SPI 的概念简介
SPI 是 Service Provider Interface 的简称,一般是指由厂商来实现并部署在应用程序 ClassPath 下的服务提供者接口。
ServiceLoader 类
ServiceLoader 是 JDK6 中提供的一种 SPI 的实现解决方案,下面以 JDBC 编程的使用步骤展开 ServiceLoader 的内部机制剖析。JDBC 编程一般有五个步骤:
1、执行数据库驱动类加载
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.driver")2、创建数据库连接
DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password) 3、创建SQL语句
Connection#creatstatement();4、执行SQL语句并处理结果集
Statement#executeQuery()5、释放资源
ResultSet#close()
Statement#close()
Connection#close()上面第 2 步创建数据库连接中就使用了 ServiceLoader 来实现数据库驱动类的加载。下面进行相关的开发步骤和源码分析:
第一步、定义服务接口
public interface Driver {
Connection connect(String url, java.util.Properties info)
throws SQLException;
}第二步、实现服务接口
数据库厂商提供一个或多个实现 Driver 接口的驱动实现类,下面以 mysql 为例:
package com.mysql.cj.jdbc;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}第三步、注册实现类到配置文件
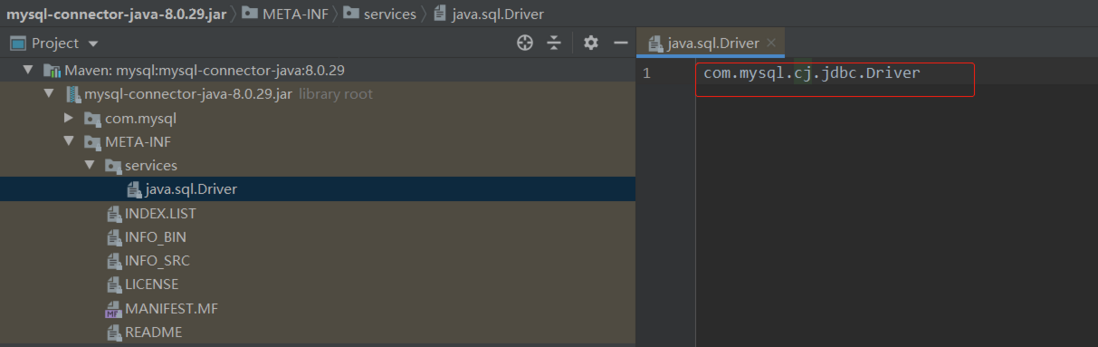
在工程目录 java 的同级目录中新建目录 resources/META-INF/services,在 services 目录下新建一个配置文件 java.sql.Driver(文件名为服务接口的全限定名),文件中每一行是实现类的全限定名。
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver第四步、(使用方)加载服务
服务加载在 DriverManager 类中实现,进入 DriverManager 类,静态初始化块代码。
static {
loadInitialDrivers();
println("JDBC DriverManager initialized");
}进入 loadInitialDrivers() 方法,这个方法内部使用了 ServiceLoader。
private static void loadInitialDrivers() {
String drivers;
try {
drivers = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<String>() {
public String run() {
return System.getProperty("jdbc.drivers");
}
});
} catch (Exception ex) {
drivers = null;
}
// If the driver is packaged as a Service Provider, load it.
// Get all the drivers through the classloader
// exposed as a java.sql.Driver.class service.
// ServiceLoader.load() replaces the sun.misc.Providers()
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
ServiceLoader<Driver> loadedDrivers = ServiceLoader.load(Driver.class);
Iterator<Driver> driversIterator = loadedDrivers.iterator();
/* Load these drivers, so that they can be instantiated.
* It may be the case that the driver class may not be there
* i.e. there may be a packaged driver with the service class
* as implementation of java.sql.Driver but the actual class
* may be missing. In that case a java.util.ServiceConfigurationError
* will be thrown at runtime by the VM trying to locate
* and load the service.
*
* Adding a try catch block to catch those runtime errors
* if driver not available in classpath but it's
* packaged as service and that service is there in classpath.
