1 前言
在之前的文章里,我分享了Js版的堆实现和C语言版的堆实现, 理解的话,堆的实现其实并不难,以大顶堆为例,简单归纳就是插入时候,比节点小,就不断向下沉,让更大的上浮,直到最大的上浮到根节点。
2. 数据结构与算法: 堆 优先队列 JavaScript语言描述
优先队列基于堆实现,顾名思义是一个有优先级的队列,最高优先级的最先出列,低优先级最后出列(如果是最小堆则刚好相反)。今天我们就用堆和优先队列高效解决一些问题,分别是经典的TopK问题-堆解法,以及3D接雨水-优先队列解法。
2 TopK问题-堆解法
2.1 思路
在之前的文章里,我分享了基于Partition和ThreePartition算法的原地排序,来高效求解TopK问题,原地排序,没有使用额外的空间,空间复杂度很低,但是时间复杂度波动比较大,如果随机取的基准值很理想,那么效率超高,但如果数组里值分布很发散,随机取的基准值也很不理想,那么这种极端情况下,那么效率就不是很高,虽然《算法导论》证明了Partition算法是近似线性,但其线性常数项绝对比1大多了;
而堆解法呢,就是稳定的时间空间复杂度,建堆的最差复杂度是确定的,遍历一遍的复杂度只有O(N),可以确定在kLog(k) + O(N)。
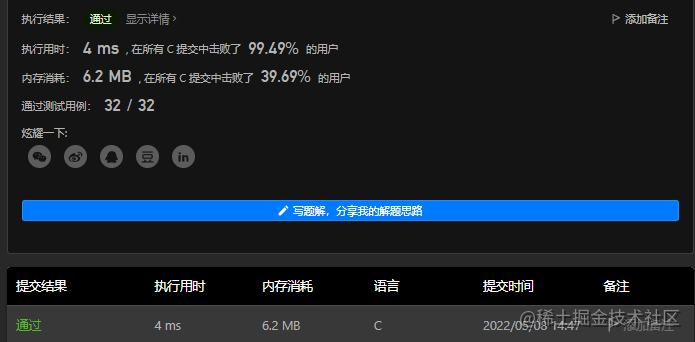
2.2 C语言描述
先建立一个容量为k的最小堆,后续的元素,只有比堆顶大的,才入堆,否则直接略过,最后堆顶元素就是第K大元素。
typedef struct MinHeap {
int *data; //数据域
int size; //长度
int max;//最大长度
} MinHeap;
void insert(struct MinHeap *p, int item){
if (p->size == p->max)
{
printf("******:\n");
return;
}
int i = ++p->size;
for (; p->data[i/2] > item; i/=2)
{
if (i <= 1)
{
break;
}
p->data[i] = p->data[i/2];
}
p->data[i] = item;
}
void delete(struct MinHeap *p){
p->data[1] = p->data[p->size--];
int i = 1;
int tmp;
while(2*i <= p->size){
//如果有右节点
if (2*i + 1 <= p->size)
{
if (p->data[2*i + 1] < p->data[i] || p->data[2*i] < p->data[i])
{
if (p->data[2*i + 1] < p->data[2*i])
{
tmp = p->data[i];
p->data[i] = p->data[2*i + 1];
p->data[2*i + 1] = tmp;
i = 2*i + 1;
}else{
tmp = p->data[i];
p->data[i] = p->data[2*i];
p->data[2*i] = tmp;
i = 2*i;
}
}else{
return;
}
}else{
//只有左节点
if (p->data[2*i] < p->data[i])
{
tmp = p->data[i];
p->data[i] = p->data[2*i];
p->data[2*i] = tmp;
i = 2*i;
}else{
return;
}
}
}
}
int findKthLargest(int* nums, int numsSize, int k){
struct MinHeap *heap;
heap=(struct MinHeap *)malloc(sizeof(struct MinHeap));
if (heap == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error \n");
return 0;
}
heap->size = 0;
heap->max = k + 1;
heap->data = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*heap->max);
if(heap->data == NULL)
{
printf("malloc error \n");
return 0;
}
heap->data[0] = 9999;
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i)
{
if(i < k){
insert(heap, nums[i]);
}else{
if(nums[i] > heap->data[1]){
delete(heap);
insert(heap, nums[i]);
}
}
}
return heap->data[1];
}3 3D接雨水-优先队列解法
题目:407. 接雨水 II
3.1 思路
之前在单调栈进阶里分享过2D接雨水,那个虽然是hard但比较简单;3D接雨水考虑的比2D多了些,不能只考虑两边的高度,而是要考虑四周,只有四周都比自己高,才能接得住雨水;思路呢其实就是把最外围的记录下来,扔到优先队列里(小堆),然后不断让堆顶出队,去更新堆顶元素的四周,然后把四周的入堆,如果四周的元素有比堆顶还低的,显然可以接到雨水。PS:觉得我讲解的肯定没有题解清晰,建议看题解。
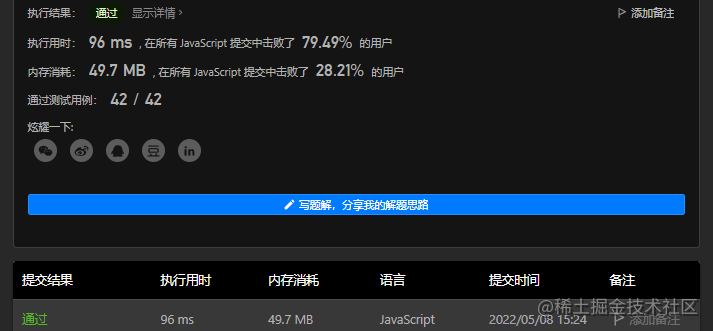
## 3.2 Js语言描述
var Heap = function () {
this.data = []
this.insert = (obj) => {
let i = this.data.length
for (; i > 0 && this.data[Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)].val >= obj.val; i = Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)) {
