader,所以我们这里从当前线程中取到的ClassLoader也是RestartClassLoader:
那么在命中缓存后反序列化就会使用我们传入的这个RestartClassLoader而不是去从VM.latestUserDefinedLoader()这里获取。
其实到这里第二个解决方案也就浮出水面了,我们可以给RedisCacheConfiguration指定一个序列化工具,比如用fastjson作为spring-cache的序列化组件,向下面这样:
final RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer()));
)来看下fastjson是如何做的:com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer#deserialize的源码
public Object deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException {
if (bytes == null || bytes.length == 0) {
return null;
}
try {
return JSON.parseObject(new String(bytes, IOUtils.UTF8), Object.class, defaultRedisConfig);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new SerializationException("Could not deserialize: " + ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}从JSON.parseObject往下一直找到很深处,会在com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#loadClass(java.lang.String, java.lang.ClassLoader, boolean)中找到如下代码,看到了吧它也是从当前线程上下文中取ClassLoader
public static Class<?> loadClass(String className, ClassLoader classLoader, boolean cache) {
.....去除一大段保障代码
try{
ClassLoader contextClassLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if(contextClassLoader != null && contextClassLoader != classLoader){
clazz = contextClassLoader.loadClass(className);
if (cache) {
mappings.put(className, clazz);
}
return clazz;
}
} catch(Throwable e){
// skip
}
.....去除一大段保障代码
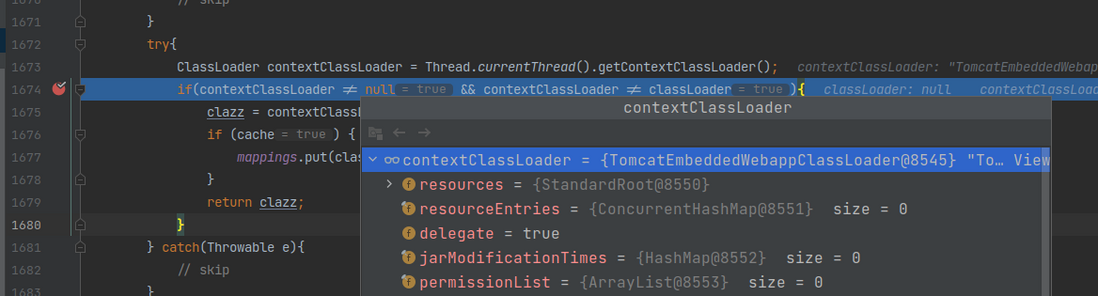
}来看下这个ClassLoader是什么类型:
这里竟然不是RestartClassLoader而是org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader? 为什么这里不像配置CacheManager那里一样是RestartClassloader呢?因为这里的当前线程是用户请求线程,用户请求线程是由Web容器创建的,而配置CacheManager的代码是由springboot程序启动线程执行的:restartMain线程。而实际上TomcatEmbeddedWebappClassLoader的父ClassLoader就是RestartClassLoader,根据类加载双亲委派机制可知实际上最终还是由RestartClassLoader负责加载工作:
总结
问题本质:
- Springboot devtools更换了主线程及类加载器为RestartClassLoader
- spring-cache的缓存配置使用了默认的序列化配置:JdkSerializationRedisSerializer,且没有指定ClassLoader
解决方案:
- 在RedisCacheConfiguration缓存配置里指定当前线程的ClassLoader
- 或者不使用默认的序列化组件,更换序列化器组件:GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。