*/
try{
while(driversIterator.hasNext()) {
driversIterator.next();
}
} catch(Throwable t) {
// Do nothing
}
return null;
}
});
println("DriverManager.initialize: jdbc.drivers = " + drivers);
if (drivers == null || drivers.equals("")) {
return;
}
String[] driversList = drivers.split(":");
println("number of Drivers:" + driversList.length);
for (String aDriver : driversList) {
try {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: loading " + aDriver);
Class.forName(aDriver, true,
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} catch (Exception ex) {
println("DriverManager.Initialize: load failed: " + ex);
}
}
}进入 ServiceLoader 的 load() 方法,这里获取线程上下文类加载器 ContextClassLoader,这个类加载器默认是应用程序类加载器,可以找到应用程序中的类进行加载。
public static <S> ServiceLoader<S> load(Class<S> service) {
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
return ServiceLoader.load(service, cl);
}继续进入 ServiceLoader 的重载 load() 方法,里面调用了 ServiceLoader 的构造函数
private ServiceLoader(Class<S> svc, ClassLoader cl) {
service = Objects.requireNonNull(svc, "Service interface cannot be null");
loader = (cl == null) ? ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader() : cl;
acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null) ? AccessController.getContext() : null;
reload();
}其中 reload() 方法中首先清空 providers,然后构建了一个 LazyIterator。LazyIterator 是 ServiceLoader 内部实现的一个懒加载迭代器,这个迭代器在进行遍历的时候才会真正的加载资源。
public void reload() {
providers.clear();
lookupIterator = new LazyIterator(service, loader);
}下面看看 LazyIterator 的 hasNextService() 方法实现
private boolean hasNextService() {
if (nextName != null) {
return true;
}
if (configs == null) {
try {
String fullName = PREFIX + service.getName();
if (loader == null)
configs = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fullName);
else
configs = loader.getResources(fullName);
} catch (IOException x) {
fail(service, "Error locating configuration files", x);
}
}
while ((pending == null) || !pending.hasNext()) {
if (!configs.hasMoreElements()) {
return false;
}
pending = parse(service, configs.nextElement());
}
nextName = pending.next();
return true;
}通过 PREFIX + service.getName() 构建出了 fullName,PREFIX 的定义如下:
private static final String PREFIX = "META-INF/services/";service.getName() 的返回结果是 java.sql.Driver,所以 fullName 的值就是 META-INF/services/java.sql.Driver ,即配置文件的路径。其中配置的是厂商的数据库驱动实现类,比如:com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver,nextName 的值就是 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver。
真正的驱动实现类的实例化是在 nextService() 方法中
private S nextService() {
if (!hasNextService())
throw new NoSuchElementException();
String cn = nextName;
nextName = null;
Class<?> c = null;
try {
c = Class.forName(cn, false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not found");
}
if (!service.isAssignableFrom(c)) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " not a subtype");
}
try {
S p = service.cast(c.newInstance());
providers.put(cn, p);
return p;
} catch (Throwable x) {
fail(service,
"Provider " + cn + " could not be instantiated",
x);
}
throw new Error(); // This cannot happen
}其中通过 nextName(数据库驱动类的全限定名)得到 Class 对象,然后进行 isAssignableFrom 验证,验证通过后通过反射机制实例化一个实例,并缓存到 providers 中,key 就是数据库驱动类的全限定名,value 就是对应的实例化对象。providers 的定义是一个 LinkedHashMap。
private LinkedHashMap<String,S> providers = new LinkedHashMap<>();到此,所有的数据库驱动类的实例就缓存到了 ServiceLoader 类的 providers 中。ServiceLoader 实现了 Iterable 接口,可以通过遍历 ServiceLoader 实现对 providers 中数据库驱动类实例的遍历查找。
数据库驱动类已加载,驱动类的实例对象也已经生成了,建立连接的动作是 DriverManager 中的 getConnection 方法,源码如下:
// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
/*
* When callerCl is null, we should check the application's
* (which is invoking this class indirectly)
* classloader, so that the JDBC driver class outside rt.jar
* can be loaded from here.
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
// Walk through the loaded registeredDrivers attempting to make a connection.
// Remember the first exception that gets raised so we can reraise it.
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// If the caller does not have permission to load the driver then
// skip it.
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
// if we got here nobody could connect.
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
println("getConnection: no suitable driver found for "+ url);
throw new SQLException("No suitable driver found for "+ url, "08001");
}getConnection 方法中主要是遍历 registeredDrivers,通过其中注册的 Driver 进行连接建立,而 registeredDrivers 里面的 Driver 是什么时候创建并注册到 registeredDrivers 中的呢?以 mysql 为例,上面也有提到 com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 类的代码如下:
public class Driver extends NonRegisteringDriver implements java.sql.Driver {
public Driver() throws SQLException {
}
static {
try {
DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException var1) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
}static 代码块在 Driver 类加载的初始化阶段会被调用,将自己的实例对象注册到了 registeredDrivers 中,在 JDBC 的 SPI 加载流程中,ServiceLoader 的作用可以简单总结为是数据区驱动类的加载(注册驱动类实例对象到 registeredDrivers)和实例对象的缓存。
总结
SPI 的加载机制是一种接口与实现分离的设计思想,通过简单改变配置(比如:更换数据库驱动类)可以很容易在多个具体的实现之间切换,其中也体现了一种配置大于编码的思想。
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。