引用 Getting Started with Web Audio API
http://www.html5rocks.com/en/tutorials/webaudio/intro/
Introduction
Audio on the web has been fairly primitive up to this point and until very recently has had to be delivered through plugins such as Flash and QuickTime. The introduction of the audio element in HTML5 is very important, allowing for basic streaming audio playback. But, it is not powerful enough to handle more complex audio applications. For sophisticated web-based games or interactive applications, another solution is required. It is a goal of this specification to include the capabilities found in modern game audio engines as well as some of the mixing, processing, and filtering tasks that are found in modern desktop audio production applications.
在网络上的音频已经相当普遍的时代,但直到最近我们想听音频,不得不通过如Flash和QuickTime的插件播放。在HTML5音频元素的引入是非常重要的,音频元素允许基本的流式音频播放。但是,它无法处理更复杂的音频应用。对于复杂的基于Web的游戏或交互式应用,另一种解决方案是必需的。这是本说明书的目的,包括在现代游戏音频引擎音频混合处理,现代桌面音频制作应用程序所包含的处理和过滤任务。
The APIs have been designed with a wide variety of use cases in mind. Ideally, it should be able to support any use case which could reasonably be implemented with an optimized C++ engine controlled via JavaScript and run in a browser. That said, modern desktop audio software can have very advanced capabilities, some of which would be difficult or impossible to build with this system. Apple's Logic Audio is one such application which has support for external MIDI controllers, arbitrary plugin audio effects and synthesizers, highly optimized direct-to-disk audio file reading/writing, tightly integrated time-stretching, and so on. Nevertheless, the proposed system will be quite capable of supporting a large range of reasonably complex games and interactive applications, including musical ones. And it can be a very good complement to the more advanced graphics features offered by WebGL. The API has been designed so that more advanced capabilities can be added at a later time.
这些API已经设计可以满足各种各样的使用案例。理想的是,它应该能够支持任何使用情况下它可以合理地具有优化C ++引擎通过JavaScript控制并在浏览器中运行来实现。这就是说,现代台式音频软件可以有非常高级的功能,其中的一些将难以或不可能建立与该系统。苹果公司的Logic音频就是这样一个应用程序,它具有外部MIDI控制器,任意插件音频效果和合成,高度优化的直接到磁盘的音频文件读取/写入,支持紧密集成的时间伸缩,等等。尽管如此,所提出的系统将是相当能够支持大范围的相当复杂的游戏和交互式应用程序,包括音乐的。它可以是一个很好的补充,通过WebGL的提供更先进的图形功能。该API被设计成使更高级的功能可以在以后的时间被加入。
Features
The API supports these primary features:
Modular routing for simple or complex mixing/effect architectures,
including multiple sends and submixes.
High dynamic range, using 32bits floats for internal processing.
Sample-accurate scheduled sound playback with low latency for musical
applications requiring a very high degree of rhythmic precision such
as drum machines and sequencers. This also includes the possibility
of dynamic creation of effects.
模块化路由简单或复杂的混合/效果架构,包括多个发送和子混音。
高动态范围,采用32bits floats进行内部处理。
采样精确定时播放的声音与音乐的低延迟 需要的节奏等精密程度非常高的应用 作为鼓机和定序。 这也包括了可能性动态创建的效果。
Automation of audio parameters for envelopes, fade-ins / fade-outs,
granular effects, filter sweeps, LFOs etc.
Flexible handling of channels in an audio stream, allowing them to be
split and merged.
Processing of audio sources from an audio or video media element.
自动化音频参数信封,淡入/淡出,颗粒效果,过滤器扫描,低频振荡器等。
灵活的处理在音频流的信道,使它们成为拆分和合并。
处理从音频或视频的媒体元素的音频源。
Processing live audio input using a MediaStream from getUserMedia().
Integration with WebRTC Processing audio received from a remote peer
using a MediaStreamAudioSourceNode and [webrtc].
Sending a generated or processed audio stream to a remote peer using
a MediaStreamAudioDestinationNode and [webrtc].
Audio stream synthesis and processing directly in JavaScript.
