本文基于
vue-router 4.1.6版本源码进行分析本文重点分析
Vue Router的WebHashHistory模式,不会对WebHistory和MemoryHistory模式过多分析
文章内容
从Vue Router的初始化代码入手,逐步分析对应的代码流程和涉及到的操作方法(push、replace、pop)
本文将着重于:
Vue Router是如何利用routes数组建立路由映射,路由权重是如何初始化Vue Router的push、replace、pop流程具体执行了什么?是如何找到对应的路由数据Vue Router提供的RouterView和RouterLink源码分析Vue Router提供的多个组合式API的源码分析,包括onBeforeRouteLeave、onBeforeRouteLeave、useRouter、useRoute、useLinkVue Router源码注释中涉及到的issues的问题讲解和对应的修复代码分析
本文的最后将基于多个问题进行Vue Router源码的系统性总结
前置知识
Vue Router介绍
摘录于Vue Router官方文档
Vue Router 是 Vue.js 的官方路由。它与 Vue.js 核心深度集成,让用 Vue.js 构建单页应用变得轻而易举。功能包括:
- 嵌套路由映射
- 动态路由选择
- 模块化、基于组件的路由配置
- 路由参数、查询、通配符
- 展示由 Vue.js 的过渡系统提供的过渡效果
- 细致的导航控制
- 自动激活 CSS 类的链接
- HTML5 history 模式或 hash 模式
- 可定制的滚动行为
- URL 的正确编码
window.location属性
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| href | https://test.example.com:8090/vue/router#test?search=1 |
| protocol | https: |
| host/hostname | test.example.com |
| port | 8090 |
| pathname | /vue/router |
| search | ?search=1 |
| hash | #test |
<base>:文档根 URL 元素
摘录于https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/base
- HTML
<base>元素 指定用于一个文档中包含的所有相对 URL 的根 URL - 只能有一个
<base>元素 - 一个文档的基本 URL,可以通过使用 document.baseURI(en-US) 的 JS 脚本查询,如果文档不包含
<base>元素,baseURI默认为document.location.href
前置问题
- 外部定义的路由,是如何在
Vue Router内部建立联系的 Vue Router是如何实现push、replace、pop操作的Vue Router是如何命中多层嵌套路由,比如/parent/child/child1需要加载多个组件,是如何实现的Vue Router有什么导航?触发的流程是怎样的Vue Router的导航守卫是如何做到链式调用的Vue Router的beforeRouteEnter和beforeRouteUpdate的触发时机Vue Router中route和router的区别hash模式跟h5 history模式在Vue Router中有什么区别Vue Router的hash模式重定向后还会保留浏览记录吗?比如重定向后再使用router.go(-1)会返回重定向之前的页面吗Vue Router的hash模式什么地方最容易导致路由切换失败
上面所有问题将在第二篇文章Vue3相关源码-Vue Router源码解析(二)中进行解答
示例代码
代码来自于Vue Router官方文档
// 1. 定义路由组件.
// 也可以从其他文件导入
const Home = { template: '<div>Home</div>' }
const About = { template: '<div>About</div>' }
// 2. 定义一些路由
// 每个路由都需要映射到一个组件。
// 我们后面再讨论嵌套路由。
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
]
// 3. 创建路由实例并传递 `routes` 配置
// 你可以在这里输入更多的配置,但我们在这里
// 暂时保持简单
const router = VueRouter.createRouter({
// 4. 内部提供了 history 模式的实现。为了简单起见,我们在这里使用 hash 模式。
history: VueRouter.createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // `routes: routes` 的缩写
})
// 5. 创建并挂载根实例
const app = Vue.createApp({})
//确保 _use_ 路由实例使
//整个应用支持路由。
app.use(router)
app.mount('#app')分析的核心示例代码
const router = VueRouter.createRouter({
history: VueRouter.createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
const app = Vue.createApp({})
app.use(router)下面将按照创建history、初始化router、Vue使用router的顺序进行源码分析
createWebHashHistory创建history
hash模式是用createWebHashHistory() 创建的历史记录模式
从下面代码可以知道,处理了base数据:如果没有传入url,则拼接location.pathname + location.search,然后加上#
最后还是调用了createWebHistory(base)的方法进行history的创建
function createWebHashHistory(base) {
// Make sure this implementation is fine in terms of encoding, specially for IE11
// for `file://`, directly use the pathname and ignore the base
// href="https://example.com"的location.pathname也是"/"
base = location.host ? (base || location.pathname + location.search) : '';
// allow the user to provide a `#` in the middle: `/base/#/app`
if (!base.includes('#'))
base += '#';
return createWebHistory(base);
}直接看上面的代码会有点懵,直接看官方文档会比较好理解点,下面内容参考自https://router.vuejs.org/zh/api/#createwebhashhistory,是createWebHashHistory(base)的参数说明| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| base | string | 提供可选的 base。默认是 location.pathname + location.search。如果 head 中有一个 <base>,它的值将被忽略,而采用这个参数。但请注意它会影响所有的 history.pushState() 调用,这意味着如果你使用一个 <base> 标签,它的 href 值必须与这个参数相匹配 (请忽略 # 后面的所有内容) |
// at https://example.com/folder
createWebHashHistory() // 给出的网址为 `https://example.com/folder#`
createWebHashHistory('/folder/') // 给出的网址为 `https://example.com/folder/#`
// 如果在 base 中提供了 `#`,则它不会被 `createWebHashHistory` 添加
createWebHashHistory('/folder/#/app/') // 给出的网址为 `https://example.com/folder/#/app/`
// 你应该避免这样做,因为它会更改原始 url 并打断正在复制的 url
createWebHashHistory('/other-folder/') // 给出的网址为 `https://example.com/other-folder/#`
// at file:///usr/etc/folder/index.html
// 对于没有 `host` 的位置,base被忽略
createWebHashHistory('/iAmIgnored') // 给出的网址为 `file:///usr/etc/folder/index.html#`从上面例子可以看出,如果传入base字符串,会以传入base优先级最高去拼接,然后才是location.pathname + location.search
同时会检测传入base是否含有"#",如果没有,则在后面添加"#"
当然,也会存在传入base跟location.pathname不一样的情况,如上面例子/other-folder/所示,会直接更改网址去除location.pathname,改为base
createWebHistory创建history
整体概述
routerHistory对标的是原生的history对象,routerHistory在原生的history对象的API基础上,增添了一些逻辑处理,实现Vue的路由切换、路由映射组件、组件切换的功能
function createWebHistory(base) {
// 步骤1: normalizeBase整理url
base = normalizeBase(base);
// 步骤2: useHistoryStateNavigation
const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation(base);
// 步骤3: useHistoryListeners
const historyListeners = useHistoryListeners(base,
historyNavigation.state, historyNavigation.location, historyNavigation.replace);
// 步骤4: 合并historyNavigation和historyListeners,整合为routerHistory
const routerHistory = assign({
// it's overridden right after
location: '',
base,
go,
createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),
}, historyNavigation, historyListeners);
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
enumerable: true,
get: () => historyNavigation.location.value,
});
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {
enumerable: true,
get: () => historyNavigation.state.value,
});
return routerHistory;
}
function go(delta, triggerListeners = true) {
if (!triggerListeners)
historyListeners.pauseListeners();
history.go(delta);
}步骤1: normalizeBase
从上面分析可以知道,如果有传入base 或者 本身存在location.pathname,那么到达normalizeBase(base)的base就不可能为空
但是也有可能存在
- 没有传入
base+本身不存在location.pathname - 没有传入
base+本身不存在location.host(file://xxx)
当没有base时,我们就会检测是否具有<base>标签,<base>标签的含义可以参考https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTML/Element/base,如果没有<base>标签,则使用location.href作为基础的链接,如果有<base>标签,则使用该标签作为基础链接
For example, given <base href="https://example.com/"> and this link: #anchor">To anchor. The link points tohttps://example.com/#anchor
然后替换域名部分的字符串,最终返回base="/xxxx"或者"#xxxxx"
function normalizeBase(base) {
if (!base) {
if (isBrowser) {
// respect <base> tag
const baseEl = document.querySelector('base');
base = (baseEl && baseEl.getAttribute('href')) || '/';
// 剔除https://xx.xxxx.com这部分的字母
base = base.replace(/^\w+:\/\/[^\/]+/, '');
} else {
base = '/';
}
}
if (base[0] !== '/' && base[0] !== '#')
base = '/' + base;
// 删除尾部的斜杠
return removeTrailingSlash(base);
}
const TRAILING_SLASH_RE = /\/$/;
const removeTrailingSlash = (path) => path.replace(TRAILING_SLASH_RE, '');一般情况下,经过normalizeBase()得到的base的结构为location.pathname+location.search+"#",具体结构如下面所示:
下面链接为测试链接,仅仅表示不考虑特殊情况下的base结构,没有其它含义base = "/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#"步骤2: useHistoryStateNavigation
整体概述
该方法初始化的historyNavigation包含了当前的路由、当前的堆栈信息以及对应的push加操作和replace覆盖操作,同时检测history.state是否为空,如果为空,需要压入一个初始化的currentLocation
除了push、replace等常规操作,我们知道一个路由还需要具备路由后退的监听,Vue Router将后退操作的监听放在下一节要分析的useHistoryListeners中
