声明
以下只是学习完慕课网huangyi老师实战视频课程的笔记内容,仅供个人参考学习使用。
如果对Vue2.0实战高级-开发移动端音乐WebApp感兴趣的话,请移步这里:
https://coding.imooc.com/clas...
谢谢。
项目GitHub地址: https://github.com/bjw1234/vu...
项目演示地址: http://music.baijiawei.top
项目初始化
// 安装vue脚手架工具
npm install vue-cli -g
// 初始化webpack应用
vue init webpack vue-music项目中使用到的mixin
// 背景图片
bg-image($url)
background-image: url($url + "@2x.png")
@media (-webkit-min-device-pixel-ratio: 3),(min-device-pixel-ratio: 3)
background-image: url($url + "@3x.png")
// 不换行
no-wrap()
text-overflow: ellipsis
overflow: hidden
white-space: nowrap
// 扩展点击区域
extend-click()
position: relative
&:before
content: ''
position: absolute
top: -10px
left: -10px
right: -10px
bottom: -10px配置路径别名
resolve: {
extensions: ['.js', '.vue', '.json'],
alias: {
'@': resolve('src'),
'common': resolve('src/common')
}
}移动端300毫秒延时和点透问题
fastclick:处理移动端click事件300毫秒延迟和点透问题。
先执行安装fastclick的命令。
npm install fastclick --save之后,在main.js中引入,并绑定到body
import FastClick from 'fastclick';
FastClick.attach(document.body); 注意: 当fastclick和其他的模块点击冲突,导致点击事件不可用时,可以给对应的dom添加needsclick类来解决。
对jsonp进一步封装
下载原始的jsonp模块:
npm install jsonp --save再次封装:
import originJSONP from 'jsonp';
/**
* 做一个简单的jsonp封装
* @param url
* @param data
* @param option
* @return {Promise}
*/
export default function jsonp (url, data, option) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
url = `${url}?${_obj2String(data)}`;
originJSONP(url, option, (err, data) => {
if (!err) {
resolve(data);
} else {
reject(err);
}
});
});
};
function _obj2String (obj, arr = [], index = 0) {
for (let item in obj) {
arr[index++] = [item, obj[item]];
}
return new URLSearchParams(arr).toString();
}vue的生命周期函数
注意: 当使用keep-alive组件时,当切换到其他路由,会调用前组件的deactivated钩子函数,当切回来时,会调用activated函数。
better-scroll组件的使用
注意:
- 1.better-scroll只处理容器的第一个子元素的滚动。
- 2.一定得保证子元素超出父元素,这样才能正确的滚动。
初始化:
import BScroll from 'better-scroll';
let wrapper = document.querySelector('.wrapper');
let scroll = new BScroll(wrapper,{
// 配置项
});.wrapper
position: fixed
width: 100%
top: 88px
bottom: 0
.scroll
height: 100%
overflow: hidden问题排查(无法滚动原因:)
- 1.内层容器的高度没有超过外层容器。
- 2.dom没有渲染完毕就初始化
better-scroll。 - 3.改变了dom的显隐性,没有对scroll进行重新计算。
- 针对3:当dom显示出来之后,加20毫秒延时,然后调用
refresh方法。
开发模式下的请求代理
当在开发模式下,需要使用一些后台接口,为了防止跨域问题,vue-cli提供了非常强大的http-proxy-middleware包。可以对我们的请求进行代理。
进入 config/index.js 代码下如下配置即可:
proxyTable: {
'/getDescList': {
target: 'http://127.0.0.1:7070/desclist', // 后端接口地址
changeOrigin: true,
// secure: false,
pathRewrite: {
'^/getDescList': '/'
}
}
}负外边距的作用效果
-
marin-left或者margin-top是负值:它会将元素在相应的方向进行移动。left就是左右方向移动,top就是上下方向移动。也就是会使元素在文档流里的位置发生变化。 -
margin-right或者margin-bottom是负值:它不会移动该元素(该元素不变化),但会使该元素后面的元素往前移动。也就是说,如果margin-bottom为负值,那么该元素下面的元素会往上移动;如果margin-right为负值,那么该元素右边的元素会往左移动,从而覆盖该元素。
配置子路由
需求:在歌手页面下需要一个歌手详情页。
export default new Router({
routes:[
{
path: '/',
component: Singer,
children: [
{
path: ':id',
compoonent: SingerDetail
}
]
},
...