使用MediaStream的getUserMedia()方法处理现场音频输入。
使用MediaStreamAudioSourceNode和[WebRTC],以实现将WebRTC从远程对等体接收的音频处理整合利用发送生成或处理的音频流发送到远程对等 一个MediaStreamAudioDestinationNode和[WebRTC]。
在JavaScript中直接处理音频流合成和加工。
Spatialized audio supporting a wide range of 3D games and immersive environments:
Panning models: equalpower, HRTF, pass-through
Distance Attenuation
Sound Cones
Obstruction / Occlusion
Doppler Shift
Source / Listener based
-
A convolution engine for a wide range of linear effects, especially very high-quality room effects. Here are some examples of possible effects:
Small / large room
Cathedral
Concert hall
Cave
Tunnel
Hallway
Forest
Amphitheater
Sound of a distant room through a doorway
Extreme filters
Strange backwards effects
Extreme comb filter effects
Dynamics compression for overall control and sweetening of the mix
Efficient real-time time-domain and frequency analysis / music visualizer support
Efficient biquad filters for lowpass, highpass, and other common filters.
A Waveshaping effect for distortion and other non-linear effects
Oscillators
立体音效支持多种3D游戏和沉浸式环境
卷积引擎广泛的非线性效应,特别是非常高品质的室内效果。
动态压缩混合的总体控制和甜味剂
高效的实时的时域和频分析/音乐可视化支持
高效双二阶滤波器的低通,高通,和其他常用的过滤器
失真等非线性效应整波效应
Modular Routing
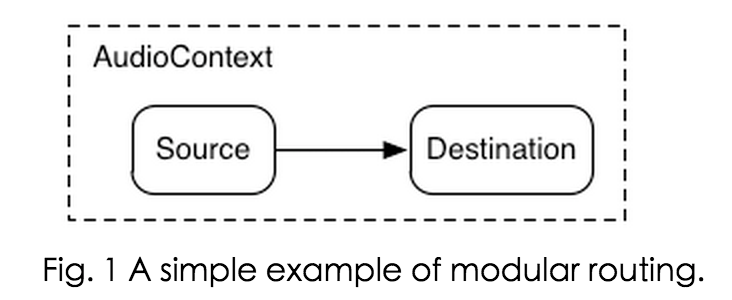
Modular routing allows arbitrary connections between different AudioNode objects. Each node can have inputs and/or outputs. A source node has no inputs and a single output. A destination node has one input and no outputs, the most common example being AudioDestinationNode the final destination to the audio hardware. Other nodes such as filters can be placed between the source and destination nodes. The developer doesn't have to worry about low-level stream format details when two objects are connected together; the right thing just happens. For example, if a mono audio stream is connected to a stereo input it should just mix to left and right channels appropriately.
模块化路由允许不同的对象AudioNode之间的任意连接。每个节点可以具有输入和/或输出。
源节点没有输入和一个输出。目的节点有一个输入和没有输出,最常见的例子是AudioDestinationNode最终目的地到音频硬件。如过滤器的其他节点可以放置在源和目的地节点之间。开发人员不必担心低级别的流格式的细节时,两个物体连接在一起;正确的事情只是发生。
例如,如果一个单声道的音频流被连接到立体声输入应该只是混合到左和右声道适当。
In the simplest case, a single source can be routed directly to the output. All routing occurs within an AudioContext containing a single AudioDestinationNode:
在最简单的情况下,单个源可直接路由到输出。所有的路由时包含一个AudioDestinationNode的AudioContext内
AudioContext
一个AudioContext是用于管理和播放所有的声音。为了生产使用Web音频API声音,创建一个或多个声源,并将它们连接到由所提供的声音目的地AudioContext 实例。这方面并不需要是直接的,并且可以通过任何数量的中间的AudioNodes充当用于音频信号处理的模块。