// const historyNavigation = useHistoryStateNavigation(base);
function useHistoryStateNavigation(base) {
const { history, location } = window;
// currentLocation.value=除去"#"后的字符串
const currentLocation = {
value: createCurrentLocation(base, location),
};
const historyState = { value: history.state };
// build current history entry as this is a fresh navigation
if (!historyState.value) {
changeLocation(currentLocation.value, {
back: null,
current: currentLocation.value,
forward: null,
// the length is off by one, we need to decrease it
position: history.length - 1,
replaced: true,
// don't add a scroll as the user may have an anchor, and we want
// scrollBehavior to be triggered without a saved position
scroll: null,
}, true);
}
function changeLocation(to, state, replace) {...}
function replace(to, data) {...}
function push(to, data) {...}
return {
location: currentLocation,
state: historyState,
push,
replace,
};
}createCurrentLocation()
从 window.location对象中创建一个规范化的数据作为当前的路径,可以简单认为最后得到的路径就是上面注册的routes中的其中一个路由路径
具体逻辑分析请看下面的例子分析
function createCurrentLocation(base, location) {
const { pathname, search, hash } = location;
// allows hash bases like #, /#, #/, #!, #!/, /#!/, or even /folder#end
const hashPos = base.indexOf('#');
if (hashPos > -1) {
let slicePos = hash.includes(base.slice(hashPos))
? base.slice(hashPos).length
: 1;
let pathFromHash = hash.slice(slicePos);
// prepend the starting slash to hash so the url starts with /#
if (pathFromHash[0] !== '/')
pathFromHash = '/' + pathFromHash;
return stripBase(pathFromHash, '');
}
const path = stripBase(pathname, base);
return path + search + hash;
}
function stripBase(pathname, base) {
// no base or base is not found at the beginning
if (!base || !pathname.toLowerCase().startsWith(base.toLowerCase()))
return pathname;
return pathname.slice(base.length) || '/';
}延续上面例子所用的文件路径,我们可以知道:
location.href = "http://localhost:63342/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#/about";
base = "/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#";
location.hash = "#/about";
location.pathname = "/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html";经过hash.slice(slicePos)得到的pathFromHash为
pathFromHash = "/about"最终经过stripBase(pathFromHash, ''),直接返回pathFromHash = "/about"
!!!!上面的举例是比较正常一点的路径,但是现实中肯定会存在各种各样的路径=_=后面遇到奇怪的路径再回来补充例子,暂时跳过这部分规范化路径逻辑的思考
最终得到目前的路由路径为
const currentLocation = {
value: "/about"
};changeLocation()
function changeLocation(to, state, replace) {
const hashIndex = base.indexOf('#');
const url = hashIndex > -1
? (location.host && document.querySelector('base')
? base
: base.slice(hashIndex)) + to
: createBaseLocation() + base + to;
try {
// BROWSER QUIRK
// NOTE: Safari throws a SecurityError when calling this function 100 times in 30 seconds
history[replace ? 'replaceState' : 'pushState'](state, '', url);
historyState.value = state;
} catch (err) {
// Force the navigation, this also resets the call count
location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url);
}
}传入要跳转的路径to,然后拼接要跳转的路径url
在上面的例子中,我们知道
base = "/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#";
url = base.slice(hashIndex)) + to = "#/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#/about"changeLocation()本质就是拼接了跳转路径,然后
- 调用浏览器原生API提供的
window.history.pushState/window.history.replaceState方法 - 更新
historyState.value
一开始调用changeLocation()传入的state数据如下所示
{
back: null,
current: currentLocation.value,
forward: null,
// the length is off by one, we need to decrease it
position: history.length - 1,
replaced: true,
// don't add a scroll as the user may have an anchor, and we want
// scrollBehavior to be triggered without a saved position
scroll: null,
}changeLocation()的过程中如果发生错误,则强制跳转,调用原生的window.location.assign(url):使窗口加载并显示指定url处的document
导航发生后,用户可以通过按“后退”按钮导航回到
location.assign替换的页面,即这个方法会产生浏览器历史记录,不是直接覆盖当前页面
window.location.assign可以参考文档assign,跟window.location.replace不同点在于,replace不会保留目前要替换的页面记录
push()
代码逻辑也比较清晰和简单,主要分为5个步骤
- 使用
forward: to记录要跳转的路由,并且放入currentState中 - 使用
changeLocation()进行history.replaceState()替换当前的浏览记录 - 使用
buildState()构建出新的路由对象,形成新的路由state - 使用
changeLocation()进行history.pushState()新增一条新的浏览记录 - 更新多个方法都使用的变量
currentLocation为当前的新的路由地址currentLocation.value=to
function push(to, data) {
const currentState = assign({},
// use current history state to gracefully handle a wrong call to
// history.replaceState
// https://github.com/vuejs/router/issues/366
historyState.value, history.state, {
forward: to,
scroll: computeScrollPosition(),
});
if (!history.state) {
// 如果当前没有history.state,报错提示:
// 如果您手动调用 history.replaceState,请确保保留现有的历史状态
}
changeLocation(currentState.current, currentState, true);
const state = assign({}, buildState(currentLocation.value, to, null), { position: currentState.position + 1 }, data);
changeLocation(to, state, false);
currentLocation.value = to;
}
function buildState(back, current, forward, replaced = false, computeScroll = false) {
return {
back,
current,
forward,
replaced,
position: window.history.length,
scroll: computeScroll ? computeScrollPosition() : null,
};
}replace()
构建出新的路由对象,形成新的路由state,然后使用changeLocation()进行history.replaceState()替换当前的浏览记录
在changeLocation()中也进行historyState.value=state
更新多个方法都使用的变量currentLocation为当前的新的路由地址currentLocation.value=to
function replace(to, data) {
const state = assign({}, history.state, buildState(historyState.value.back,
// keep back and forward entries but override current position
to, historyState.value.forward, true), data, { position: historyState.value.position });
changeLocation(to, state, true);
currentLocation.value = to;
}小结
从上面的代码可以知道,historyNavigation最终是一个对象,具有location、state、push、replace属性,其中
location:代表除去"#"之后的路径内容,管理当前页面的路径数据,比如location="/about"state:保存原生的window.history.state数据,比如下面的histroyState就是代表window.history.state数据// history.state格式如下 const histroyState = { back: null, current: "/Frontend-Articles/vue3-debugger/router/vue-router.html?_ijt=q70k46ba94eddqp8fu39ta28fh&_ij_reload#/about", forward: null, position: 14, replaced: true, scroll: null } const state = { value: histroyState };push():新增路由时调用的方法replace():替换路由时调用的方法
步骤3: useHistoryListeners
整体概述
传入初始化路径以及historyNavigation维护的状态和方法,进行historyListeners的初始化
const historyListeners = useHistoryListeners(base,
historyNavigation.state, historyNavigation.location, historyNavigation.replace);function useHistoryListeners(base, historyState, currentLocation, replace) {
let listeners = [];
let teardowns = [];
let pauseState = null;
const popStateHandler = ({ state, }) => {...};
function pauseListeners() {...}
function listen(callback) {...}
function beforeUnloadListener() {...}
function destroy() {...}
// set up the listeners and prepare teardown callbacks
window.addEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler);
window.addEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener);
return {
pauseListeners,
listen,
destroy,
};
}popStateHandler()
监听后退事件,这个监听方法比较复杂并且非常重要!