if (i < 1) {
break
}
this.data[i] = this.data[Math.floor((i - 1) / 2)]
}
this.data[i] = obj
}
this.pop = () => {
if (this.data.length == 0) {
return null
}
if (this.data.length == 1) {
return this.data.pop()
}
let top = this.data[0]
this.data[0] = this.data.pop()
let i = 0
while (2 * i + 1 < this.data.length) {
if (2 * i + 2 < this.data.length) {
if (this.data[2 * i + 2].val < this.data[i].val || this.data[2 * i + 1].val < this.data[i].val) {
if (this.data[2 * i + 2].val < this.data[2 * i + 1].val) {
this.swap(i, 2 * i + 2)
i = 2 * i + 2
} else {
this.swap(i, 2 * i + 1)
i = 2 * i + 1
}
} else {
break
}
} else {
if (this.data[2 * i + 1].val < this.data[i].val) {
this.swap(i, 2 * i + 1)
i = 2 * i + 1
} else {
break
}
}
}
return top
}
this.swap = (i, j) => {
let tmp = this.data[j]
this.data[j] = this.data[i]
this.data[i] = tmp
}
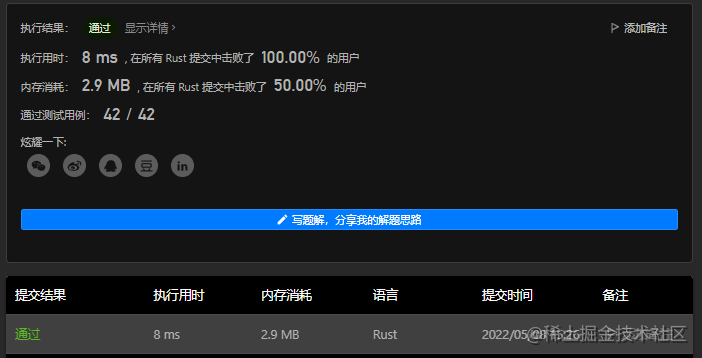
};3.3 Rust语言描述
思路都是一样的,仅仅语言不同
use std::cmp::Ordering;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
#[derive(Copy, Clone, Eq, PartialEq)]
struct Item {
val: i32,
i: usize,
j: usize,
}
impl Ord for Item {
fn cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> Ordering {
other.val.cmp(&self.val)
}
}
impl PartialOrd for Item {
fn partial_cmp(&self, other: &Self) -> Option<Ordering> {
Some(self.cmp(other))
}
}
impl Solution {
pub fn trap_rain_water(height_map: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let h = height_map.len();
let w = height_map[0].len();
if h <= 2 || w <= 2 {
return 0;
}
let mut water = vec![vec![-1; w]; h];
let mut pq: BinaryHeap<Item> = BinaryHeap::new();
let mut i = 0;
while i < h {
water[i][0] = height_map[i][0];
water[i][w - 1] = height_map[i][w - 1];
pq.push(Item {
val: height_map[i][0],
i: i,
j: 0,
});
pq.push(Item {
val: height_map[i][w - 1],
i: i,
j: w - 1,
});
i += 1;
}
i = 1;
while i < w - 1 {
water[0][i] = height_map[0][i];
water[h - 1][i] = height_map[h - 1][i];
pq.push(Item {
val: height_map[0][i],
i: 0,
j: i,
});
pq.push(Item {
val: height_map[h - 1][i],
i: h - 1,
j: i
});
i += 1;
}
let dirs :[i32;5] = [-1, 0, 1, 0, -1];
let mut res = 0;
let mut k;
while pq.len() > 0 {
if let Some(Item { val, i, j }) = pq.pop() {
k = 0;
while k < 4 {
let nx = (i as i32 + dirs[k]) as usize;
let ny = (j as i32 + dirs[k+1]) as usize;
if 0 < nx && nx < h as usize && 0 < ny && ny < w && water[nx][ny] == -1 {
if height_map[nx][ny] < val {
res += val - height_map[nx][ny];
}
water[nx][ny] = val;
pq.push(Item {
val: val.max(height_map[nx][ny]),
i: nx,
j: ny
});
}
k += 1;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。