]
});当监听到用户点击之后进行路由跳转:
this.$router.push({
path: `singer/${singer.id}`
});
// 别忘了在`Singer`页面中:
<router-view></router-view>Vuex的使用
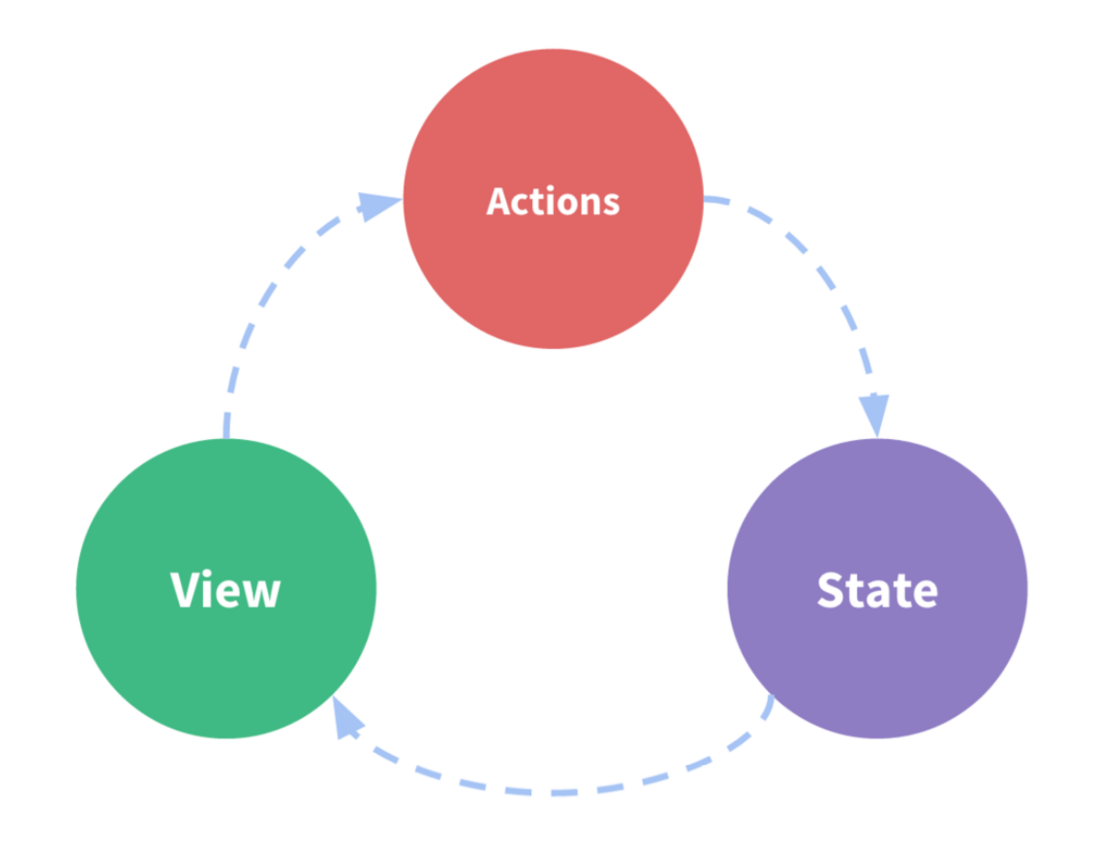
Vuex是什么?
简单来说:Vuex解决项目中多个组件之间的数据通信和状态管理。
Vuex将状态管理单独拎出来,应用统一的方式进行处理,采用单向数据流的方式来管理数据。用处负责触发动作(Action)进而改变对应状态(State),从而反映到视图(View)上。
Vuex怎么用?