简单示例
window.addEventListener("popstate", (event) => {
console.log(
`location: ${document.location}, state: ${JSON.stringify(event.state)}`
);
});
history.pushState({ page: 1 }, "title 1", "?page=1");
history.pushState({ page: 2 }, "title 2", "?page=2");
history.replaceState({ page: 3 }, "title 3", "?page=3");
history.back(); // Logs "location: http://example.com/example.html?page=1, state: {"page":1}"
history.back(); // Logs "location: http://example.com/example.html, state: null"
history.go(2); // Logs "location: http://example.com/example.html?page=3, state: {"page":3}"触发时机
history.pushState()或者history.replaceState()不会触发popStateHandler()- 用户手动点击浏览器的后退按钮、
history.back()、history.forward()都会触发popStateHandler() history.go(数字)本质就是history.back()/history.forward()调用1次或者多次,也会触发popStateHandler()
触发时携带的参数state
摘录于https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/popstate_event#the_history_stack
如果被激活的历史条目是通过调用 history.pushState() 创建的,或者受到调用 history.replaceState() 的影响,则 popstate 事件的状态属性包含历史条目状态对象的副本
换句话说,popStateHandler({state})中state不为空的前提是我们一直都有使用pushState/replaceState
源码分析
从上面的简单示例可以知道,携带的参数state是后退后当前的路由参数,如果存在,直接把它当作目前最新的historyState.value=state,然后根据后退前缓存的数据fromState计算出对应的delta,最终调用listeners进行监听方法的触发
const popStateHandler = ({ state, }) => {
const to = createCurrentLocation(base, location);
const from = currentLocation.value;
const fromState = historyState.value;
let delta = 0;
if (state) {
currentLocation.value = to;
historyState.value = state;
// ignore the popstate and reset the pauseState
if (pauseState && pauseState === from) {
pauseState = null;
return;
}
delta = fromState ? state.position - fromState.position : 0;
} else {
replace(to);
}
listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener(currentLocation.value, from, {
delta,
type: NavigationType.pop,
direction: delta
? delta > 0
? NavigationDirection.forward
: NavigationDirection.back
: NavigationDirection.unknown,
});
});
};
window.addEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler);如果没有携带参数state,我们就无法知道目前的状态,因此会直接使用const to = createCurrentLocation(base, location)构建出新的路由对象,形成新的路由state,然后使用changeLocation()进行history.replaceState()替换当前的浏览记录
没有携带参数state时,listeners进行监听方法触发的状态为NavigationDirection.unknown
function replace(to, data) {
const state = assign({}, history.state, buildState(historyState.value.back,
// keep back and forward entries but override current position
to, historyState.value.forward, true), data, { position: historyState.value.position });
changeLocation(to, state, true);
currentLocation.value = to;
}listen() and pauseListeners()
提供给外部注册监听的方法,并且返回停止该监听的方法teardown
function listen(callback) {
// set up the listener and prepare teardown callbacks
listeners.push(callback);
const teardown = () => {
const index = listeners.indexOf(callback);
if (index > -1)
listeners.splice(index, 1);
};
teardowns.push(teardown);
return teardown;
}
function pauseListeners() {
pauseState = currentLocation.value;
}问题:
- 什么时候触发
listen()注册监听方法? listen()注册的监听方法有什么用处?- 为什么要使用
pauseListeners()暂停监听? pauseListeners()是如何暂停方法执行的?
这些问题将在第二篇文章Vue3相关源码-Vue Router源码解析(二)的总结Vue Router的hash模式什么地方最容易导致路由切换失败进行解答beforeUnloadListener()注册监听
beforeunload 事件在即将离开当前页面(刷新或关闭)时触发,触发时会重置history.replaceState保留当前的scroll(来自Vue Router的代码git提交记录描述)
该事件可用于弹出对话框,提示用户是继续浏览页面还是离开当前页面,比如“确定要离开此页吗?”
function beforeUnloadListener() {
const { history } = window;
if (!history.state)
return;
history.replaceState(assign({}, history.state, { scroll: computeScrollPosition() }), '');
}
window.addEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener);destroy()
清除所有listeners监听方法,移除全局注册的事件
function destroy() {
for (const teardown of teardowns)
teardown();
teardowns = [];
window.removeEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler);
window.removeEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener);
}步骤4: go()和routerHistory初始化
除了上述的3个步骤,最后一个步骤就是将上面步骤得到的historyNavigation、historyListeners以及对应的其它基础数据进行合并成为routerHistory
其中go()事件除了第一个参数回退的层级,还有第二个参数triggerListeners,阻止监听器触发执行,该方法的分析将放在第二篇文章Vue3相关源码-Vue Router源码解析(二)的总结中进行解答
function go(delta, triggerListeners = true) {
if (!triggerListeners)
historyListeners.pauseListeners();
history.go(delta);
}
const routerHistory = assign({
// it's overridden right after
location: '',
base,
go,
createHref: createHref.bind(null, base),
}, historyNavigation, historyListeners);
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'location', {
enumerable: true,
get: () => historyNavigation.location.value,
});
Object.defineProperty(routerHistory, 'state', {
enumerable: true,
get: () => historyNavigation.state.value,
});
return routerHistory;createMemoryHistory创建history
createMemoryHistory会创建一个基于内存的history,主要目的是为了处理SSR
与前面两个方法不同的是,createMemoryHistory维护一个队列queue和一个position,来保证历史记录存储的正确性
这里不展开详细分析,请读者自行研究
createRouter创建VueRouter对象
整体概述
createRouter()对VueRouter.createWebHashHistory()和routes的数据进行合并和拼接,组合成router对象
// Vue初始化Vue Router时的示例代码
const router = VueRouter.createRouter({
// 4. 内部提供了 history 模式的实现。为了简单起见,我们在这里使用 hash 模式。
history: VueRouter.createWebHashHistory(),
routes, // `routes: routes` 的缩写
})function createRouter(options) {
const matcher = createRouterMatcher(options.routes, options);
//...多个方法,基本都是为下面初始化router的属性
//比如addRoute()、removeRoute()、hasRoute()
const router = {
currentRoute,
listening: true,
addRoute,
removeRoute,
hasRoute,
getRoutes,
resolve,
options,
push,
replace,
go,
back: () => go(-1),
forward: () => go(1),
beforeEach: beforeGuards.add,
beforeResolve: beforeResolveGuards.add,
afterEach: afterGuards.add,
onError: errorHandlers.add,
isReady,
install(app) {
//...省略,外部app.use()时调用
},
};
return router;
}这个方法的逻辑非常繁杂,本文不会具体展开讲,后面会讲一些重点的方法以及根据一些业务去分析createRouter里面的方法,我们只需要明白,这个方法创建的数据就是Vue Router提供给外部使用的对象即可
createRouterMatcher: 根据外部传入的options.routes初始化路由配置
整体概述
根据外部传入的options.routes初始化路由配置,建立matchers数组
注意:createRouterMatcher()内部有addRoute()方法,上面createRouter()内部也有addRoute()方法,不要搞混
// globalOptions={history, routes}
function createRouterMatcher(routes, globalOptions) {
// normalized ordered array of matchers
const matchers = [];
const matcherMap = new Map();
globalOptions = mergeOptions({ strict: false, end: true, sensitive: false }, globalOptions);
function getRecordMatcher(name)
function addRoute(record, parent, originalRecord) {...}
function removeRoute(matcherRef) {...}
function getRoutes() {...}
function insertMatcher(matcher) {...}
function resolve(location, currentLocation) {...}
// add initial routes
routes.forEach(route => addRoute(route));
return { addRoute, resolve, removeRoute, getRoutes, getRecordMatcher };
}从上面的代码,我们可以知道,除了一些方法的初始化之外,主要就执行了两个步骤:mergeOptions()和routers.forEach(route=>addRoute(route))
mergeOptions
合并传递过来的参数
// partialOptions={history, routes}
// defaults={ strict: false, end: true, sensitive: false }
function mergeOptions(defaults, partialOptions) {
const options = {};
for (const key in defaults) {
options[key] = key in partialOptions ? partialOptions[key] : defaults[key];
}
return options;
}routers.forEach(route=>addRoute(route))
function addRoute(record, parent, originalRecord) {
//...
const mainNormalizedRecord = normalizeRouteRecord(record);
const normalizedRecords = [
mainNormalizedRecord,
];
if ('alias' in record) {
const aliases = typeof record.alias === 'string' ? [record.alias] : record.alias;
for (const alias of aliases) {
// ...省略处理别名的逻辑
normalizedRecords.push(assign({}, mainNormalizedRecord, {...}));
}
}
let matcher;
let originalMatcher;
for (const normalizedRecord of normalizedRecords) {
//...
// 步骤1: 创建matcher对象
matcher = createRouteRecordMatcher(normalizedRecord, parent, options);
//...
// 步骤2: 创建matcher对象和它的children-matcher之间的关系
if (mainNormalizedRecord.children) {
const children = mainNormalizedRecord.children;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
addRoute(children[i], matcher, originalRecord && originalRecord.children[i]);
}
}
//...
