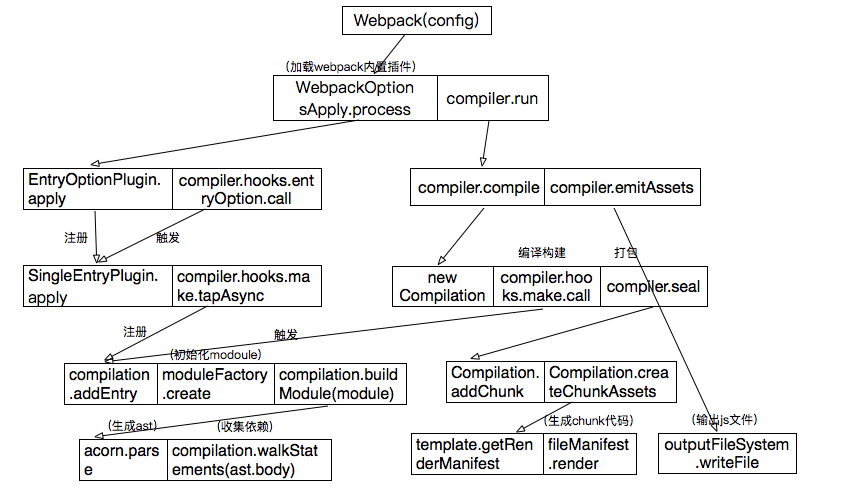
先上一张流程图
一般webpack打包文件是通过cli调用
webpack.js --config=webpack.build.js这实际上等同于通过node调用
const Webpack = require('./node_modules/webpack');
const config = require('./config1.js');
const compiler = Webpack(config);
compiler.run();Webpack(config)源码如下:
const webpack = (options, callback) => {
//将用户本地的配置文件拼接上webpack内置的参数
options = new WebpackOptionsDefaulter().process(options);
//初始化compiler对象(webpack编辑器对象,包含所有webpack主环境相关内容)
compiler = new Compiler(options.context);
compiler.options = options;
//注册NodeEnvironmentPlugin插件和用户配置的插件
new NodeEnvironmentPlugin().apply(compiler);
if (options.plugins && Array.isArray(options.plugins)) {
for (const plugin of options.plugins) {
plugin.apply(compiler);
}
}
//触发environment和afterEnvironment上注册的事件
compiler.hooks.environment.call();
compiler.hooks.afterEnvironment.call();
//注册webpack内置插件,源码如下
compiler.options = new WebpackOptionsApply().process(options, compiler);
return compiler;
})
class WebpackOptionsApply extends OptionsApply {
process(options, compiler) {
//注册EntryOptionPlugin
new EntryOptionPlugin().apply(compiler);
//触发entryOption钩子
var a = compiler.hooks.entryOption.call(options.context, options.entry);
//触发afterPlugins钩子
compiler.hooks.afterPlugins.call(compiler);
//触发afterResolvers钩子
compiler.hooks.afterResolvers.call(compiler);
}
}主要是初始化compiler对象和注册插件,下面介绍下EntryOptionPlugin插件
EntryOptionPlugin.apply方法
apply(compiler) {
//将回调函数注册到hooks.entryOption上
//上文调用compiler.hooks.entryOption.call(options.context, options.entry)时触发
compiler.hooks.entryOption.tap("EntryOptionPlugin", (context, entry) => {
//取出entry文件入口配置,判断是否数组,调用对应的插件
for (const name of Object.keys(entry)) {
itemToPlugin(context, entry[name], name).apply(compiler);
}
}
}
const itemToPlugin = (context, item, name) => {
if (Array.isArray(item)) {
return new MultiEntryPlugin(context, item, name);
}
return new SingleEntryPlugin(context, item, name);
}
//本文介绍entry[name]为字符串的情况,调用new SingleEntryPlugin().apply方法,源码如下
apply(compiler) {
//在compilation钩子上注册回调,compilation.call时触发
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(
"SingleEntryPlugin",
(compilation, { normalModuleFactory }) => {
//设置SingleEntryDependency使用normalModuleFactory创建Module
compilation.dependencyFactories.set(
SingleEntryDependency,
normalModuleFactory
);
}
);
compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync(
"SingleEntryPlugin",
(compilation, callback) => {
const { entry, name, context } = this;
const dep = SingleEntryPlugin.createDependency(entry, name);
compilation.addEntry(context, dep, name, callback);
}
);
}
经过上一步的分析可以对webpack的插件机制有一定的了解,插件主要是挂载一些回调函数在compiler的生命周期上,当执行到该阶段时触发(事件的发布订阅,继承自tapable)。
compiler的生命周期可参考:webpack hooks,下面再看下compiler.run()方法
run(callback) {
this.compile(onCompiled);
}
compile(callback) {
//初始化compilation,compilation对象代表了一次单一的版本构建和生成资源过程