安装:
npm install vuex --save引入:
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import Vue from 'Vue';
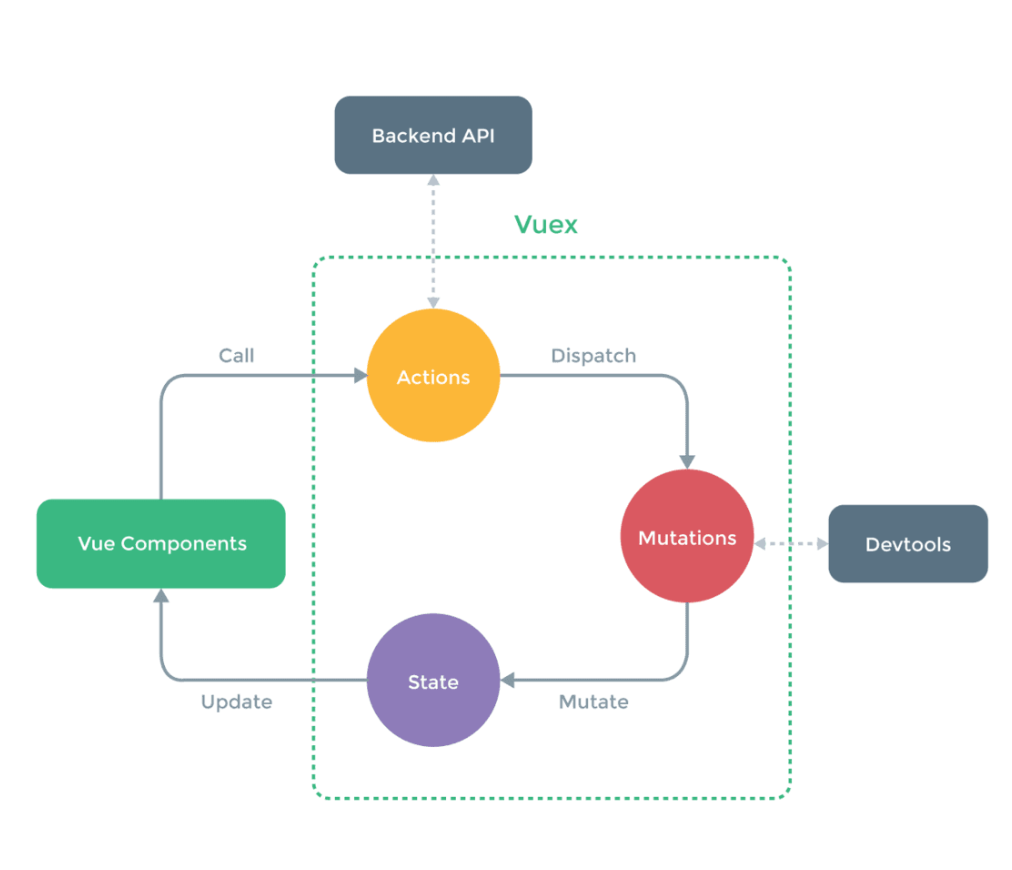
Vue.use(Vuex);Vuex的组成部分
使用Vuex开发的应用结构应该是这样的:
- State
State负责存储整个应用的状态数据,一般需要在使用的时候在根节点注入store对象,后期就可以使用this.$store.state直接获取状态。
import store from './store';
..
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
render: h => h(App)
});那么这个store又是什么?从哪来的呢?
store可以理解为一个容器,包含应用中的state。实例化生成store的过程是:
const mutations = {...};
const actions = {...};
const state = {...};
// 实例化store对象并导出
export defautl new Vuex.Store({
state,
actions,
mutations
});- Mutations
中文意思是“变化”,利用它可以来更改状态,本质上就是用来处理数据的函数。store.commit(mutationName)是用来触发一个mutation的方法。
需要记住的是,定义的mutation必须是同步函数。
const mutations = {
changState(state) {
// 在这里改变state中的数据
}
};
// 可以在组件中这样触发
this.$store.commit('changeState');
- Actions
Actions也可以用于改变状态,不过是通过触发mutation实现的,重要的是可以包含异步操作。
直接触发可以使用this.$store.dispatch(actionName)方法。
简单的多组件数据交互
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 状态
const state = {
singer: {}
};
// 跟踪状态的变化
const mutations = {
setSinger (state, singer) {
state.singer = singer;
}
};
// 实例化store对象
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
mutations
});
// 在singer组件中提交数据
this.$store.commit('setSinger',singer);
// 在singer-detail组件中接收数据
let singer = this.$store.state.singer;vuex稍微复杂点的使用
在上面的小栗子中,我们把sate、mutations等其他一些内容写在了一起,
但是这种方式不适合大型点的项目。最好能将这些内容拎出来,单独作为一个文件来使用。
在src/store目录中新建以下文件:
- state.js 用于存储状态信息
const sate = {
singer: {}
};
export default state;- mutation-types.js 保存一些常量(mutations中函数的函数名)
export const SET_SINGER = 'SET_SINGER';- mutations.js 用于更改状态(state中的数据)
import * as types from './mutation-types';
// 通过这个函数可以传入payload信息
const mutations = {
[types.SET_SINGER](state,singer){
state.singer = singer;
}
};
export default mutations;- getters.js 对状态获取的封装
export const singer = state => state.singer;- actions.js 对mutation进行封装,或者执行一些异步操作
// 暂时没有什么异步操作- index.js store的入口文件
// 入口文件
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from 'vuex';
import state from './state';
import mutations from './mutations';
import * as actions from './actions';
import * as getters from './getters';
import createLogger from 'vuex/dist/logger';
Vue.use(Vuex);
// 调试环境下开启严格模式
const debug = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production';
// 创建store对象并导出
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
actions,
getters,
mutations,
strict: debug,
plugins: debug ? [createLogger()] : []
});使用:
// main.js中引入
import store from './store';
有了以上内容,那么我们就可以在业务中去使用了:
例如:多组件之间的的数据交互。
需求:singer组件中需要将用户点击的那个singer对象传递给组件singer-detail组件。
singer.vue 组件中:
// 使用这个语法糖
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex';
methods:{
...mapMutations({