// 步骤3: 将创建好的matcher插入到matchers数组中
insertMatcher(matcher);
}
return originalMatcher
? () => fcd
// since other matchers are aliases, they should be removed by the original matcher
removeRoute(originalMatcher);
}
: noop;
}步骤1: createRouteRecordMatcher创建matcher对象
在路由对象record的基础上进行路由权重的计算以及正则表达式的构建,为后面路径的映射提供对应的matcher对象
function createRouteRecordMatcher(record, parent, options) {
const parser = tokensToParser(tokenizePath(record.path), options);
// warn against params with the same name
const existingKeys = new Set();
for (const key of parser.keys) {
existingKeys.add(key.name);
}
const matcher = assign(parser, {
record,
parent,
// these needs to be populated by the parent
children: [],
alias: [],
});
if (parent) {
// both are aliases or both are not aliases
// we don't want to mix them because the order is used when
// passing originalRecord in Matcher.addRoute
if (!matcher.record.aliasOf === !parent.record.aliasOf)
parent.children.push(matcher);
}
return matcher;
}tokenizePath()和tokensToParser()解析多种模式下的路由路径,下面将着重分析Vue Router4中的路由权重计算逻辑
多种类型的路由介绍
下面内容参考自Vue Router官方文档
静态路由
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: Home },
{ path: '/about', component: About },
]带参数的动态路由匹配
像 /users/johnny 和 /users/jolyn 这样的 URL 都会映射到同一个路由
const routes = [
// 动态字段以冒号开始
{ path: '/users/:id', component: User },
]正则表达式路由
常规参数只匹配url 片段之间的字符,用/分隔。如果我们想匹配任意路径,我们可以使用自定义的路径参数正则表达式,在路径参数后面的括号中加入 正则表达式
const routes = [
// 将匹配所有内容并将其放在 `$route.params.pathMatch` 下
{ path: '/:pathMatch(.*)*', name: 'NotFound', component: NotFound }
]const routes = [
// 将匹配以 `/user-` 开头的所有内容,并将其放在 `$route.params.afterUser` 下
{ path: '/user-:afterUser(.*)', component: UserGeneric }
]const routes = [
// /:orderId -> 仅匹配数字
{ path: '/:orderId(\\d+)' },
// /:productName -> 匹配其他任何内容
{ path: '/:productName' },
]const routes = [
// /:chapters -> 匹配 /one, /one/two, /one/two/three, 等
{ path: '/:chapters+' },
// /:chapters -> 匹配 /, /one, /one/two, /one/two/three, 等
{ path: '/:chapters*' },
]具体例子分析
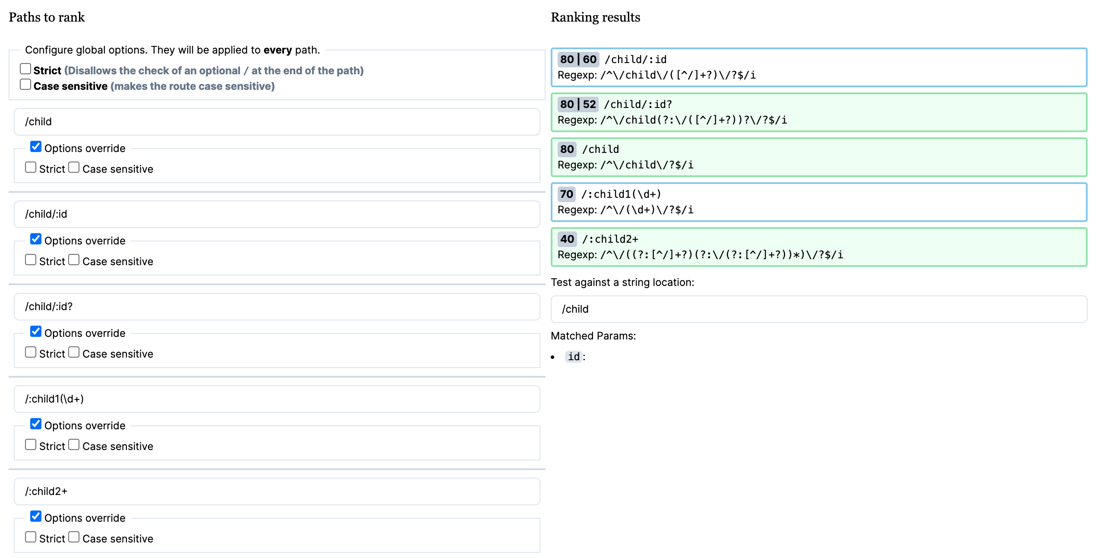
const routes = [
{path: '/', component: Home},
{path: '/child', component: Child1}, // 静态路由
{path: '/child/:id', component: Child2}, // 动态路由
{path: '/child/:id?', component: Child3}, // 动态路由(可选)
{path: '/:child1(\\d+)', component: Child4}, // 动态路由(限制数字)TokenizerState.ParamRegExp
{path: '/:child2+', component: Child5}, // 动态路由(可重复)
]具体例子使用Vue Router官方文档提供的在线测试链接Path Ranker进行测试,结果为下图所示
下面将分析如何得到上面图中的分数以及对应的路由匹配逻辑
tokenizePath()
该方法就是直接根据不同的const char=path[i++]进行不同状态的赋值,然后形成对应的数据
下面就是Vue Router源码中标记的几种状态
const enum TokenizerState {
Static, // 静态数据,比如/child这种类型中的"child"
Param, // 动态路由以及常见的正则表达式,比如"/:child1(\\d+)"
ParamRegExp, // custom re for a param
ParamRegExpEnd, // check if there is any ? + *
EscapeNext,
}直接使用debugger断点调试该方法即可清晰明白整个流程取一个比较复杂的正则表达式例子为:path: "/c\\hil\\d3/new:c\\hild1(\\d+)?",这个例子中有静态数据/child3,有动态数据:child1,也有一些正则表达式\d+以及?,还有一些中间乱入的\\tokenizePath()核心方法为下面代码块,根据判断目前item是"/",还是":",还是"(",然后进行不同的状态的赋值
function tokenizePath(path) {
while (i < path.length) {
char = path[i++];
if (char === '\\' && state !== 2 /* TokenizerState.ParamRegExp */) {
previousState = state;
state = 4 /* TokenizerState.EscapeNext */;
continue;
}
switch (state) {
case 0 /* TokenizerState.Static */:
break;
case 4 /* TokenizerState.EscapeNext */:
break;
case 1 /* TokenizerState.Param */:
break;
case 2 /* TokenizerState.ParamRegExp */:
break;
case 3 /* TokenizerState.ParamRegExpEnd */:
break;
default:
crash('Unknown state');
break;
}
}
}TokenizerState.Static: 遇到"/",进入该状态,处理静态路径,比如"/child3"TokenizerState.Param: 遇到":",进入该状态,处理动态路径,比如":child1"TokenizerState.ParamRegExp: 遇到"(",进入该状态,开始处理正则表达式TokenizerState.ParamRegExpEnd: 遇到")",进入该状态,结束处理正则表达式,然后重新回到TokenizerState.Static状态TokenizerState.EscapeNext: 在不是TokenizerState.ParamRegExp(处理正则表达式)的状态下遇到了"\\",直接跳过"\\",比如/c\\hil\\d3->/child3
最终形成segment数组为:
segment.push({
type: 1 /* TokenType.Param */,
value: buffer, // path的部分内容
regexp: customRe, // 正则表达式的内容
repeatable: char === '*' || char === '+', // 是否允许重复,代表"+"或者"*"这些表示重复的正则表达式
optional: char === '*' || char === '?', // 是否可选,代表"?"或者"*"这些表示可选的正则表达式
});segment代表每一个片段的值,在path: "/c\\hil\\d3/new:c\\hild1(\\d+)?"中,可以分为2个片段
c\\hil\\d3new:c\\hild1(\\d+)?
最终要根据segment再形成一个总体的数组tokens
function finalizeSegment() {
if (segment)
tokens.push(segment);
segment = [];
}path: "/c\\hil\\d3/new:c\\hild1(\\d+)?"形成tokens如下所示
c\\hil\\d3: 静态路径new:c\\hild1(\\d+)?: 静态路径+动态路径(包含正则表达式+可选)
[
[
{
"type": 0,
"value": "child3"
}
],
[
{
"type": 0,
"value": "new"
},
{
"type": 1,
"value": "child1",
"regexp": "\\d+",
"repeatable": false,
"optional": true
}
]
]tokensToParser()
遍历tokenizePath()拿到的tokens进行权重得分、正则表达式的计算
function tokensToParser(segments, extraOptions) {
//...
for (const segment of segments) {
//...
