本节开始,将对 ResourceManager 中一些常见行为进行分析探究,看某些具体关键的行为,在 RM 中是如何流转的。本节将深入源码探究「启动 ApplicationMaster」的具体流程。
一、整体流程
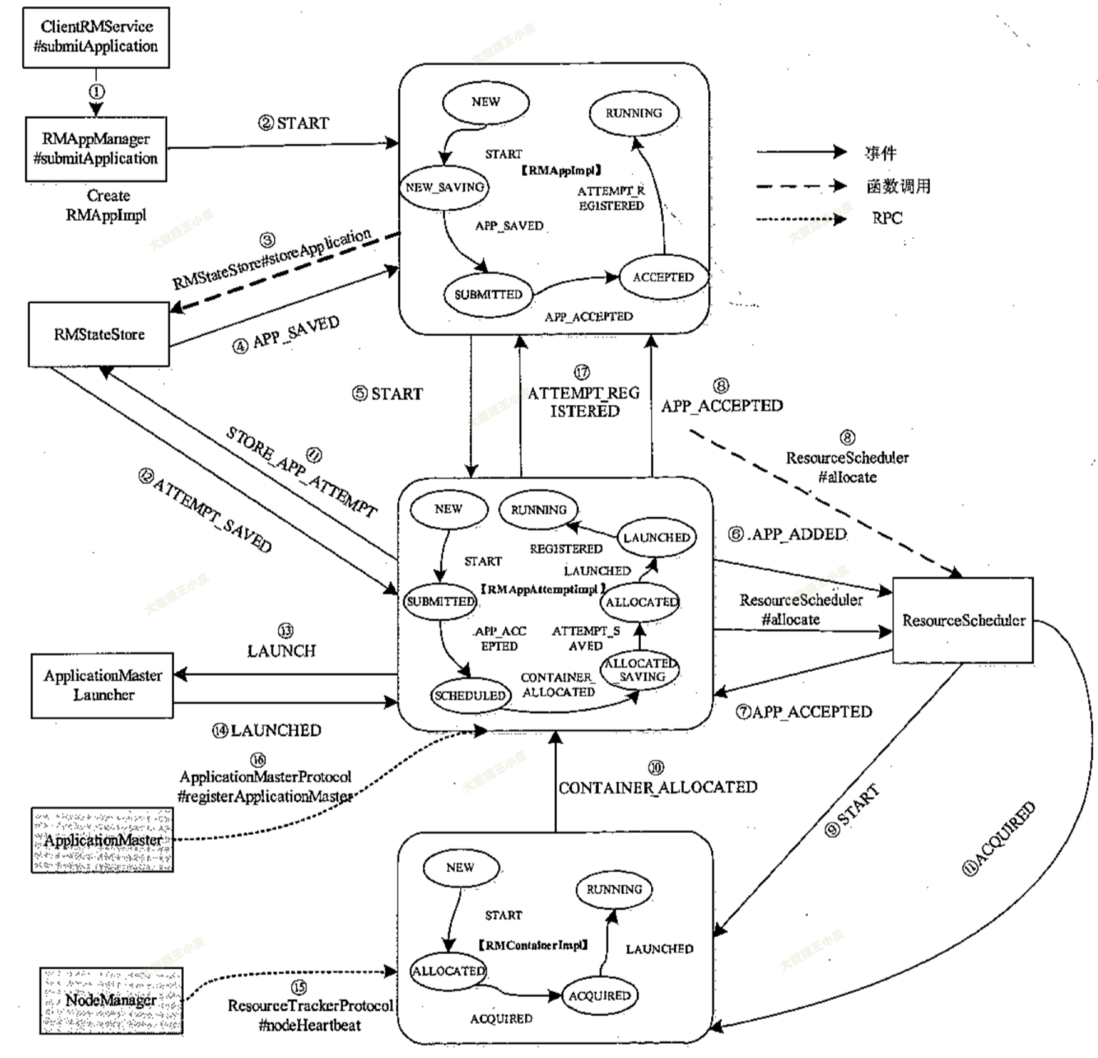
本小节介绍从应用程序提交到启动 ApplicationMaster 的整个过程,期间涉及 Client、RMService、 RMAppManager、RMApplmpl、RMAppAttemptImpl、RMNode、ResourceScheduler 等几个主要组件。当客户端调用 RPC 函数 ApplicationClientProtocol#submitApplication 后, ResourceManager 端的处理过程如下图所示。
二、具体流程分析
接下来跟随上面的流程图,我们深入源码具体分析每一步都是如何执行的:
最开始由客户端发起任务提交 submitApplication(),经过 ClientRMService 和 RMAppManager 发送 RMAppEventType.START 事件,之后交由 RMAppImpl 处理。
protected void submitApplication(
ApplicationSubmissionContext submissionContext, long submitTime,
String user) throws YarnException {
ApplicationId applicationId = submissionContext.getApplicationId();
RMAppImpl application =
createAndPopulateNewRMApp(submissionContext, submitTime, user, false);
Credentials credentials = null;
try {
credentials = parseCredentials(submissionContext);
if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {
this.rmContext.getDelegationTokenRenewer()
.addApplicationAsync(applicationId, credentials,
submissionContext.getCancelTokensWhenComplete(),
application.getUser());
} else {
// Dispatcher is not yet started at this time, so these START events
// enqueued should be guaranteed to be first processed when dispatcher
// gets started.
// 这里发送 RMAppEventType.START 事件
this.rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler()
.handle(new RMAppEvent(applicationId, RMAppEventType.START));
}RMAppImpl 这东西是个状态机,收到事件之后会自己转换状态并且处理相应的逻辑。
(状态机还不熟悉的同学,可翻到我前面的文章进行学习《2-4 Yarn 基础库 - 状态机库》)
截取一部分状态转换代码:
private static final StateMachineFactory<RMAppImpl,
RMAppState,
RMAppEventType,
RMAppEvent> stateMachineFactory
= new StateMachineFactory<RMAppImpl,
RMAppState,
RMAppEventType,
RMAppEvent>(RMAppState.NEW)
// Transitions from NEW state
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW, RMAppState.NEW,
RMAppEventType.NODE_UPDATE, new RMAppNodeUpdateTransition())
// 收到 RMAppEventType.START 事件
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW, RMAppState.NEW_SAVING,
RMAppEventType.START, new RMAppNewlySavingTransition())
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW, EnumSet.of(RMAppState.SUBMITTED,
RMAppState.ACCEPTED, RMAppState.FINISHED, RMAppState.FAILED,
RMAppState.KILLED, RMAppState.FINAL_SAVING),
RMAppEventType.RECOVER, new RMAppRecoveredTransition())
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW, RMAppState.KILLED, RMAppEventType.KILL,
