标签(空格分隔):python爬虫
一、爬取网页,获取需要内容
我们今天要爬取的是豆瓣电影top250
页面如下所示:
我们需要的是里面的电影分类,通过查看源代码观察可以分析出我们需要的东西。直接进入主题吧!
知道我们需要的内容在哪里了,接下来就使用我们python强大的request库先获取网页内容下来吧!获取内容后,再使用一个好用的lxml库来分析网页内容,然后获取我们的内容就可以做下一步操作了。
先贴出使用request库和lxml分析的代码
def get_page(i):
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/top250?start={}&filter='.format(i)
html = requests.get(url).content.decode('utf-8') # 使用request库获取网页内容
selector = etree.HTML(html) # 使用lxml库提取内容
'''
通过观察页面就能发现内容在<div class="info">下的一部分
'''
content = selector.xpath('//div[@class="info"]/div[@class="bd"]/p/text()')
print(content)
for i in content[1::2]:
print(str(i).strip().replace('\n\r', ''))
# print(str(i).split('/'))
i = str(i).split('/')
i = i[len(i) - 1]
key = i.strip().replace('\n', '').split(' ') # 这里的strip和replace的使用目的是去除空格和空行之类
print(key)
通过获取下来的内容我们发现一部电影的各项内容都是用'/'分隔着,我们只需要提取电影分类中的东西,所以我们需要使用
i = str(i).split('/')来把内容分隔成几项内容,因为电影分类排在最后,所以我们通过
i = i[len(i) - 1]来获取分隔后的最后一项也就是我们需要的电影分类,还有最后一步我们需要完成的,因为一部电影里面一般都有多个电影分类的标签,所以我们还要继续分隔获取到的电影分类,并且观察可以知道电影分类之间只是用一个空格隔开,所以我们使用下面一行代码就可以分离出各个分类:
key = i.strip().replace('\n', '').split(' ')二、接下来就是保存到mysql数据库
把电影分类保存在mysql数据库以便下面进行数据分析,这里我们使用到pymysql来连接mysql数据库,首先我们需要在mysql数据库建好表:
然后我们通过pymysql把数据保存到数据库中,代码如下:
首先要连接数据库:
# 连接mysql数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(host = 'localhost', user = 'root', passwd = '2014081029', db = 'mysql', charset = 'utf8') # user为数据库的名字,passwd为数据库的密码,一般把要把字符集定义为utf8,不然存入数据库容易遇到编码问题
cur = conn.cursor() # 获取操作游标
cur.execute('use douban') # 使用douban这个数据库在保存到数据库之前,我们还有一个需要做得,那就是把250部电影的分类汇总数量,所以我们定义了一个字典来统计电影分类的个数,这里的代码是get_page函数的一部分,代码如下:
for i in content[1::2]:
print(str(i).strip().replace('\n\r', ''))
# print(str(i).split('/'))
i = str(i).split('/')
i = i[len(i) - 1]
key = i.strip().replace('\n', '').split(' ')
print(key)
for i in key:
if i not in douban.keys():
douban[i] = 1
else:
douban[i] += 1然后定义一个保存函数,执行插入操作,如果出现插入失败,就执行回滚操作,还有记得在操作完成之后,使用conn.close()和cur.close()来关闭数据库连接,代码如下:
def save_mysql(douban):
print(douban) # douban在主函数中定义的字典
for key in douban:
print(key)
print(douban[key])
if key != '':
try:
sql = 'insert douban(类别, 数量) value(' + "\'" + key + "\'," + "\'" + str(douban[key]) + "\'" + ');'
cur.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
except:
print('插入失败')
conn.rollback()
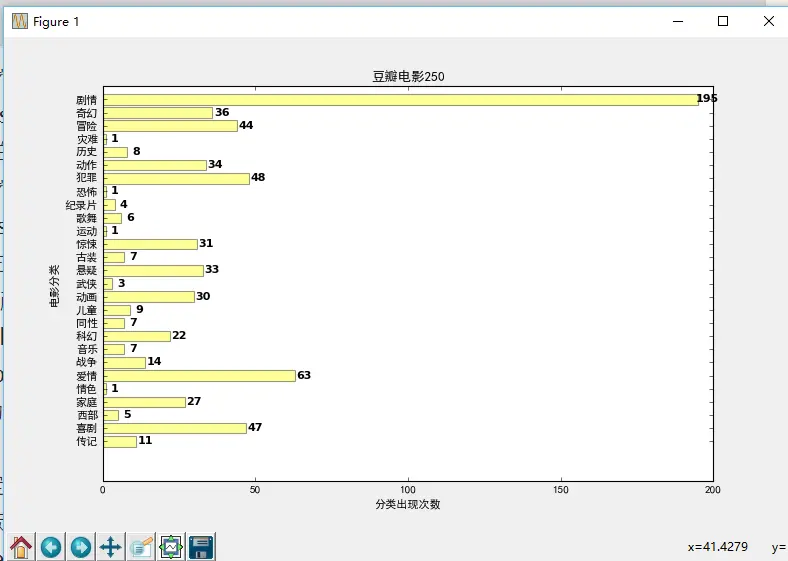
三、使用matplotlib进行数据可视化操作
首先,从数据库中把电影分类和每个分类的数量分别存入一个列表中,然后使用matplotlib进行可视化操作,具体如下:
def pylot_show():
sql = 'select * from douban;'
cur.execute(sql)
rows = cur.fetchall() # 把表中所有字段读取出来
count = [] # 每个分类的数量
category = [] # 分类
for row in rows:
count.append(int(row[2]))
category.append(row[1])
y_pos = np.arange(len(category)) # 定义y轴坐标数
plt.barh(y_pos, count, align='center', alpha=0.4) # alpha图表的填充不透明度(0~1)之间
plt.yticks(y_pos, category) # 在y轴上做分类名的标记
for count, y_pos in zip(count, y_pos):
# 分类个数在图中显示的位置,就是那些数字在柱状图尾部显示的数字
plt.text(count, y_pos, count, horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center', weight='bold')
plt.ylim(+28.0, -1.0) # 可视化范围,相当于规定y轴范围
plt.title(u'豆瓣电影250') # 图表的标题
plt.ylabel(u'电影分类') # 图表y轴的标记