AudioContext的单个实例可以支持多个声音输入和复杂的音频图表,所以我们只需要其中的一个,因为我们创建的每一个音频应用程序。
许多有趣的网络音频API的功能,如创建AudioNodes和音频文件数据进行解码的AudioContext的方法
下面的代码片段创建了一个AudioContext:
var context;
window.addEventListener('load', init, false);
function init() {
try {
// Fix up for prefixing
window.AudioContext = window.AudioContext||window.webkitAudioContext;
context = new AudioContext();
}
catch(e) {
alert('Web Audio API is not supported in this browser');
}
}
Loading sounds
网络音频API使用AudioBuffer用于中短长度的声音。
其基本方法是使用XMLHttpRequest进行提取声音文件。
API支持加载多种格式的音频文件数据,如WAV,MP3,AAC,OGG等。
针对不同的音频格式支持的浏览器有所不同。
var dogBarkingBuffer = null;
// Fix up prefixing
window.AudioContext = window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext;
var context = new AudioContext();
function loadDogSound(url) {
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open('GET', url, true);
request.responseType = 'arraybuffer';
// Decode asynchronously
request.onload = function() {
context.decodeAudioData(request.response, function(buffer) {
dogBarkingBuffer = buffer;
}, onError);
}
request.send();
}音频文件数据为二进制(非文本),所以我们设置要求responseType是“arraybuffer”。
有关ArrayBuffers的更多信息,
一旦(未译码)的音频文件数据已被接收,则可以保持左右购买解码,或者它可被解码马上使用AudioContext decodeAudioData()方法。
这种方法需要存储在request.response音频文件数据的ArrayBuffer并异步进行解码(不阻塞主JavaScript的执行线程)。
当decodeAudioData()完成后,它调用的回调函数,它提供解码PCM音频数据作为AudioBuffer。
一旦被加载一个或多个AudioBuffers,那么我们就可以播放声音。
让我们假设我们刚刚加载的AudioBuffer有狗叫的声音,并且已完成加载过程。
然后我们就可以玩这个缓冲区用下面的代码。
// Fix up prefixing
window.AudioContext = window.AudioContext || window.webkitAudioContext;
var context = new AudioContext();
function playSound(buffer) {
var source = context.createBufferSource(); // creates a sound source
source.buffer = buffer; // tell the source which sound to play
source.connect(context.destination); // connect the source to the context's destination (the speakers)
source.start(0); // play the source now
// note: on older systems, may have to use deprecated noteOn(time);
}Dealing with time: playing sounds with rhythm
网络音频API允许开发者精确安排播放。为了证明这一点,让我们建立一个简单的节奏轨道。
其中hihat是发挥每一个八分音符,又踢又网罗玩法交替每季度,在4/4的时间。
假设我们已经加载了踢,圈套和hihat缓冲区,要做到这一点的代码很简单:
for (var bar = 0; bar < 2; bar++) {
var time = startTime + bar * 8 * eighthNoteTime;
// Play the bass (kick) drum on beats 1, 5
playSound(kick, time);
playSound(kick, time + 4 * eighthNoteTime);
// Play the snare drum on beats 3, 7
playSound(snare, time + 2 * eighthNoteTime);
playSound(snare, time + 6 * eighthNoteTime);
// Play the hi-hat every eighth note.