// 将这个函数(setSinger)和mutations中用于修改状态的函数关联起来
setSinger: 'SET_SINGER'
});
}
// 传参
this.setSinger(singer);
// 语法糖的本质
this.$store.commit('setSinger', singer); singer-detail.vue 组件中:
我们就可以去使用这个数据了,当然也是使用我们的语法糖啦。
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export default {
// 使用一个计算属性
computed: {
...mapGetters([
'singer' // 这个就是getters.js中的那个singer
]);
},
created(){
console.log(this.singer);
}
}
// 语法糖的本质:
let singer = this.$store.state.singer;js中给CSS添加prefix
我们一定遇到过这种情况:
需要用JS写CSS动画。但我们又不得不处理前缀的问题。
所以一般是这样写的:
this.$refs.image.style.transform = `scale(${scale})`;
this.$refs.image.style.webkitTansform = `scale(${scale})`;
...那么问题来了,怎样用JS处理这种情况呢?
思路:
- 检测浏览器的能力。
- 返回带着前缀的CSS样式。
代码实现:
let elementStyle = document.createElement('div').style;
// 得到合适的浏览器前缀
let vendor = (() => {
let transformNames = {
webkit: 'webkitTransform',
Moz: 'MozTransform',
O: 'OTransform',
ms: 'msTransform',
standard: 'transform'
};
for (let key in transformNames) {
let support = elementStyle[transformNames[key]] !== undefined;
if (support) {
return key;
}
}
return false;
})();
// 对外暴露的方法
export function prefixStyle (style) {
if (vendor === false) {
return style;
}
if (vendor === 'standard') {
return style;
}
let result = vendor + style.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + style.substr(1);
return result;
}使用案例:
// 导入该模块
import { prefixStyle } from 'common/js/dom';
// 加了合适前缀的CSS属性
const TRANSFORM = prefixStyle('transform');
// 使用该CSS属性
this.$refs.image.style[TRANSFORM] = `scale(${scale})`;移动端的touch事件
随着触屏设备的普及,w3c为移动端web新增了touch事件。
最基本的touch事件包括4个事件:
- touchstart 当在屏幕上按下手指时触发
当用户手指触摸到的触摸屏的时候触发。事件对象的 target 就是 touch 发生位置的那个元素。
- touchmove 当在屏幕上移动手指时触发
即使手指移出了 原来的target元素,但 touchmove 仍然会被一直触发,而且 target 仍然是原来的 target 元素。
- touchend 当在屏幕上抬起手指时触发
当用户的手指抬起的时候,会触发 touchend 事件。如果用户的手指从触屏设备的边缘移出了触屏设备,也会触发 touchend 事件。
touchend 事件的 target 也是与 touchstart 的 target 一致,即使已经移出了元素。
- touchcancel 当一些更高级别的事件发生的时候(如电话接入或者弹出信息)会取消当前的touch操作,即触发touchcancel。一般会在touchcancel时暂停游戏、存档等操作。
如果你使用了触摸事件,可以调用 event.preventDefault()来阻止鼠标事件被触发。
与移动端相关的interface主要有三个:
- TouchEvent 表示触摸状态发生改变时触发的event
可以通过检查触摸事件的 TouchEvent.type 属性来确定当前事件属于哪种类型。
dom.addEventListener('touchstart',(e) => {
// 获取事件类型
let type = e.type;
// toch事件发生时那个位置的元素对象
let target = e.target;
});- Touch 表示用户和触屏设备之间接触时单独的交互点(a single point of contact)
screenX、screenY:触点相对于屏幕左边缘或上边缘的x、y坐标。clientX、clientY:触点相对于浏览器viewport左边缘或上边缘的x、y坐标。(不包含滚动距离)
pageX、pageY:触点相对于document的左边缘或上边缘的x、y坐标。与client不同的是,包含左边滚动的距离。
target:触摸开始时的element。
// 获取touchList
let touchList = e.changedTouches;
// 获取第i个touch对象
let touch = touchList[i];
touch.screenX
touch.clientX
touch.pageX
touch.target
...- TouchList 表示一组touches。当发生多点触摸的时候才用的到。
如果一个用户用三根手指接触屏幕(或者触控板), 与之相关的TouchList对于每根手指都会生成一个 Touch 对象, 共计 3 个.