new AppKilledTransition())
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW, RMAppState.FINAL_SAVING,
RMAppEventType.APP_REJECTED,
new FinalSavingTransition(new AppRejectedTransition(),
RMAppState.FAILED))一)RMAppImpl - START
收到 RMAppEventType.START 事件之后,会执行 RMAppNewlySavingTransition()。
private static final class RMAppNewlySavingTransition extends RMAppTransition {
@Override
public void transition(RMAppImpl app, RMAppEvent event) {
// If recovery is enabled then store the application information in a
// non-blocking call so make sure that RM has stored the information
// needed to restart the AM after RM restart without further client
// communication
LOG.info("Storing application with id " + app.applicationId);
app.rmContext.getStateStore().storeNewApplication(app);
}
}跟下去会发现它发出 RMStateStoreEventType.STORE_APP 事件,去 RMStateStore 中找一下对应的事件处理。发现也是个状态机:
.addTransition(RMStateStoreState.ACTIVE,
EnumSet.of(RMStateStoreState.ACTIVE, RMStateStoreState.FENCED),
RMStateStoreEventType.STORE_APP, new StoreAppTransition())跟着 StoreAppTransition 看看做了啥(发送 RMAppEventType.APP_NEW_SAVED 事件)
private static class StoreAppTransition
implements MultipleArcTransition<RMStateStore, RMStateStoreEvent,
RMStateStoreState> {
@Override
public RMStateStoreState transition(RMStateStore store,
RMStateStoreEvent event) {
if (!(event instanceof RMStateStoreAppEvent)) {
// should never happen
LOG.error("Illegal event type: " + event.getClass());
return RMStateStoreState.ACTIVE;
}
boolean isFenced = false;
ApplicationStateData appState =
((RMStateStoreAppEvent) event).getAppState();
ApplicationId appId =
appState.getApplicationSubmissionContext().getApplicationId();
LOG.info("Storing info for app: " + appId);
try {
store.storeApplicationStateInternal(appId, appState);
// 这里发送了 RMAppEventType.APP_NEW_SAVED 事件
store.notifyApplication(new RMAppEvent(appId,
RMAppEventType.APP_NEW_SAVED));
} catch (Exception e) {
LOG.error("Error storing app: " + appId, e);
isFenced = store.notifyStoreOperationFailedInternal(e);
}
return finalState(isFenced);
};
}二)RMAppImpl - APP_NEW_SAVED
我们再回到 RMAppImpl,找到对应的状态转移逻辑。
// 刚刚我们的状态是 NEW_SAVING,收到了 APP_NEW_SAVED 事件,执行 AddApplicationToSchedulerTransition() 后,转换为 SUBMITTED 状态
.addTransition(RMAppState.NEW_SAVING, RMAppState.SUBMITTED,
RMAppEventType.APP_NEW_SAVED, new AddApplicationToSchedulerTransition())在 AddApplicationToSchedulerTransition() 中会发送 SchedulerEventType.APP_ADDED 事件。之后 RMAppImpl 转换为 RMAppState.SUBMITTED 状态。SchedulerEventType.APP_ADDED 会被多个事件处理器捕获处理:
