常见数据结构(二)-树(二叉树,红黑树,B树)
标签: algorithms
[TOC]
本文介绍数据结构中几种常见的树:二分查找树,2-3树,红黑树,B树
写在前面
本文所有图片均截图自coursera上普林斯顿的课程《Algorithms, Part I》中的Slides
相关命题的证明可参考《算法(第4版)》
源码可在官网下载,也可以在我的github仓库 algorithms-learning下载,已经使用maven构建
仓库下载:
git clone git@github.com:brianway/algorithms-learning.git
Binary Search Tree(二分查找树)
定义:A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order.
A binary tree is either:
Empty.
Two disjoint binary trees (left and right).
Symmetric order.Each node has a key, and every node’s key is:
Larger than all keys in its left subtree.
Smaller than all keys in its right subtree.
在java的实现中,每个节点(Node)由四个域组成:key,value,left,right。即:键,值,左子树,右子树。
private class Node {
private Key key;
private Value val;
private Node left, right;
public Node(Key key, Value val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}查找:得到相应键的值,若无此键则返回null.
/* 查找 */
public Value get(Key key) {
Node x = root;
while (x != null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x = x.left;
} else if (cmp > 0) {
x = x.right;
} else { // if (cmp == 0)
return x.val;
}
}
return null;
}插入:如果小,往左;如果大,往右;如果null,插入;如果存在,覆盖。
/* 插入 */
public void put(Key key, Value val) {
root = put(root, key, val);
}
/* 辅助函数,递归调用 */
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
if (x == null) return new Node(key, val);
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
} else { // if (cmp == 0)
x.val = val;
}
return x;
}比较的次数为节点的深度+1,由于插入节点的顺序会有差异,所以树的高度不确定,最坏的情况是N个节点的树高度为N。
-
删除:列出下面几种处理方法
将值置为null,在树中保留键
删除最小值:一直向左找到左子树为null的节点,用它的右子节点代替它。
Hibbard deletion
下面重点讲一下Hibbard deletion,分为三种情况:
没有子节点的节点,将其parent link置为null即可。
有一个子节点的节点,删除该节点并以子节点代替即可。
有两个子节点的节点,找到该节点t的下一个节点x(即右子树的最小节点),在右子树删除这个节点,并将该节点x放到t的位置。
/* 删除 */
private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
if (x == null) return null;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
} else {
if (x.right == null) return x.left; // no right child
if (x.left == null) return x.right; // no left child
Node t = x;
x = min(t.right); // replace with successor
x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
x.left = t.left;
}
x.count = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
return x;
}2-3 Search Trees(2-3树)
在介绍红黑树前,先介绍一下2-3树,便于后面理解红黑树。
2-3树是二分查找树的变形,每个节点是下面两种情况之一:
2-node:一个键,两个分叉(smaller,larger)
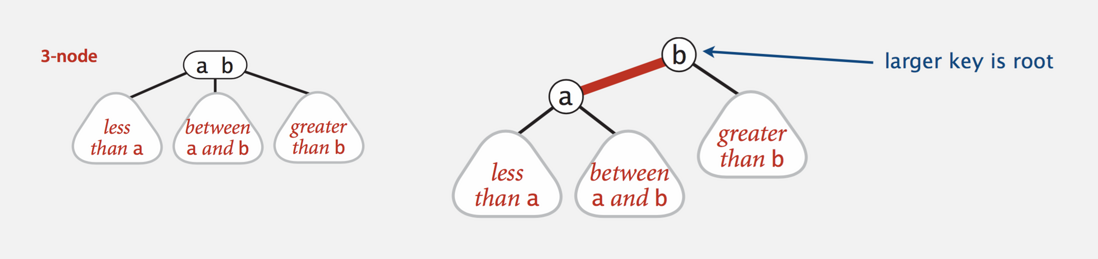
3-node:两个键,三个分叉(smaller,between,larger)
在底部向一个3-node插入。
向3-node插入一个键,临时成为一个4-node
将4-node中间的key移动到父节点
向上重复
如果到了顶端的根节点,且根节点是4-node,将其分成3个2-nodes.
总结起来就是:当插入的值导致节点变四叉时进行分裂,将中间的值传给上一个节点,并将另外两个值作为两个子节点分开,若上一节点也因此变成四叉,依次类推。分裂4-node是一个local transformation,只会进行常数次数的操作。高度加一由且仅由顶节点分裂造成
树的高度,在查找和插入时,保证了logarithmic的性能。
Worst case: lg N. [all 2-nodes]
Best case: log3 N ≈ 0.631 lg N. [all 3-nodes]
Red-Black BSTs(红黑树)
这里的红黑树均指Left-leaning red-black BSTs。主要是用二叉树的形式来表示2-3树,用一个“内部”的left-leaning连接来表示3-node。red link是2-3tree的三叉节点的连接两个key的内部link,大值作为根节点,小值作为左子节点,故名left leaning 红黑树。
一个等价的定义,A BST such that:
No node has two red links connected to it.
Every path from root to null link has the same number of black links.
Red links lean left.