const compilation = this.newCompilation(params);
// 触发注册在make上的事件函数,
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, err => {
//make上注册的事件执行完毕后触发回调,源码后面给出
}
}
//触发上文提到的SingleEntryPlugin注册事件
compiler.hooks.make.tapAsync(
"SingleEntryPlugin",
(compilation, callback) => {
const { entry, name, context } = this;
// 入口文件的依赖对象,
const dep = SingleEntryPlugin.createDependency(entry, name);
compilation.addEntry(context, dep, name, callback);
}
);
addEntry(context, entry, name, callback) {
this._addModuleChain(context, dep, ...)
}
_addModuleChain(context, dependency, onModule, callback) {
//获取dependency
const Dep = /** @type {DepConstructor} */ (dependency.constructor);
//获取moduleFactory,根据上文的介绍此处是normalModuleFactory
const moduleFactory = this.dependencyFactories.get(Dep);
//获取module
moduleFactory.create((err, module) => {
dependency.module = module;
this.buildModule(module, false, null, null, err => {
//初始化moudle后生成ast对象,计算依赖,后面介绍
})
)
}
//获取module的实现
//normalModuleFactory.create
create(data, callback) {
// 获取在constructor中注册的factory方法
const factory = this.hooks.factory.call(null);
factory(result, (err, module) => {})
}
class NormalModuleFactory extends Tapable {
constructor(context, resolverFactory, options) {
this.hooks.factory.tap("NormalModuleFactory", () => (result, callback) => {
//返回初始的module对象
callback(null, {
context: context,
request: loaders
.map(loaderToIdent)
.concat([resource])
.join("!"),
dependencies: data.dependencies,
...
});
}
}
}
buildModule回调
this.buildModule(module, false, null, null, err => {
// 根据js代码获取ast语法树对象
ast = acorn.parse(code, parserOptions);
// 根据ast加载模块的依赖
this.prewalkStatements(ast.body);
this.walkStatements(ast.body);make主要是以entry为入口,生成一个modoule对象,其中的关键是根据js代码生成ast语法树对象,同时分析语法树加载需要使用到的依赖(dependency),如果存在import依赖,就会生成新的modoule,知道所有依赖加在完毕,下图是部分dependency示例
make阶段完成之后会进入seal阶段
this.hooks.make.callAsync(compilation, err => {
compilation.seal(err => {})
})
seal() {
for (const preparedEntrypoint of this._preparedEntrypoints) {
const module = preparedEntrypoint.module;
const name = preparedEntrypoint.name;
const chunk = this.addChunk(name);
chunk.entryModule = module;
}
this.createChunkAssets();
}
createChunkAssets(){
const manifest = template.getRenderManifest({
chunk,
hash: this.hash,
fullHash: this.fullHash,
outputOptions,
moduleTemplates: this.moduleTemplates,
dependencyTemplates: this.dependencyTemplates
}); // [{ render(), filenameTemplate, pathOptions, identifier, hash }]
for (const fileManifest of manifest) {
source = fileManifest.render();
}
}compile结束后调用compiler.emitAssets
emitAssets() {
const targetPath = this.outputFileSystem.join(
outputPath,
targetFile
);
let content = source.source();
//this.writeFile = fs.writeFile.bind(fs);
this.outputFileSystem.writeFile(targetPath, content, callback);
}


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。