for (var i = 0; i < 8; ++i) {
playSound(hihat, time + i * eighthNoteTime);
}
}不要轻易尝试 那画面太美 我不敢直视
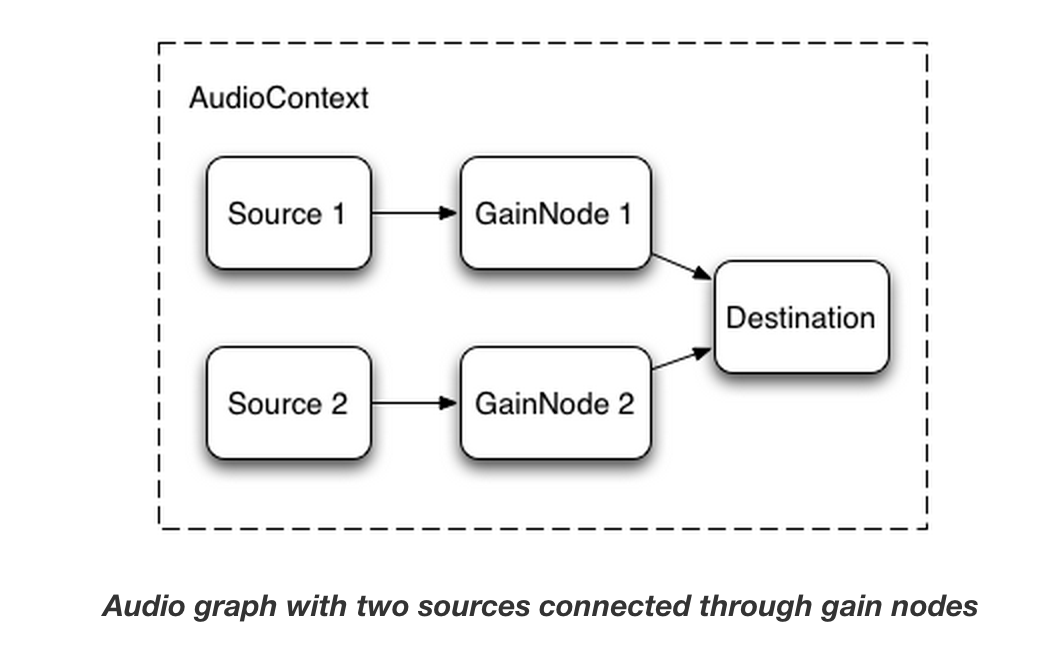
Changing the volume of a sound
一,你可能想要做一个声音的最基本的操作是改变它的音量。
通过GainNode才能使用Web API的音频,我们可以路由我们的源到目的地操纵量:
此连接建立可以实现如下:
// Create a gain node.
var gainNode = context.createGain();
// Connect the source to the gain node.
source.connect(gainNode);
// Connect the gain node to the destination.
gainNode.connect(context.destination);
经过图已经成立,你可以通过编程操纵gainNode.gain.value如下改变音量:
// Reduce the volume.
gainNode.gain.value = 0.5;
你们试下调个几千倍 那场面不敢直视
Cross-fading between two sounds
现在,假设我们有一个稍微复杂的情况,我们正在玩多种声音,但要跨越二者之间褪色。
这是在一个DJ状的应用,其中,我们有两个唱盘和希望能够从一个声源到平移到另一种常见的情况。
要使用这样的功能设置此,我们简单地创建两个GainNodes,并通过连接节点每个源
function createSource(buffer) {
var source = context.createBufferSource();
// Create a gain node.
var gainNode = context.createGain();
source.buffer = buffer;
// Turn on looping.
source.loop = true;
// Connect source to gain.
source.connect(gainNode);
// Connect gain to destination.
gainNode.connect(context.destination);
return {
source: source,
gainNode: gainNode
};
}
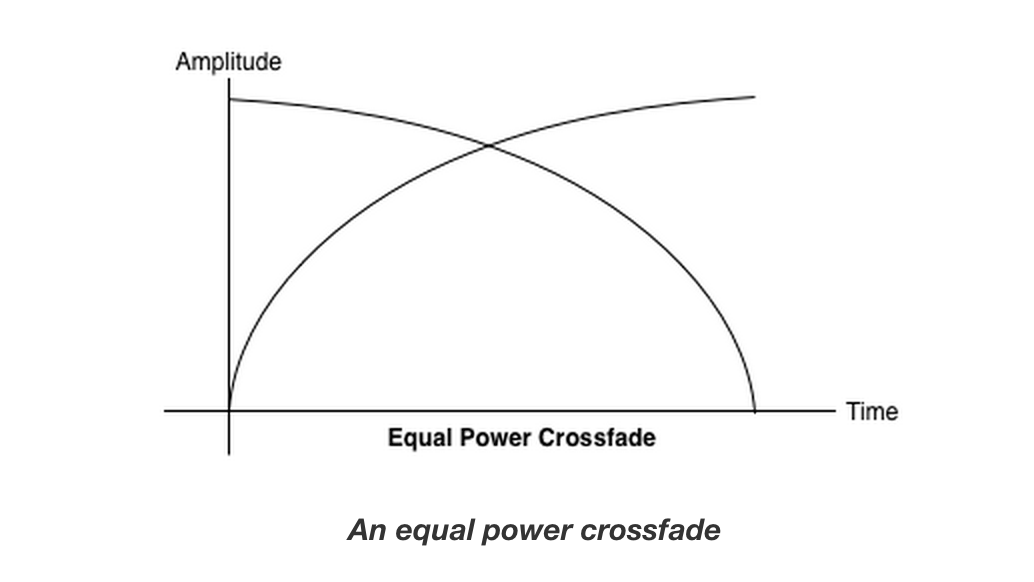
Equal power crossfading
一个天真的线性淡入淡出的方式表现出你的样本之间平移量畅游。
为了解决这一问题,我们使用一个等功率曲线,其中所述相应增益曲线是非线性的,并相交以更高的幅度。
这最大限度地减少体积骤降音频区域之间,从而导致更均匀的交叉衰减,可能是在电平略有不同区域之间。
Playlist crossfading
另一种常见的平滑转换应用是一个音乐播放器应用。
当一首歌曲的变化,我们希望在淡出当前曲目了,褪去了新的,避免了不和谐的过渡。
要做到这一点,安排交叉淡入淡出的未来。
虽然我们可以使用的setTimeout执行此调度,这是不准确的。
随着Web API的音频,我们可以使用AudioParam界面安排为参数的未来值,如GainNode的增益值。
因此,给定播放列表,我们可以轨道之间通过调度当前播放的曲目上的增益下降,并在接下来的一个增益提高升学,双双小幅之前,当前曲目播放结束:
function playHelper(bufferNow, bufferLater) {
var playNow = createSource(bufferNow);
var source = playNow.source;
