Java的线程和线程池的理解
一:概念
在Java中,使用线程来异步执行任务。Java的线程既是工作单元,也是执行机制。从JDK 5开始,把工作单元与执行机制分离开来。工作单元包括Runnable和Callable,而执行机制由Executor框架提供。
二:什么是Executor框架?
我们知道线程池就是线程的集合,线程池集中管理线程,以实现线程的重用,降低资源消耗,提高响应速度等。线程用于执行异步任务,单个的线程既是工作单元也是执行机制,从JDK1.5开始,为了把工作单元与执行机制分离开,Executor框架诞生了,他是一个用于统一创建与运行的接口。Executor框架实现的就是线程池的功能
三:Executor的结构
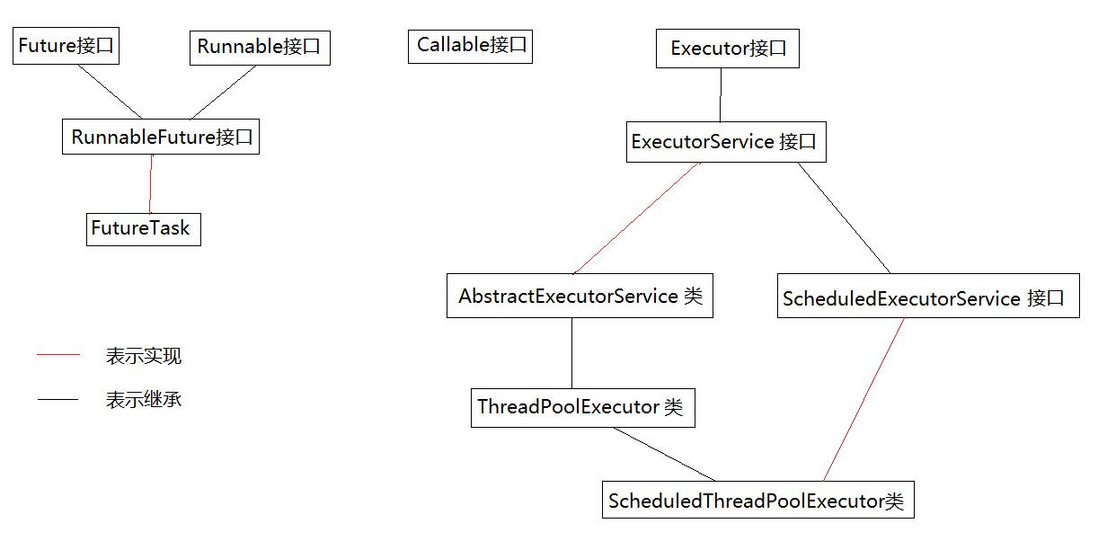
Executor框架主要由3大部分组成如下。
1.任务:包括被执行任务需要实现的接口:Runnable接口或Callable接口。
2.任务的执行:包括任务执行机制的核心接口Executor,以及继承自Executor的ExecutorService接口。Executor框架有两个关键类实现了ExecutorService接口(ThreadPoolExecutor和ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor)。
3.异步计算的结果:包括接口Future和实现Future接口的FutureTask类。
Executor框架包含的主要的类与接口如下图所示
四:对框架的理解
Executor是一个接口,它是Executor框架的基础,它将任务的提交与任务的执行分离开来
//我理解的这是一个定义线程一个行为,任务执行,具体交由其实现完成
public interface Executor {
void execute(Runnable command);
}ExecutorService 也是一个接口 继承Executor接口 扩展Executor
public interface ExecutorService extends Executor {
//停止接收新任务,原来的任务继续执行
void shutdown();
//停止接收新任务,原来的任务停止执行
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
//接收的参数不一样 submit()可以接受runnable无返回值和callable有返回值
execute()接受runnable 无返回值
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
}
AbstractExecutorService 是一个抽象类 实现ExecutorService接口扩展功能
ScheduledExecutorService(延迟的线程池服务)是一个接口 继承ExecutorService接口扩展功能
线程池核心类:
ThreadPoolExecutor 继承AbstractExecutorService 的线程池类
public class ThreadPoolExecutor extends AbstractExecutorService {
//构造方法
//corePoolSize 核心线程 指定了线程池中的线程数量,它的数量决定了添加的任务是开辟新的线程去执行,还是放到workQueue任务队列中去;
//maximumPoolSize 指定了线程池中的最大线程数量,这个参数会根据你使用的workQueue任务队列的类型,决定线程池会开辟的最大线程数量;
//keepAliveTime 当线程池中空闲线程数量超过corePoolSize时,多余的线程会在多长时间内被销毁;(空闲线程包活时间)
//unit:keepAliveTime的单位
//workQueue:任务队列,被添加到线程池中,但尚未被执行的任务;它一般分为直接提交队列、有界任务队列、无界任务队列、优先任务队列几种;(阻塞队列长度设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE)
//threadFactory:线程工厂,用于创建线程,一般用默认即可;
//handler:拒绝策略;当任务太多来不及处理时,如何拒绝任务;
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), handler);
}
}
//例如线程池核心线程数为1,最大线程数为10,任务队列容量(阻塞队列)queueCapacity也就是BlockingQueue任务10个
默认线程池的数量为1,当任务不超过10个,会在任务队列排队等待线程池里一个线程处理
当任务>10个,会创建一个新的线程处理
当线程数达到最大线程数的时候 RejectedExecutionHandler(任务拒绝处理器) 拒绝策略
RejectedExecutionHandler(拒绝策略) 接口有下面几个实现类 如果没有设置,默认是AbortPolicy,会抛出异常。
AbortPolicy:丢弃任务,抛运行时异常
CallerRunsPolicy:执行任务
DiscardOldestPolicy:从队列中踢出最先进入队列(最后一个执行)的任务
DiscardPolicy: 忽视,什么都不会发生
五:线程池的具体实现类
举例:Glide的线程池实现类FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor 先进先出的策略线程池