1)ResourceSchedulerWrapper 事件处理器,仅记录
} else if (schedulerEvent.getType() == SchedulerEventType.APP_ADDED
&& schedulerEvent instanceof AppAddedSchedulerEvent) {
AppAddedSchedulerEvent appAddEvent =
(AppAddedSchedulerEvent) schedulerEvent;
String queueName = appAddEvent.getQueue();
appQueueMap.put(appAddEvent.getApplicationId(), queueName);
}2)各个 AbstractYarnScheduler 的实现类。以 CapacityScheduler 为例:
执行 addApplication()
case APP_ADDED:
{
AppAddedSchedulerEvent appAddedEvent = (AppAddedSchedulerEvent) event;
String queueName = resolveReservationQueueName(appAddedEvent.getQueue(),
appAddedEvent.getApplicationId(), appAddedEvent.getReservationID(),
appAddedEvent.getIsAppRecovering());
if (queueName != null) {
if (!appAddedEvent.getIsAppRecovering()) {
addApplication(appAddedEvent.getApplicationId(), queueName,
appAddedEvent.getUser(), appAddedEvent.getApplicatonPriority());
} else {
addApplicationOnRecovery(appAddedEvent.getApplicationId(), queueName,
appAddedEvent.getUser(), appAddedEvent.getApplicatonPriority());
}
}
}在 addApplication() 中会提交 Application 并发送 RMAppEventType.APP_ACCEPTED 事件。
queue.submitApplication(applicationId, user, queueName);
rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler()
.handle(new RMAppEvent(applicationId, RMAppEventType.APP_ACCEPTED));三)RMAppImpl - APP_ACCEPTED(重点)
继续回到 RMAppImpl,执行 StartAppAttemptTransition(),创建 newAttempt,发送事件RMAppAttemptEventType.START
.addTransition(RMAppState.SUBMITTED, RMAppState.ACCEPTED,
RMAppEventType.APP_ACCEPTED, new StartAppAttemptTransition()) private static final class StartAppAttemptTransition extends RMAppTransition {
@Override
public void transition(RMAppImpl app, RMAppEvent event) {
app.createAndStartNewAttempt(false);
};
} private void
createAndStartNewAttempt(boolean transferStateFromPreviousAttempt) {
createNewAttempt();
handler.handle(new RMAppStartAttemptEvent(currentAttempt.getAppAttemptId(),
transferStateFromPreviousAttempt));
}在 RMAppAttemptImpl 中会捕获这个事件,执行 AttemptStartedTransition(),其中会发送 SchedulerEventType.APP_ATTEMPT_ADDED 事件,由 AbstractYarnScheduler 实现类处理
.addTransition(RMAppAttemptState.NEW, RMAppAttemptState.SUBMITTED,
RMAppAttemptEventType.START, new AttemptStartedTransition())如在 CapacityScheduler 中由 addApplicationAttempt 处理,会提交 ApplicationAttempt,并发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_ADDED 事件
private synchronized void addApplicationAttempt() {
// 提交 attempt