}
return {
re,
score,
keys,
parse,
stringify,
};
}下面分析正则表达式re和权重分数score的构建流程
正则表达式re的构建
TokenType.Static: 静态路径,比如path="/child",使用原来的路径值,会进行一些特殊字符的转译,最终形成re=/^\/child$/i
const REGEX_CHARS_RE = /[.+*?^${}()[\]/\\]/g;
if (!tokenIndex)
pattern += '/';
pattern += token.value.replace(REGEX_CHARS_RE, '\\$&');TokenType.Param: 动态匹配路径,包含各种正则表达式
当动态匹配路径不包含正则表达式时,直接使用BASE_PARAM_PATTERN = '[^/]+?'作为最终re的值
比如path="/child/:id",最终形成re=/^\/child\/([^/]+?)$/i
由于path包含静态路径+动态路径,因此re= 静态路径+动态路径 =^\/child\/+([^/]+?)+i
当动态匹配路径包含正则表达式时,直接路径中的正则表达式,即segment.regexp去构建最终的re的值
比如path="/:child1(\\d+)?",得到的segment.regexp="\\d+",最终形成re=/^(?:\/(\d+))?$/i
const BASE_PARAM_PATTERN = '[^/]+?';
const re = regexp ? regexp : BASE_PARAM_PATTERN;
let subPattern = repeatable ? `((?:${re})(?:/(?:${re}))*)` : `(${re})`;
// prepend the slash if we are starting a new segment
if (!tokenIndex)
subPattern =
// avoid an optional / if there are more segments e.g. /:p?-static
// or /:p?-:p2
optional && segment.length < 2
? `(?:/${subPattern})`
: '/' + subPattern;
if (optional)
subPattern += '?';如果path中包含可重复的正则表达式,比如path="/:child1(\\d+)+",得到的segment.regexp="\\d+",由于最后有个+,因此repeatable=true,最终形成re=/^\/((?:\d+)(?:\/(?:\d+))*)$/i
权重分数score的构建
const enum PathScore {
_multiplier = 10,
Root = 9 * _multiplier, // just /
Segment = 4 * _multiplier, // /a-segment
SubSegment = 3 * _multiplier, // /multiple-:things-in-one-:segment
Static = 4 * _multiplier, // /static
Dynamic = 2 * _multiplier, // /:someId
BonusCustomRegExp = 1 * _multiplier, // /:someId(\\d+)
BonusWildcard = -4 * _multiplier - BonusCustomRegExp, // /:namedWildcard(.*) we remove the bonus added by the custom regexp
BonusRepeatable = -2 * _multiplier, // /:w+ or /:w*
BonusOptional = -0.8 * _multiplier, // /:w? or /:w*
// these two have to be under 0.1 so a strict /:page is still lower than /:a-:b
BonusStrict = 0.07 * _multiplier, // when options strict: true is passed, as the regex omits \/?
BonusCaseSensitive = 0.025 * _multiplier, // when options strict: true is passed, as the regex omits \/?
}原始分数为PathScore.Segment=40
- 如果对大小写敏感(
options.sensitive=true),则增加分数PathScore.BonusCaseSensitive=0.25,即使40+0.25=40.25 - 如果最后一个
segment设置了options.strict=true,额外得到PathScore.BonusStrict的0.7
上面是初始化的分数,下面将针对各种状态进行分析
TokenType.Static
静态路径会额外得到PathScore.Static的+40分,如/child的分数是40+40+0.7=80.7
TokenType.Param
动态匹配路径会额外得到PathScore.Dynamic的+20分,如/:child的分数是40+20+0.7=60.7
- 如果包含正则表达式,正则表达式会额外得到
PathScore.BonusCustomRegExp的+10分,如/:child1(\\d+)的分数是60+10+0.7=70.7 - 如果包含可选
optional符号,额外得到PathScore.BonusOptional的-10分,如/:child1?的分数是60-10+0.7=60.7 - 如果包含匹配所有字符
.*符号,额外得到PathScore.BonusWildcard的-50分,如/:child1(.*)的分数是60+10-50+0.7=20.7 - 如果包含重复
repeatable符号,额外得到PathScore.BonusRepeatable的-20分,如/:child1+的分数是60-20+0.7=40.7
/:child1+的正则表达式为空,即TokenizePath [[{"type":1,"value":"child1","regexp":"","repeatable":true,"optional":false}]]
/:child1?同理,正则表达式也为空,因此没有PathScore.BonusCustomRegExp的+10分
如果存在多段segment
/child/:child1,分数为child+:child1=[[80], [60.7]]/child/pre-:child1,分数为child+pre-+:child1=[[80],[80,60.7]]
小结
通过tokenizePath()拿到routes解析后的路由数据
{
"type": 1,
"value": "child1",
"regexp": "\\d+",
"repeatable": false,
"optional": true
}根据tokenizePath()解析后的数据,进行路由权重的计算,通过tokensToParser()拿到权重以及拼接对应的正则表达式,形成一个更加完善的路由数据
parse()和stringify()会在使用RouterMatcher匹配路径时用到
{
re, //正则表达式
score, //权重分数
keys, //{name,repeatable,optional}
parse, //动态路由匹配,匹配出动态路由对应那个静态路径的方法
stringify //格式化params得到path的方法
}最终拼接所有数据形成matcher,createRouteRecordMatcher()返回数据如下所示
function createRouteRecordMatcher(record, parent, options) {
const parser = tokensToParser(tokenizePath(record.path), options);
const matcher = assign(parser, {
record,
parent,
// these needs to be populated by the parent
children: [],
alias: [],
});
return matcher;
}步骤2: 创建matcher对象和它的children-matcher之间的关系
遍历目前route的children,将当前route创建的matcher作为parent传入addRoute(),递归调用addRoute()创建新的matcher
if (mainNormalizedRecord.children) {
const children = mainNormalizedRecord.children;
for (let i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
addRoute(children[i], matcher, originalRecord && originalRecord.children[i]);
}
}步骤3: insertMatcher()将创建好的matcher插入到matchers数组和matcherMap对象中
- 使用
comparePathParserScore()对matchers进行排序,每次从头开始遍历let i=0,如果目前matchers[i]权重较大,则i++,否则直接调用matchers.splice(i, 0, matcher)插入matcher进去 matcherMap以路由对象record的名称作为key,matcher作为value
在使用matchers查找路径时,会使用matcher=matchers.find(m => m.re.test(path)),权重越大的元素放在越前面,会最先被找到,因此查找路径时会先找到权重最大的那个matcher
function insertMatcher(matcher) {
let i = 0;
while (i < matchers.length &&
comparePathParserScore(matcher, matchers[i]) >= 0 &&
// Adding children with empty path should still appear before the parent
// https://github.com/vuejs/router/issues/1124
(matcher.record.path !== matchers[i].record.path ||
!isRecordChildOf(matcher, matchers[i])))
i++;
matchers.splice(i, 0, matcher);
// only add the original record to the name map
if (matcher.record.name && !isAliasRecord(matcher))
matcherMap.set(matcher.record.name, matcher);
}而权重的比较也比较简单,不是按照总分计算权重,而是根据数组中的每一项从头到尾进行比较,如果a<b,则返回大于0的数字
如果相同
index比较能出结果,直接返回结果- 长度相同时,直接比较相同
index,直接返回差值 - 如果
a的长度只有1,并且a[0]=PathScore.Static+PathScore.Segment,表示a是一个静态路径,并且只有一个元素,那么a的权重较大,返回-1,反之返回1 - 如果
b的长度只有1,并且b[0]=PathScore.Static+PathScore.Segment,表示b是一个静态路径,并且只有一个元素,那么b的权重较大,返回-1,反之返回1 - 如果
a和b的长度相同,每一个值比较都等于0,证明a===b,返回0,继续下面流程
- 长度相同时,直接比较相同
- 如果相同
index的结果都一样,并且长度相差1,则比较最后一位是否为负数,哪个为负数,就比较小 - 如果相同
index的结果都一样,并且长度不止1,则比较谁的长度大,谁大权重就大
function comparePathParserScore(a, b) {
let i = 0;
const aScore = a.score;
const bScore = b.score;
while (i < aScore.length && i < bScore.length) {
const comp = compareScoreArray(aScore[i], bScore[i]);
// do not return if both are equal
if (comp)
return comp;
i++;
}
if (Math.abs(bScore.length - aScore.length) === 1) {
if (isLastScoreNegative(aScore))
return 1;
if (isLastScoreNegative(bScore))
return -1;
}
return bScore.length - aScore.length;
}
function compareScoreArray(a, b) {
let i = 0;
while (i < a.length && i < b.length) {
const diff = b[i] - a[i];
// only keep going if diff === 0
if (diff)
return diff;
i++;
}
if (a.length < b.length) {
return a.length === 1 && a[0] === 40 /* PathScore.Static */ + 40 /* PathScore.Segment */
? -1
: 1;
}else if (a.length > b.length) {
return b.length === 1 && b[0] === 40 /* PathScore.Static */ + 40 /* PathScore.Segment */
? 1
: -1;
}
return 0;
}使用RouterMatcher匹配路由
在上面createRouterMatcher()中,我们知道了怎么初始化匹配路由,在这个小节中,我们将分析如何利用matcher进行路由的匹配
// 只保留matcher匹配的代码逻辑
function createRouter(options) {
const matcher = createRouterMatcher(options.routes, options);
//...多个方法,基本都是为下面初始化router的属性
//比如addRoute()、removeRoute()、hasRoute()
const router = {
currentRoute,
listening: true,
addRoute,
removeRoute,
hasRoute,
getRoutes,
resolve,
options,
push,
replace,
go,
back: () => go(-1),
forward: () => go(1),
beforeEach: beforeGuards.add,
beforeResolve: beforeResolveGuards.add,
afterEach: afterGuards.add,
onError: errorHandlers.add,
isReady,
install(app) {
//...省略,外部app.use()时调用
},
};
return router;
}push(routerHistory.location)整体概述
这个push()方法是在createRouter()创建的局部方法,不是上面useHistoryStateNavigation()创建的router.push()方法
当外部调用router.push()跳转到新的路由时,实际调用的是pushWithRedirect(),而在pushWithRedirect()中第一行代码,使用resolve(to)进行当前要跳转的路由的计算
function push(to) {
return pushWithRedirect(to);
}
function pushWithRedirect(to, redirectedFrom) {
const targetLocation = (pendingLocation = resolve(to));
const from = currentRoute.value;
const data = to.state;
const force = to.force;
// to could be a string where `replace` is a function
const replace = to.replace === true;
const shouldRedirect = handleRedirectRecord(targetLocation);
if (shouldRedirect) {
//...处理重定向的逻辑
return pushWithRedirect(...)