红黑树的java表示
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
private class Node {
Key key;
Value val;
Node left, right;
boolean color;// color of parent link
}
private boolean isRed(Node x) {
if (x == null) return false;
return x.color == RED;
}左转-右转-变色
红黑树插入过程中可能用到的三个基本操作(左转,右转,变色):
left rotate
right rotate
flip colors
下面依次介绍
左转
/* left rotate */
private Node rotateLeft(Node h) {
assert isRed(h.right);
Node x = h.right;
h.right = x.left;
x.left = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
return x;
}右转
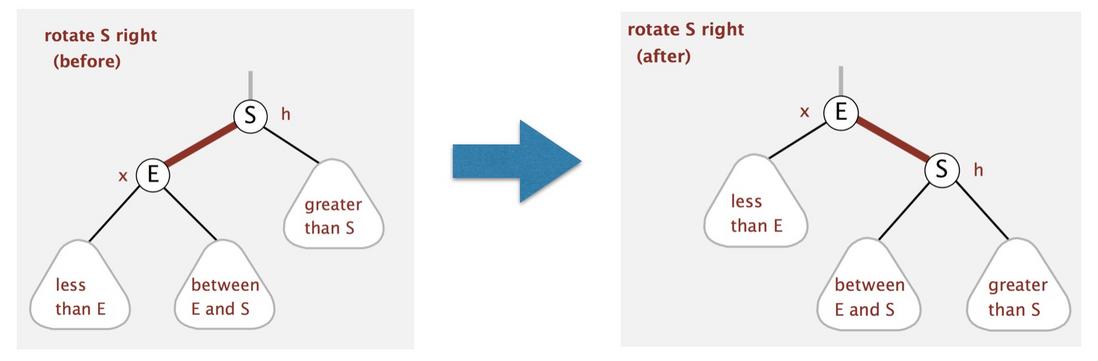
/* right rotate */
private Node rotateRight(Node h) {
assert isRed(h.left);
Node x = h.left;
h.left = x.right;
x.right = h;
x.color = h.color;
h.color = RED;
return x;
}变色
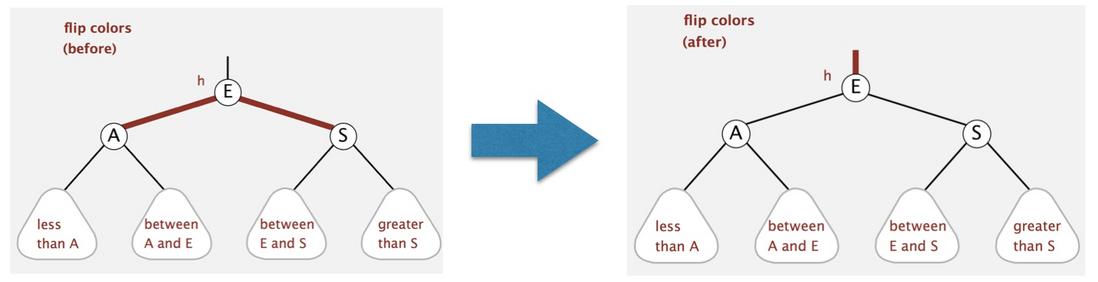
/* flip colors */
private void flipColors(Node h) {
assert !isRed(h);
assert isRed(h.left);
assert isRed(h.right);
h.color = RED;
h.left.color = BLACK;
h.right.color = BLACK;
}插入操作
从图中可以看出,插入的次序不同,需要转换的操作也不同,分三种情况(图中每一列是一种情况):
已有a和b时,c插入在b的右子节点,直接变色即可
已有b和c时,a插入在b的左子节点,先右转把b滑上去,成1中的状态,再变色即可
已有a和c时,b插入在a的右子节点,先左转把a滑下去,成2中的状态,再右转+变色即可
从上面的分析可以看出,三种情况之间有转换关系,且逐步趋向简单,如下图所示:
根本原因在于,2-3树中,是把3-node中处于中间的那个键传递给父节点,所以在红黑树中,当有一个节点连了两个 red link时,说明这三个点是一个3-node,但次序还需要调整,从而达到中间键在最上的状态,进而变色。而这个这个调整的趋势则是先让b处于a,c中间(即a的父,c的左子,成一条线),再让b成为a,c的父节点,最后变色。记住这个顺序和原因,写代码就简单了,状态3->状态2->状态1
private Node put(Node h, Key key, Value val) {
//insert at bottom (and color it red)
if (h == null) return new Node(key, val, RED);
int cmp = key.compareTo(h.key);
if (cmp < 0) {
h.left = put(h.left, key, val);
} else if (cmp > 0) {
h.right = put(h.right, key, val);
} else {
h.val = val;
}
if (isRed(h.right) && !isRed(h.left)) h = rotateLeft(h);// lean left
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.left.left)) h = rotateRight(h);//balance 4-node
if (isRed(h.left) && isRed(h.right)) flipColors(h);//split 4-node
return h;
}红黑树的高度 h <= 2 lg N,证明:
Every path from root to null link has same number of black links.
Never two red links in-a-row.
B-Trees(B树)
最后简单提一下B树,就是将2-3树一般化,将每个节点的key-link pairs增加到 M - 1
At least 2 key-link pairs at root.
At least M / 2 key-link pairs in other nodes.
External nodes contain client keys.
Internal nodes contain copies of keys to guide search.
在B树中查找
Start at root.
Find interval for search key and take corresponding link.
Search terminates in external node.
在B树中插入
Search for new key.
Insert at bottom.
Split nodes with M key-link pairs on the way up the tree.
命题:A search or an insertion in a B-tree of order M with N keys requires between log M-1 N and log M/2 N probes









**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。