queue.submitApplicationAttempt(attempt, application.getUser());
// 发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_ADDED 事件
rmContext.getDispatcher().getEventHandler().handle(
new RMAppAttemptEvent(applicationAttemptId,
RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_ADDED));
}RMAppAttemptImpl 收到 event 后继续处理,在 ScheduleTransition 会 allocate am container 资源。
.addTransition(RMAppAttemptState.SUBMITTED,
EnumSet.of(RMAppAttemptState.LAUNCHED_UNMANAGED_SAVING,
RMAppAttemptState.SCHEDULED),
RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_ADDED,
new ScheduleTransition()) // AM resource has been checked when submission
Allocation amContainerAllocation =
appAttempt.scheduler.allocate(
appAttempt.applicationAttemptId,
Collections.singletonList(appAttempt.amReq),
EMPTY_CONTAINER_RELEASE_LIST,
amBlacklist.getBlacklistAdditions(),
amBlacklist.getBlacklistRemovals(), null, null);ResourceScheduler 将资源返回给它之前,会向 RMContainerlmpl 发送一个 RMContainerEventType.ACQUIRED 事件。
在 RMContainerImpl 接到 RMContainerEventType.START,发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.CONTAINER_ALLOCATED 事件。
.addTransition(RMContainerState.NEW, RMContainerState.ALLOCATED,
RMContainerEventType.START, new ContainerStartedTransition()) private static final class ContainerStartedTransition extends
BaseTransition {
@Override
public void transition(RMContainerImpl container, RMContainerEvent event) {
container.eventHandler.handle(new RMAppAttemptEvent(
container.appAttemptId, RMAppAttemptEventType.CONTAINER_ALLOCATED));
}
}又回到RMAppAttemptImpl 后续状态机,执行 AMContainerAllocatedTransition,在其中又一次为 am allocate,和上一个状态中 allocate 仅参数不同,没搞懂为啥。这里如果发现 allocate container 资源还是 0,会退回上一步,状态还是 RMAppAttemptState.SCHEDULED 等待再次获取资源。如果正常获取到了资源,就会转为 RMAppAttemptState.ALLOCATED_SAVING 状态。
.addTransition(RMAppAttemptState.SCHEDULED,
EnumSet.of(RMAppAttemptState.ALLOCATED_SAVING,
RMAppAttemptState.SCHEDULED),
RMAppAttemptEventType.CONTAINER_ALLOCATED,
new AMContainerAllocatedTransition()) Allocation amContainerAllocation =
appAttempt.scheduler.allocate(appAttempt.applicationAttemptId,
EMPTY_CONTAINER_REQUEST_LIST, EMPTY_CONTAINER_RELEASE_LIST, null,
null, null, null);日志记录完成后,RMStateStore 向 RMAppAttemptImpl 发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_NEW_SAVED 事件。RMAppAttemptImpl 后续向 ApplicationMasterLauncher 发 送 AMLauncherEventType.LAUNCH 事件(实际执行是在 AMLauncher 中),并将状态从 ALLOCATED_SAVING 转移为 ALLOCATED。
.addTransition(RMAppAttemptState.ALLOCATED_SAVING,
RMAppAttemptState.ALLOCATED,