}
// if it was a redirect we already called `pushWithRedirect` above
const toLocation = targetLocation;
toLocation.redirectedFrom = redirectedFrom;
//...处理SameRouteLocation的情况
// ...去除failure的处理,默认都成功
return navigate(toLocation, from)
.then((failure) => {
failure = finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, true, replace, data);
triggerAfterEach(toLocation, from, failure);
return failure;
});
}resolve(rawLocation, currentLocation)解析跳转路径
传递的rawLocation主要分为2种情况进行分析
rawLocation为字符串,比如rawLocation="./child1",然后调用parseURL()->matcher.resolve()->routerHistory.createHref()rawLocation为Object数据,处理它携带的path、params,然后调用matcher.resolve()
->routerHistory.createHref()
下面将先对parseURL()、matcher.resolve()、routerHistory.createHref()展开分析,然后再分析resolve()的整体流程
parseURL()解析路径拿到fullPath、path、query、hash
传入参数
parseQuery()是一个方法,可以解析链接中?A=xx&B=xx的部分,返回一个key-value数据,开发者可在初始化传入自定义的解析方法location代表即将要跳转的路由路径currentLocation代表目前的路由路径
在这个方法中,我们通过"#"以及"?"拿到对应的字符串片段,塞入到hash和query字段中,将删除掉"#"和"?"的部分塞入到path字段中
function parseURL(parseQuery, location, currentLocation = '/') {
let path, query = {}, searchString = '', hash = '';
// Could use URL and URLSearchParams but IE 11 doesn't support it
// TODO: move to new URL()
const hashPos = location.indexOf('#');
let searchPos = location.indexOf('?');
// the hash appears before the search, so it's not part of the search string
if (hashPos < searchPos && hashPos >= 0) {
searchPos = -1;
}
if (searchPos > -1) {
path = location.slice(0, searchPos);
searchString = location.slice(searchPos + 1, hashPos > -1 ? hashPos : location.length);
query = parseQuery(searchString);
}
if (hashPos > -1) {
path = path || location.slice(0, hashPos);
// keep the # character
hash = location.slice(hashPos, location.length);
}
// no search and no query
path = resolveRelativePath(path != null ? path : location, currentLocation);
// empty path means a relative query or hash `?foo=f`, `#thing`
return {
fullPath: path + (searchString && '?') + searchString + hash,
path,
query,
hash,
};
}然后触发resolveRelativePath()方法,代码逻辑也非常简单,就是判断toPosition是否是相对路径
- 如果是
"/"开头,不处理直接返回 - 如果是
"."开头,则代表跟fromSegments同级目录,不进行position的处理 - 如果是
".."开头,代表是fromSegments的上一级目录,进行position--
最终拼接绝对路径进行返回
function resolveRelativePath(to, from) {
if (to.startsWith('/'))
return to;
if (!from.startsWith('/')) {
warn(`Cannot resolve a relative location without an absolute path. Trying to resolve "${to}" from "${from}". It should look like "/${from}".`);
return to;
}
if (!to)
return from;
const fromSegments = from.split('/');
const toSegments = to.split('/');
let position = fromSegments.length - 1;
let toPosition;
let segment;
for (toPosition = 0; toPosition < toSegments.length; toPosition++) {
segment = toSegments[toPosition];
// we stay on the same position
if (segment === '.')
continue;
// go up in the from array
if (segment === '..') {
// we can't go below zero, but we still need to increment toPosition
if (position > 1)
position--;
// continue
}
// we reached a non-relative path, we stop here
else
break;
}
return (fromSegments.slice(0, position).join('/') +
'/' +
toSegments
// ensure we use at least the last element in the toSegments
.slice(toPosition - (toPosition === toSegments.length ? 1 : 0))
.join('/'));
}最终返回绝对路径下的全路径fullPath(包括query和hash)以及对应的path、query、hash
function parseURL(parseQuery, location, currentLocation = '/') {
//...
return {
fullPath: path + (searchString && '?') + searchString + hash,
path,
query,
hash,
};
}matcher.resolve(location, currentLocation)拿到路径上所有对应的matcher数组
注意,matcher是createRouterMatcher()返回的对象,具有多个方法属性createRouterMatcher()内部会进行addRoute()创建对应的matcherMap对象,提供给matcher.resolve()使用
// globalOptions={history, routes}
function createRouterMatcher(routes, globalOptions) {
//...
function resolve(location, currentLocation) {...}
return { addRoute, resolve, removeRoute, getRoutes, getRecordMatcher };
}matcher.resolve()方法,主要分为3个条件进行查找
function resolve(location, currentLocation) {
let matcher;
let params = {};
let path;
let name;
if ('name' in location && location.name) {
//...传递name查找路由
} else if ('path' in location) {
//...传递path查找路由
} else {
//...其它
}
const matched = [];
let parentMatcher = matcher;
while (parentMatcher) {
matched.unshift(parentMatcher.record);
parentMatcher = parentMatcher.parent;
}
return {
name,
path,
params,
matched,
meta: mergeMetaFields(matched),
};
}
function insertMatcher(matcher) {
//...
