原文参考我的公众号文章 threejs平滑路线规划
Astar寻路算法配合THREE.CatmullRomCurve3生成平滑的三维样条曲线,超有意思👍
一开始学threejs时,角色移动都是通过一个点直线移动到另一个点,但是现在情况不一样了,若将地图网格化处理后,利用以上技术点,将玩家移动的路线从「直来直往」进化到「平滑过渡」不是梦😄
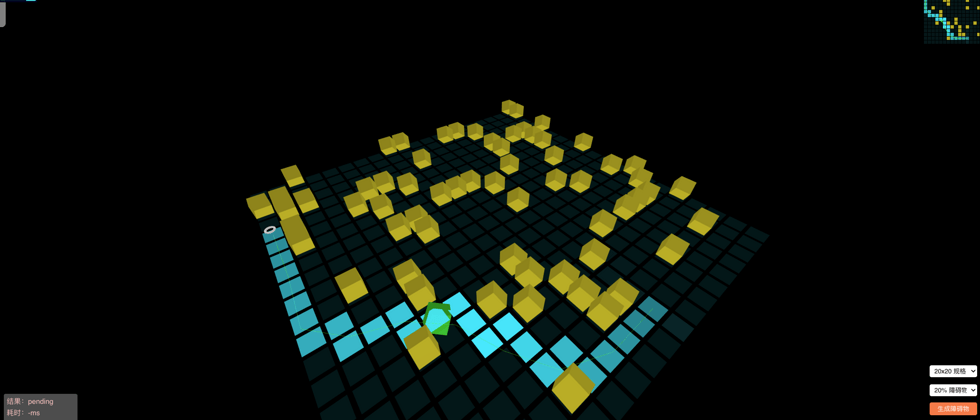
效果图
- 无平滑路径处理
- 有平滑路径处理
体验 DEMO
Astar 算法
创建地图:二维数组,设置哪些点位是障碍物,哪些是自由移动区域。grid 和 map 每一项互为映射
比如生成一个如下地图:
// 地图网格化坐标数组
let grid = [
[
{ x, y, z }, //网格内某个Mesh的坐标
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
],
[
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
],
[
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
],
[
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
],
[
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
{ x, y, z },
],
];
// 抽象地图覆盖物数组
let map = [
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 0, 1],
]; // 0表示对应项上的Mesh是障碍物-不可通过,1表示对应项上的Mesh是自由区域-可通过创建 Graph:将 map 二维数组转成 Astar 可识别的图 Graph
let graph = new Graph(map);
console.log("graph:", graph); //{ diagonal, dirtyNodes, grid, nodes }路径搜索:提供 start、end 点和 graph,利用 Astar 的 search 方法搜索可移动路径。
let start = graph.grid[0][0];
let end = graph.grid[4][2];
let sTime = +new Date();
// 搜索结果
let result = astar.search(graph, start, end);
let eTime = +new Date();
let spendTime = eTime - sTime; //耗时N毫秒
if (!result.length) {
console.log("未找到可以到达的路径");
return;
} else {
console.log("找到可以到达的路径");
}THREE.CatmullRomCurve3
生成路径曲线:根据提供的 Astar 算法搜索结果,提取关键路径点(必要),得到一条平滑过渡的曲线。
/** 1.提取关键节点 */
// 生成路径动画
let path = []; //关键路径节点
// 这里定义gap去稀释result,让运动路线以合适数量的点生成,然后利用CatmullRomCurve3自动过渡形成圆滑的曲线。
let gap = result.length > 6 ? 3 : result.length > 4 ? 2 : 1;
result.map((item, index) => {
const { x, y, z } = item;
let pos = grid[x][y];
if (index % gap == 0 || index == result.length - 1) {
path.push(new THREE.Vector3(pos.x, pos.y, pos.z));
}
});
console.log("path:", path);
/**2.生成平滑路线 */
let divisions = 30; //分段数量
let curve = new THREE.CatmullRomCurve3(path, false); //得到平滑曲线curve对象
let curveLength = curve.getLength(); //曲线长度
// 路线线条
const points = curve.getPoints(divisions);
const geometry = new THREE.BufferGeometry().setFromPoints(points);
const material = new THREE.LineBasicMaterial({ color: 0xff0000 });
let curveMesh = new THREE.Line(geometry, material);
scene.add(curveMesh);物体移动:让物体沿着曲线移动
const moveSpeed = 0.01; //移动速度
const lerpSpeed = 0.001; //转弯细腻程度
let distance = 0; //已移动距离
let curveLength = curve.getLength(); //曲线长度
let moveMeshPosition: new THREE.Vector3(); //物体当前帧率在curve曲线上所处的位置
let moveMeshTarget: new THREE.Vector3(); //物体下一帧在curve曲线上要移动到的位置
let moveMesh = new THREE.Mesh(
new THREE.BoxBufferGeometry(0.3, 0.3, 0.5),
new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0xffdd00 })
); //移动物体
scene.add(moveMesh);
function update() {
distance += moveSpeed; //累加移动的距离
let percent = distance / curveLength; // 当前位置占弧长的百分比,也就是在弧长上的位置
// 路径走完
if (percent >= 1) {
distance = curveLength;
console.log("抵达目的地");
// 移除该路线
scene.remove(curveMesh);
// 移除该物体
scene.remove(moveMesh);
return;
}
// 继续移动
item.distance = distance;
//目标点到目标的距离
const targetOffset = lerpSpeed; // !!!这个值越小,运动轨迹就越圆滑
//从曲线上获取物体的点位。.getPointAt ( u : Float, optionalTarget : Vector ) : Vector,u - 根据弧长在曲线上的位置。必须在范围[0,1]内。
curve.getPointAt(percent % 1, moveMeshPosition);
//从曲线上获取物体的目标点位
curve.getPointAt((percent + targetOffset) % 1, moveMeshTarget);
//物体的定位(现在在哪儿)
moveMesh.position.copy(moveMeshPosition);
//实现软旋转(现在看哪儿)
moveMesh.lookAt(moveMeshTarget);
// or 圆滑位置
//moveMesh.position.lerpVectors(moveMeshPosition, moveMeshTarget, 0.5);
}以上就是实现大致的思路了~


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。