RMAppAttemptEventType.ATTEMPT_NEW_SAVED, new AttemptStoredTransition())ApplicationMasterLauncher 收到 AMLauncherEventType.LAUNCH 事件后,会将该事件放到事件队列中,等待 AMLauncher 线程池中的线程处理该事件。它将与对应的 NodeManager 通信,启动 ApplicationMaster,一旦成功启动后,将向 RMAppAttemptImpl 发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.LAUNCHED 事件。
public void run() {
switch (eventType) {
case LAUNCH:
try {
LOG.info("Launching master" + application.getAppAttemptId());
launch();
handler.handle(new RMAppAttemptEvent(application.getAppAttemptId(),
RMAppAttemptEventType.LAUNCHED));RMAppAttemptImpl 收到 RMAppAttemptEventType.LAUNCHED 事件后,会向 AMLivelinessMonitor 注册,以监控运行状态。RMAppAttemptImpl 状态从 ALLOCATED 转移为 LAUNCHED。
之后,NodeManager 通过心跳机制汇报 ApplicationMaster 所在 Container 已经成功启动,收到该信息后,ResourceScheduler 将发送一个 RMContainerEventType.LAUNCHED 事件,RMContainerImpl 收到该事件后,会从 ContainerAllocationExpirer 监控列表中移除。
启动的 ApplicationMaster 通过RPC 函数 ApplicationMasterProtocol#registerApplicationMaster 向 ResourceManager 注册,ResourceManager 中的 ApplicationMasterService 服务接收到该请求后,发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.REGISTERED 事件。
// ApplicationMasterService#registerApplicationMaster
LOG.info("AM registration " + applicationAttemptId);
this.rmContext
.getDispatcher()
.getEventHandler()
.handle(
// 这里发送 RMAppAttemptEventType.REGISTERED 事件
new RMAppAttemptRegistrationEvent(applicationAttemptId, request
.getHost(), request.getRpcPort(), request.getTrackingUrl()));RMAppAttemptImpl 收到该事件后,首先保存该 ApplicationMaster 的基本信息(比如所在 host、启用的 RPC 端口号等),然后向 RMApplmpl 发送一个 RMAppEventType.ATTEMPT_REGISTERED 事件。RMAppAttemptImpl 状态从 LAUNCHED 转移为 RUNNING。
.addTransition(RMAppAttemptState.LAUNCHED, RMAppAttemptState.RUNNING,
RMAppAttemptEventType.REGISTERED, REGISTERED_TRANSITION)// AMRegisteredTransition
appAttempt.eventHandler.handle(new RMAppEvent(appAttempt
.getAppAttemptId().getApplicationId(),
RMAppEventType.ATTEMPT_REGISTERED));四)RMAppImpl - ATTEMPT_REGISTERED
RMAppImpl 收到 RMAppEventType.ATTEMPT_REGISTERED 事件后,将状态从 ACCEPTED 转换为 RUNNING。
.addTransition(RMAppState.ACCEPTED, RMAppState.RUNNING,
RMAppEventType.ATTEMPT_REGISTERED, new RMAppStateUpdateTransition(
YarnApplicationState.RUNNING))到这里,启动 ApplicationMaster 的整体流程分析完毕!
三、总结
本篇文章分析了从应用程序提交到启动 ApplicationMaster 的整个过程,分析具体过程看的可能会有些繁琐。但只要抓住核心本质,就很容易捋清楚。重点就是事件处理和状态机,这两个部件理解清楚,就很容易看明白程序的流转。
实际逻辑无非就是几个服务之间互相发送对应的事件,接收到事件后会执行启动服务、记录日志、监控状态,然后再发送个新的事件。
本身不难,但需要耐下心来一点点去梳理。

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。