if (matcher.record.name && !isAliasRecord(matcher))
matcherMap.set(matcher.record.name, matcher);
}下面将针对上面这个代码进行分解
传递name查找对应的路由
router.push({ name: 'user', params: { username: 'eduardo' } })直接根据name找到对应的matcher,然后进行params的合并,这里直接利用location.params覆盖currentLocation.params重复的key
paramsFromLocation(): 筛选第一个传入Object,筛选出key存在于第二个参数,即第二个参数存在的key,才能保留下来第一个参数对应的key-value
matcher = matcherMap.get(location.name);
name = matcher.record.name;
params = assign(
paramsFromLocation(currentLocation.params,
matcher.keys.filter(k => !k.optional).map(k => k.name)),
location.params &&
paramsFromLocation(location.params, matcher.keys.map(k => k.name)));
path = matcher.stringify(params);然后根据params进行对应路径的拼接,如果是静态路径,直接拼接静态路径的值,如果是动态路径,则拼接传递的params值
如果动态匹配路由没有传递对应的参数,并且是不可选optional=false,则会报错function stringify(params) {
let path = '';
let avoidDuplicatedSlash = false;
for (const segment of segments) {
if (!avoidDuplicatedSlash || !path.endsWith('/'))
path += '/';
avoidDuplicatedSlash = false;
for (const token of segment) {
if (token.type === 0 /* TokenType.Static */) {
path += token.value;
} else if (token.type === 1 /* TokenType.Param */) {
const { value, repeatable, optional } = token;
const param = value in params ? params[value] : '';
const text = isArray(param)
? param.join('/')
: param;
if (!text) {
if (optional) {
// 可选条件下,如果path.endsWith('/'),则去掉最后面的'/'
} else { throw new Error(`Missing required param "${value}"`); }
}
path += text;
}
}
}
return path || '/';
}传递path查找对应的路由
通过正则表达式匹配路径找到对应的matcher,通过matcher.parse()解析路径,拿到路由动态匹配的字符串
路由配置为: /:child1->router.push("/test")->params: ["child1": ["test"]]
path = location.path;
matcher = matchers.find(m => m.re.test(path));
if (matcher) {
//params: ["child1": ["test"]]
params = matcher.parse(path);
name = matcher.record.name;
}没有传递name也没有传递path
获取当前路由的matcher,然后合并传递的params,使用params形成新的路径
matcher = currentLocation.name
? matcherMap.get(currentLocation.name)
: matchers.find(m => m.re.test(currentLocation.path));
name = matcher.record.name;
params = assign({}, currentLocation.params, location.params);
path = matcher.stringify(params);寻找到路由后,遍历这条路由所有segment,拿到所有的matcher,涉及路径上的多个Component
我们加载子Component的同时也会加载父Component
const matched = [];
let parentMatcher = matcher;
while (parentMatcher) {
matched.unshift(parentMatcher.record);
parentMatcher = parentMatcher.parent;
}
return {
name,
path,
params,
matched,
meta: mergeMetaFields(matched),
};routerHistory.createHref()
将base(除去域名后的剩余路径),使用正则表达式替换为"#",比如"/router/vue-router-path-ranker.html?a=1#test#xixi"->"#test#xixi"
此时location为目前的路径,比如/one/two/three,那么组合起来就是"#test#xixi/one/two/three"
一般来说应该是"#/one/two/three",不会出现两个#
const href = routerHistory.createHref(fullPath);const BEFORE_HASH_RE = /^[^#]+#/;
function createHref(base, location) {
return base.replace(BEFORE_HASH_RE, '#') + location;
}resolve()详细分析
parseURL(): 解析得到fullPath、path、query、hashmatcher.resolve(): 解析得到matchedRouted,初始化传入routes得到的数组对象,包含该路由所映射的组件,对应的参数以及一系列的路由守卫,具体的数据结构如下面代码块所示routerHistory.createHref(): 解析得到href
// matcher.resolve()
function resolve(location, currentLocation) {
return {
name,
path,
params,
matched,
meta: mergeMetaFields(matched),
};
}
// matched: RouteRecordNormalized[]
interface RouteRecordNormalized {
path: _RouteRecordBase['path']
redirect: _RouteRecordBase['redirect'] | undefined
name: _RouteRecordBase['name']
components: RouteRecordMultipleViews['components'] | null | undefined
children: RouteRecordRaw[]
meta: Exclude<_RouteRecordBase['meta'], void>
props: Record<string, _RouteRecordProps>
beforeEnter: _RouteRecordBase['beforeEnter']
leaveGuards: Set<NavigationGuard>
updateGuards: Set<NavigationGuard>
enterCallbacks: Record<string, NavigationGuardNextCallback[]>
instances: Record<string, ComponentPublicInstance | undefined | null>
aliasOf: RouteRecordNormalized | undefined
}从上面的分析,我们可以知道parseURL()、matcher.resolve()、routerHistory.createHref()的返回值,现在我们可以对resolve()方法进行具体的分析
function resolve(rawLocation, currentLocation) {
currentLocation = assign({}, currentLocation || currentRoute.value);
if (typeof rawLocation === 'string') {
const locationNormalized = parseURL(parseQuery$1, rawLocation, currentLocation.path);
const matchedRoute = matcher.resolve({ path: locationNormalized.path }, currentLocation);
const href = routerHistory.createHref(locationNormalized.fullPath);
return assign(locationNormalized, matchedRoute, {
params: decodeParams(matchedRoute.params),
hash: decode(locationNormalized.hash),
redirectedFrom: undefined,
href,
});
} else {
let matcherLocation;
if ('path' in rawLocation) {
matcherLocation = assign({}, rawLocation, {
path: parseURL(parseQuery$1, rawLocation.path, currentLocation.path).path,
});
} else {
const targetParams = assign({}, rawLocation.params);
for (const key in targetParams) {
if (targetParams[key] == null) {
delete targetParams[key];
}
}
matcherLocation = assign({}, rawLocation, {
params: encodeParams(rawLocation.params),
});
currentLocation.params = encodeParams(currentLocation.params);
}
const matchedRoute = matcher.resolve(matcherLocation, currentLocation);
const hash = rawLocation.hash || '';
matchedRoute.params = normalizeParams(decodeParams(matchedRoute.params));
const fullPath = stringifyURL(stringifyQuery$1, assign({}, rawLocation, {
hash: encodeHash(hash),
path: matchedRoute.path,
}));
const href = routerHistory.createHref(fullPath);
return assign({
fullPath,
hash,
query: stringifyQuery$1 === stringifyQuery
? normalizeQuery(rawLocation.query)
: (rawLocation.query || {}),
}, matchedRoute, {
redirectedFrom: undefined,
href,
});
}
}
parseURL(): 解析得到fullPath、path、query、hash
matcher.resolve(): 解析得到matchedRouted,初始化传入routes得到的Array,包含该路由所映射的组件,对应的参数以及一系列的路由守卫
routerHistory.createHref(): 解析得到href
typeof rawLocation === 'string'时,字符串代表路由path,通过matcher.resolve({path: xxx})获取对应的路由对象
const locationNormalized = parseURL(parseQuery$1, rawLocation, currentLocation.path);
const matchedRoute = matcher.resolve({ path: locationNormalized.path }, currentLocation);
const href = routerHistory.createHref(locationNormalized.fullPath);
// locationNormalized is always a new object
return assign(locationNormalized, matchedRoute, {
params: decodeParams(matchedRoute.params),
hash: decode(locationNormalized.hash),
redirectedFrom: undefined,
href,
});typeof rawLocation !== 'string'时,也是同样的逻辑
- 如果有
path属性,则跟上面的逻辑一致,通过matcher.resolve({path: xxx})获取对应的路由对象 - 如果没有
path属性,处理params数据(从path中提取的已解码参数字典),然后再通过matcher.resolve({path: xxx})获取对应的路由对象
fullPath:path + (searchString && '?') + searchString + hash
let matcherLocation;
//======== 第1部分:整理参数 ========
if ('path' in rawLocation) {
matcherLocation = assign({}, rawLocation, {
path: parseURL(parseQuery$1, rawLocation.path, currentLocation.path).path,
});
} else {
//...
matcherLocation = assign({}, rawLocation, {
params: encodeParams(rawLocation.params),
});
currentLocation.params = encodeParams(currentLocation.params);
}
//======== 第2部分:matcher.resolve ========
const matchedRoute = matcher.resolve(matcherLocation, currentLocation);
const hash = rawLocation.hash || '';
matchedRoute.params = normalizeParams(decodeParams(matchedRoute.params));
const fullPath = stringifyURL(stringifyQuery$1, assign({}, rawLocation, {
hash: encodeHash(hash),
path: matchedRoute.path,
}));
//======== 第3部分:routerHistory.createHref ========
const href = routerHistory.createHref(fullPath);
// ======== 第4部分:返回对象数据 ========
return assign({
fullPath,
hash,
query: stringifyQuery$1 === stringifyQuery
? normalizeQuery(rawLocation.query)
: (rawLocation.query || {}),
}, matchedRoute, {
redirectedFrom: undefined,
href,
});resolve()最终返回值对象也就是下文中targetLocation的值和toLocation的值
通过讲解上面的一系列方法,现在我们可以开始解析push()->pushWithRedirect()
pushWithRedirect()真正push逻辑
我们通过resolve(to)拿到了目前匹配的路径对象,然后处理重定向的逻辑,然后相同Route对象逻辑,然后触发navigate()方法
function pushWithRedirect(to, redirectedFrom) {
const targetLocation = (pendingLocation = resolve(to));
const from = currentRoute.value;
const data = to.state;
const force = to.force;
// to could be a string where `replace` is a function
const replace = to.replace === true;
const shouldRedirect = handleRedirectRecord(targetLocation);
if (shouldRedirect) {
//...处理重定向的逻辑
return pushWithRedirect(...)