可以通过三种方式获取这个对象:
dom.addEventListener('touchstart',(e) => {
// 这个 TouchList对象列出了和这个触摸事件对应的那些发生了变化的 Touch 对象
e.changedTouches
// 这个TouchList列出了那些 touchstart发生在这个元素,并且还没有离开 touch surface 的touch point(手指)
e.targetTouches
// 这个 TouchList 列出了事件触发时: touch suface上所有的 touch point。
e.touches
});播放器内核开发
audio标签
对于音乐的播放,我们使用了audio标签,监听它的事件和操作DOM,可以达到对音乐播放、
暂停、进度控制等操作。
<audio ref="audio" :src="currentSongUrl"
@canplay="songCanPlay"
@error="songError"
@ended="songEnd"
@timeupdate="updateTime">
</audio>
对audio进行操作
let audio = this.$refs.audio;
// 暂停和播放
audio.pause();
audio.play();
// Audio对象的属性(部分)
audio.currentTime // 设置或返回音频中的当前播放位置(以秒计)。
audio.duration // 返回音频的长度(以秒计)。
audio.loop // 设置或返回音频是否应在结束时再次播放。(默认false)
audio.volume // 设置或返回音频的音量。[0,1]
// Audio对象多媒体事件(Media Events)
onerror // 加载发生错误时的回调
ontimeupdate // 当播放位置改变时调用
updateTime(e) {
if(this.currentSongReady){
// 获取当前播放的进度
this.currentSongTime=e.traget.currentTime;
}
}
oncanplay // 能够播放时调用
// 通过监听这个事件,设置标志位,这个标志位可以帮助我们
// 防止用户快速切换歌曲引起一些错误。
songCanPlay(){
this.currentSongReady = true;
}
onended // 到达结尾时调用
onplay、onpause...进度条组件
1.progress-bar.vue接收一个percent参数,用来显示当前播放的一个进度。
2.对于进度条用户手动拖动进度的实现。
<div class="progress-btn" ref="btn"
@touchstart="touchStart"
@touchmove="touchMove"
@touchend="touchEnd">
</div>思路:主要是通过监听ontouchstart、ontouchmove、ontouchend事件来完成。
// 首先得定义一个`touch`对象
let touch = {};
// 在监听的方法中
touchStart(e){
this.touch.initialized = true;
// 获取touch的起始位置
this.touch.startX = e.touches[0].pageX;
// 获取整个进度条的宽度
this.touch.barW = xxx;
// 获取已经播放的进度
this.touch.offset = xxx;
}
touchMove(e){
// 判断有无初始化
...
// 获取用户滑动的距离
let deltaX = e.touches[0].pageX - this.touch.startX;
let barW = xxx; // 进度条的宽度 - 拖动btn的宽度
let offset = Math.min(Math.max(0, this.touch.offset + detail), barW);
// 最后设置btn的位置和progress的进度就OK
...