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom = 0.15)
plt.xlabel(u'分类出现次数') # 图表x轴的标记
plt.savefig('douban.png') # 保存图片
下面说明一下matplotlib的一些简单使用,首先我们要导入matplotlib和numpy的包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt这次可视化是柱状图,这里给出brah()函数的定义:
barh()
主要功能:做一个横向条形图,横向条的矩形大小为: left, left + width, bottom, bottom + height
参数:barh ( bottom , width , height =0.8, left =0, **kwargs )
返回类型:一个 class 类别, matplotlib.patches.Rectangle**实例
参数说明:
bottom: Bars 的垂直位置的底部边缘
width: Bars 的长度
可选参数:height: bars 的高度
left: bars 左边缘 x 轴坐标值
color: bars 颜色
edgecolor: bars 边缘颜色
linewidth: bar 边缘宽度;None 表示默认宽度;0 表示不 i 绘制边缘
xerr: 若不为 None,将在 bar 图上生成 errobars
yerr: 若不为 None,将在 bar 图上生成 errobars
ecolor: 指定 errorbar 颜色
capsize: 指定 errorbar 的顶部(cap)长度
align: ‘edge’ (默认) | ‘center’:‘edge’以底部为准对齐;‘center’以 y 轴作为中心
log: [False|True] False (默认),若为 True,使用 log 坐标
然后就可以显示出图片来了
源码在这里:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# !/usr/bin/env python
from lxml import etree
import requests
import pymysql
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pylab import *
import numpy as np
# 连接mysql数据库
conn = pymysql.connect(host = 'localhost', user = 'root', passwd = '2014081029', db = 'mysql', charset = 'utf8')
cur = conn.cursor()
cur.execute('use douban')
def get_page(i):
url = 'https://movie.douban.com/top250?start={}&filter='.format(i)
html = requests.get(url).content.decode('utf-8')
selector = etree.HTML(html)
content = selector.xpath('//div[@class="info"]/div[@class="bd"]/p/text()')
print(content)
for i in content[1::2]:
print(str(i).strip().replace('\n\r', ''))
# print(str(i).split('/'))
i = str(i).split('/')
i = i[len(i) - 1]
# print('zhe' +i)
# print(i.strip())
# print(i.strip().split(' '))
key = i.strip().replace('\n', '').split(' ')
print(key)
for i in key:
if i not in douban.keys():
douban[i] = 1
else:
douban[i] += 1
def save_mysql():
print(douban)
for key in douban:
print(key)
print(douban[key])
if key != '':
try:
sql = 'insert douban(类别, 数量) value(' + "\'" + key + "\'," + "\'" + str(douban[key]) + "\'" + ');'
cur.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
except:
print('插入失败')
conn.rollback()
def pylot_show():
sql = 'select * from douban;'
cur.execute(sql)
rows = cur.fetchall()
count = []
category = []
for row in rows:
count.append(int(row[2]))
category.append(row[1])
print(count)
y_pos = np.arange(len(category))
print(y_pos)
print(category)
colors = np.random.rand(len(count))
# plt.barh()
plt.barh(y_pos, count, align='center', alpha=0.4)
plt.yticks(y_pos, category)
for count, y_pos in zip(count, y_pos):
plt.text(count, y_pos, count, horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center', weight='bold')
plt.ylim(+28.0, -1.0)
plt.title(u'豆瓣电影250')
plt.ylabel(u'电影分类')
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom = 0.15)
plt.xlabel(u'分类出现次数')
plt.savefig('douban.png')
if __name__ == '__main__':
douban = {}
for i in range(0, 250, 25):
get_page(i)
# save_mysql()
pylot_show()
cur.close()
conn.close()


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。