//先进先出的线程池策略的核心线程和最大线程的数量的是一样的
public class FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
public FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAlive, TimeUnit timeUnit,
ThreadFactory threadFactory, UncaughtThrowableStrategy uncaughtThrowableStrategy) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAlive, timeUnit, new PriorityBlockingQueue<Runnable>(), threadFactory);
this.uncaughtThrowableStrategy = uncaughtThrowableStrategy;
}
}FifoPriorityThreadPoolExecutor 的对象有sourceService 和diskCacheService 2个。
和diskCacheService 的核心线程和最大线程数为1个
Glide 里面的会组装成Engine 负责EngineJob任务管理
if (engine == null) {
engine = new Engine(memoryCache, diskCacheFactory, diskCacheService, sourceService);
}再由Engine 组装成Glide
return new Glide(engine, memoryCache, bitmapPool, context, decodeFormat);六:线程池的分类
在Executors工厂类中提供了多种线程池,典型的有以下四种
- SingleThreadExecutor 单线程线程池
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
//测试创建线程
public static void singleThreadPool(){
ExecutorService aa= Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// 创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
aa.execute(runnable);
}核心线程数为1,最大线程数为1,也就是说SingleThreadExecutor这个线程池中的线程数固定为1。使用场景:当多个任务都需要访问同一个资源的时候
- FixedThreadPool 固定容量线程池
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
//栗子:创建线程,固定的线程池
public static void fixedThreadPool(){
ExecutorService aa= newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
aa.execute(runnable);
}核心线程数为n,最大线程数为n。使用场景:明确同时执行任务数量时。
- CachedThreadPool 缓存线程池
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
//栗子:缓存线程池
public static void cachedThreadPool(){
ExecutorService aa= Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
aa.execute(runnable);
}核心线程数为0,最大线程数无上限,线程超时时间60秒。使用场景:处理大量耗时较短的任务。
- ScheduledThreadPool 定时线程池
public static ScheduledExecutorService newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) {
return new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
DEFAULT_KEEPALIVE_MILLIS, MILLISECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
//栗子:定时任务的创建线程池
public static void scheduledThreadPool(){
ExecutorService aa= Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
// 创建任务
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("任务被执行,线程:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
};
aa.execute(runnable);
}核心线程数自定,最大线程数无上限。使用场景:处理延时任务

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。