}
// if it was a redirect we already called `pushWithRedirect` above
const toLocation = targetLocation;
toLocation.redirectedFrom = redirectedFrom;
//...处理SameRouteLocation的情况
// ...去除failure的处理,默认都成功
return navigate(toLocation, from)
.then((failure) => {
failure = finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, true, replace, data);
triggerAfterEach(toLocation, from, failure);
return failure;
});
}navigate(toLocation, from)
function navigate(to, from) {
let guards;
// 将旧的路由的beforerRouteLeave守卫函数放入guards
return (runGuardQueue(guards)// 先执行beforerRouteLeave守卫函数
.then(() => {
// 处理全局的beforeEach守卫函数
})
.then(() => {
// 处理该路由的beforeRouteUpdate守卫函数
})
.then(() => {
// 处理该路由的beforeEnter守卫函数
}).then(() => {
// 处理该路由的beforeRouteEnter守卫函数
}).then(() => {
// 处理全局的beforeResolve守卫函数
})
// catch any navigation canceled
.catch(err => isNavigationFailure(err, 8 /* ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_CANCELLED */)
? err
: Promise.reject(err)));
}
function runGuardQueue(guards) {
return guards.reduce((promise, guard) => promise.then(() => guard()), Promise.resolve());
}路由切换失败情况分析
除了执行一系列的导航守卫需要关注外,我们还需要关注下error发生时的处理情况,主要的错误情况分为
export const enum ErrorTypes {
// they must be literals to be used as values, so we can't write
// 1 << 2
MATCHER_NOT_FOUND = 1,
NAVIGATION_GUARD_REDIRECT = 2,
NAVIGATION_ABORTED = 4,
NAVIGATION_CANCELLED = 8,
NAVIGATION_DUPLICATED = 16,
}ErrorTypes.MATCHER_NOT_FOUND
当使用matcher.solve()寻找对应的matched数据时,如果传入的参数是路由的name,但是我们却无法根据name找到对应的matcher时,我们返回ErrorTypes.MATCHER_NOT_FOUND的错误
因为对于一个路由,name是唯一的标识,如果传入name,会根据matcherMap去找对应存储过的matcher
function createRouterMatcher(routes, globalOptions) {
function resolve(location, currentLocation) {
let matcher;
let params = {};
let path;
let name;
if ('name' in location && location.name) {
matcher = matcherMap.get(location.name);
if (!matcher)
throw createRouterError(1 /* ErrorTypes.MATCHER_NOT_FOUND */, {
location,
});
//...
}
return {
name,
path,
params,
matched,
meta: mergeMetaFields(matched),
};
}
}ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_ABORTED
如下面代码块所示,我们导航守卫会传递对应的next()提供给外部使用,比如开发者在外部的next()返回false,则触发NAVIGATION_ABORTED,表示取消导航
ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_GUARD_REDIRECT
如下面代码块所示,我们导航守卫会传递对应的next()提供给外部使用,比如开发者在外部的next()返回"/login"或者{"name": "login"},则isRouteLocation=true,从而返回NAVIGATION_GUARD_REDIRECT,表示导航重定向到其它路由
// guards.push(guardToPromiseFn(guard, to, from));
function guardToPromiseFn(guard, to, from, record, name) {
return () => new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const next = (valid) => {
if (valid === false) {
reject(createRouterError(4 /* ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_ABORTED */, {
from,
to,
}));
} else if (valid instanceof Error) {
reject(valid);
} else if (isRouteLocation(valid)) {
reject(createRouterError(2 /* ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_GUARD_REDIRECT */, {
from: to,
to: valid,
}));
} else {
resolve();
}
};
}
}ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_CANCELLED
如下面代码块所示,当使用push()->pushWithRedirect()->navigate()->finalizeNavigation()时,会进行checkCanceledNavigation()的检测,如果当前要跳转的路由跟pushWithRedirect()的路由不同时,说明又有新的导航已经发生,之前的导航取消
ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_DUPLICATED
如下面代码块所示,如果没有使用force,当检测到相同路由时,会产生NAVIGATION_DUPLICATED错误,阻止继续调用navigate()->finalizeNavigation()
isSameRouteLocation:matched、params、query、hash都相同
function pushWithRedirect(to, redirectedFrom) {
const targetLocation = (pendingLocation = resolve(to));
if (!force && isSameRouteLocation(stringifyQuery$1, from, targetLocation)) {
failure = createRouterError(16 /* ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_DUPLICATED */, { to: toLocation, from });
}
if(failure) return Promise.resolve(failure);
return navigate(toLocation, from).then((failure) => {
if (!failure) {
failure = finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, true, replace, data);
}
});
}
function finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, isPush, replace, data) {
// a more recent navigation took place
const error = checkCanceledNavigation(toLocation, from);
if (error)
return error;
}
function checkCanceledNavigation(to, from) {
if (pendingLocation !== to) {
return createRouterError(8 /* ErrorTypes.NAVIGATION_CANCELLED */, {
from,
to,
});
}
}finalizeNavigation()
从下面代码块可以知道,finalizeNavigation()的步骤为:
- 触发
routerHistory.replace/routerHistory.push更新 - 更新
currentRoute.value为目前的路由路径 - 检测是否是初始化阶段,如果是初始化阶段,则触发
setupListeners()方法
function finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, isPush, replace, data) {
//...处理错误
if (isPush) {
if (replace || isFirstNavigation)
routerHistory.replace(toLocation.fullPath, assign({
scroll: isFirstNavigation && state && state.scroll,
}, data));
else
routerHistory.push(toLocation.fullPath, data);
}
// accept current navigation
currentRoute.value = toLocation;
handleScroll(toLocation, from, isPush, isFirstNavigation);
markAsReady();
}
function markAsReady(err) {
if (!ready) {
// still not ready if an error happened
ready = !err;
setupListeners();
readyHandlers
.list()
.forEach(([resolve, reject]) => (err ? reject(err) : resolve()));
readyHandlers.reset();
}
return err;
}setupListeners()注册pop操作相关监听方法
初始化会进行一次
push()操作,此时就是初始化阶段
!ready,push()->navigate()->finalizeNavigation()
初始化阶段会进行routerHistory.listen()的方法注册
function finalizeNavigation(toLocation, from, isPush, replace, data) {
markAsReady();
}
function markAsReady(err) {
if (!ready) {
ready = !err;
setupListeners();
}
return err;
}
function setupListeners() {
// avoid setting up listeners twice due to an invalid first navigation
if (removeHistoryListener)
return;
removeHistoryListener = routerHistory.listen((to, _from, info) => {
if (!router.listening)
return;
// cannot be a redirect route because it was in history
const toLocation = resolve(to);
//...处理重定向的逻辑
pendingLocation = toLocation;
const from = currentRoute.value;
// TODO: should be moved to web history?
if (isBrowser) {
saveScrollPosition(getScrollKey(from.fullPath, info.delta), computeScrollPosition());
}
//...去除错误处理
navigate(toLocation, from)
.then((failure) => {
finalizeNavigation(
// after navigation, all matched components are resolved
toLocation, from, false);
triggerAfterEach(toLocation, from, failure);
})
.catch(noop);
});
}那么初始化就注册的监听在什么时候会触发呢?这个监听又有什么作用呢?
在上面我们说到useHistoryListeners()初始化的时候,我们提供了listen()方法进行事件的注册,然后在popStateHandler()触发时,进行listeners注册方法的调用
因为我们可以知道,这个监听事件本质就是为了在用户进行浏览器后退按钮点击时,能够正常监听到路由变化并且自动实现Component切换
function useHistoryListeners(base, historyState, currentLocation, replace) {
let listeners = [];
let teardowns = [];
// TODO: should it be a stack? a Dict. Check if the popstate listener
// can trigger twice
let pauseState = null;
const popStateHandler = ({ state, }) => {...};
function pauseListeners() {...}
function listen(callback) {...}
function beforeUnloadListener() {...}
function destroy() {...}
// set up the listeners and prepare teardown callbacks
window.addEventListener('popstate', popStateHandler);
window.addEventListener('beforeunload', beforeUnloadListener);
return {
pauseListeners,
listen,
destroy,
};
}
const popStateHandler = ({ state, }) => {
//...
listeners.forEach(listener => {
listener(currentLocation.value, from, {
delta,
type: NavigationType.pop,
direction: delta
? delta > 0
? NavigationDirection.forward
: NavigationDirection.back
: NavigationDirection.unknown,
});
});
};app.use(router)使用VueRouter
use(plugin, ...options) {
if (plugin && isFunction(plugin.install)) {
installedPlugins.add(plugin);
plugin.install(app, ...options);
}
else if (isFunction(plugin)) {
installedPlugins.add(plugin);
plugin(app, ...options);
}
return app;
}router.install(app)
从上面Vue3的源码可以知道,最终会触发Vue Router的install()方法
const START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED = {
path: '/',
name: undefined,
params: {},
query: {},
hash: '',
fullPath: '/',
matched: [],
meta: {},
redirectedFrom: undefined,
};
const currentRoute = vue.shallowRef(START_LOCATION_NORMALIZED);
const router = {
//....
addRoute,
removeRoute,
push,
replace,
beforeEach: beforeGuards.add,
isReady,
install(app) {
//...省略,外部app.use()时调用
},
};由于篇幅原因,接下来的分析请看下一篇文章Vue3相关源码-Vue Router源码解析(二)

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。