}
touchEnd(){
this.touch.initialized = false;
// 然后将进度推送出去就好了
this.$emit('percentChange',percent);
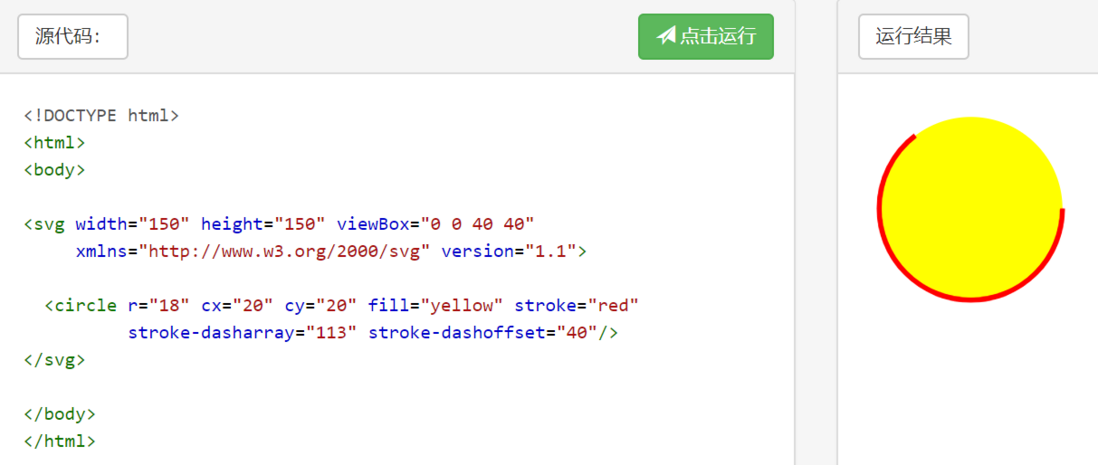
}svg实现圆形进度条
<template>
<div class="progress-circle">
<svg :width="radius" :height="radius" viewBox="0 0 100 100" version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<circle class="progress-background" r="50" cx="50" cy="50" fill="transparent"/>
<circle class="progress-bar" r="50" cx="50" cy="50" fill="transparent"
:stroke-dasharray="dashArray"
:stroke-dashoffset="offset"/>
</svg>
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>通过svg可以实现各种进度条,有一个问题,怎样去动态的修改它的进度值呢?
这就不能不提 SVG Stroke 属性
- stroke 定义一条线,文本或元素轮廓颜色
- stroke-width 文本或元素轮廓的厚度
- stroke-dasharray 该属性可用于创建虚线
- stroke-dashoffset 设置虚线边框的偏移量
OK,知道了以上属性,就足以实现一个可设置进度的SVG进度条了。
思路:stroke-dasharray适用于创建虚线的,如果这个虚线长度为整个轮廓的周长呢。stroke-dashoffset可以设置虚线的偏移量,利用这两个属性,我们就可以完成对进度的控制。
且看一个小栗子:
所以,通过父组件传入的percent,不断地修改stroke-dashoffset就能达到进度的显示了。
全屏和退出全屏
// 全屏显示
document.documentElement.webkitRequestFullScreen();
// 退出全屏
document.webkitExitFullscreen();
// 1.得根据不同的浏览器添加前缀
// 2.程序主动调用不管用,得用户操作才可以(点击按钮)歌词页的显示
通过网络接口获取的歌词:
对于歌词的解析,播放是通过一个插件lyric-parser完成的。
这个插件很简单:
1.通过正则把时间和对应的歌词切分出来创建成对象。
2.当调用play方法时,通过定时器完成歌词的播放,并将对应的行号和歌词通过回调函数传递出去。
当播放的歌词超过5行时,就可以使用封装的scroll组件完成滚动操作。
if (lineNum > 5) {
let elements = this.$refs.lyricLine;
this.$refs.lyricScroll.scrollToElement(elements[lineNum - 5], 1000);
} else {
this.$refs.lyricScroll.scrollTo(0, 0, 1000);
}Vue中的mixin
为什么要使用mixin?
多个组件公用一样的代码,我们可以将这部分抽离出来作为mixin,只要引入对应的组件中就可以了。
例如下面的mixin:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex';
export const playListMixin = {
mounted () {
this.handlePlayList(this.playList);
},
// 当路由对应的页面激活时调用
activated () {
this.handlePlayList(this.playList);
},
watch: {
playList (newPlayList) {
this.handlePlayList(newPlayList);
}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters([
'playList'
])
},
methods: {
// 这个方法需要对应的组件自己去实现,直接调用抛出错误
handlePlayList () {
throw new Error('Components must implement handlePlayList method.');
}
}
};有了mixin我们在组件中就可以这样使用了:
import { playListMixin } from 'common/js/mixin';
export default{
mixins: [playListMixin],
...