var gainNode = playNow.gainNode;
var duration = bufferNow.duration;
var currTime = context.currentTime;
// Fade the playNow track in.
gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, currTime);
gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(1, currTime + ctx.FADE_TIME);
// Play the playNow track.
source.start(0);
// At the end of the track, fade it out.
gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(1, currTime + duration-ctx.FADE_TIME);
gainNode.gain.linearRampToValueAtTime(0, currTime + duration);
// Schedule a recursive track change with the tracks swapped.
var recurse = arguments.callee;
ctx.timer = setTimeout(function() {
recurse(bufferLater, bufferNow);
}, (duration - ctx.FADE_TIME) * 1000);
}
Applying a simple filter effect to a sound
该网络音频API允许从一个音频节点到另一个你管的声音,创造一个潜在的复杂的处理器链复杂的效果添加到您的soundforms。
这样做的一个方法是把你的声源和目的地之间BiquadFilterNodes。
这种类型的音频节点可以做各种的可用于构建图形均衡器,甚至更复杂的效果,主要是为了做选择其中的声音的频谱的部分强调并制服低阶滤波器。
支持的类型的过滤器包括:
Low pass filter
High pass filter
Band pass filter
Low shelf filter
High shelf filter
Peaking filter
Notch filter
All pass filter
和所有的过滤器所包含的参数,指定一定量的增益,在该应用过滤器的频率和品质因数。
低通滤波器保持较低的频率范围,但丢弃高频。
折断点由频率值确定,并且Q因子是无单位,并确定该图的形状。
增益只影响特定的过滤器,如低货架和峰值滤波器,而不是本低通滤波器。
在一般情况下,频率控制需要进行调整工作在对数标度,因为人的听觉本身的工作原理相同(即,A 4为440Hz的,和A5是880hz)。
欲了解更多详细信息,请参阅上面的源代码链接FilterSample.changeFrequency功能。
最后,请注意,示例代码,您可以连接和断开滤波器,动态变化的AudioContext图。
我们可以通过调用node.disconnect(outputNumber)断开图AudioNodes。
例如,要重新路线图从去通过一个过滤器,以直接连接,我们可以做到以下几点:
// Disconnect the source and filter.
source.disconnect(0);
filter.disconnect(0);
// Connect the source directly.
source.connect(context.destination);



**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。