}
节流处理
在搜索页面,我们需要处理用户的输入,然后向服务器发起请求。
为了不必要的请求、节省流量和提高页面性能,我们都有必要做节流处理。
在搜索框search-box这个基础组件中:
// 在created钩子中,我们监听用户输入字符串(query)变化,然后将变化后的字符串
// 提交给父组件
// 可以看到在回调函数中,又包了一层debounce函数
created () {
this.$watch('query', debounce(() => {
this.$emit('queryChange', this.query);
}, 500));
}所以debounce函数,就是我们的节流函数,这个函数,接收一个函数,返回一个新的函数
function debounce(func,delay){
let timer = null;
return function(...args){
if(timer){
clearTimeout(timer);
}
timer = setTimeout(()=>{
func.apply(this,args);
},delay)
}
}
// 测试
function show(){
console.log('hello...');
}
var func = debounce(show,3000);
// 调用
func();
// 连续调用时,没有超过三秒是不会有任何输出的animation动画
语法:
animation: name duration timing-function delay iteration-count direction fill-mode play-state;
animation: 动画名称 执行时间 速度曲线 延时时间 执行次数 动画播放顺序 结束时应用的样式 播放的状态(paused|running)
封装localStorage操作
const __VERSION__ = '1.0.1';
const store = {
version: __VERSION__,
storage: window.localStorage,
session: {
storage: window.sessionStorage
}
};
// 操作store的api
const api = {
set (key, val) {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
if (val === undefined) {
return this.remove(key);
}
this.storage.setItem(key, this.serialize(val));
return val;
},
get (key, val) {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
let result = this.storage.getItem(key);
if (!result) {
return val;
}
return this.deSerialize(result);
},
getAll () {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
let ret = {};
for (let key in this.storage) {
if (this.storage.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
ret[key] = this.get(key);
}
}
return ret;
},
remove (key) {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
this.storage.removeItem(key);
},
removeAll () {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
this.storage.clear();
},
forEach (cb) {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
for (let key in this.storage) {
if (this.storage.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
cb && cb(key, this.get(key));
}
}
},
has (key) {
if (this.disabled) {
return false;
}
return key === this.get(key);
},
serialize (val) {
try {
return JSON.stringify(val) || undefined;
} catch (e) {
return undefined;
}
},
deSerialize (val) {
if (typeof val !== 'string') {
return undefined;
}
try {
return JSON.parse(val) || undefined;
} catch (e) {
return undefined;
}
}
};
// 扩展store对象
Object.assign(store, api);
Object.assign(store.session, api);
// 浏览器能力检测
try {
let testKey = 'test_key';
store.set(testKey, testKey);
if (store.get(testKey) !== testKey) {
store.disabled = true;
}
store.remove(testKey);
} catch (e) {
store.disabled = true;
}
export default store;
路由懒加载
为什么需要?
如果开发的App太大的话,就会导致首屏渲染过慢,为了增强用户体验,加快渲染速度,
需要用到懒加载功能。让首屏的内容先加载出来,其他路由下的组件按需加载。
vue官网描述:
异步组件
在大型应用中,我们可能需要将应用分割成小一些的代码块,并且只在需要的时候才从服务器加载一个模块。
为了简化,Vue 允许你以一个工厂函数的方式定义你的组件,这个工厂函数会异步解析你的组件定义。
Vue 只有在这个组件需要被渲染的时候才会触发该工厂函数,且会把结果缓存起来供未来重渲染。
const AsyncComponent = () => ({
// 需要加载的组件 (应该是一个 `Promise` 对象)
component: import('./MyComponent.vue'),
// 异步组件加载时使用的组件
loading: LoadingComponent,
// 加载失败时使用的组件
error: ErrorComponent,
// 展示加载时组件的延时时间。默认值是 200 (毫秒)
delay: 200,
// 如果提供了超时时间且组件加载也超时了,
// 则使用加载失败时使用的组件。默认值是:`Infinity`
timeout: 3000
})注意:如果你希望在 Vue Router 的路由组件中使用上述语法的话,你必须使用 Vue Router 2.4.0+ 版本。
当然为了简单起见:
在router/index.js路由配置文件中这样加载组件:
// import Recommend from '@/components/recommend/recommend';
const Recommend = () => ({
component: import('@/components/recommend/recommend')
});
**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。