在stackoverflow 看到一个问题,Redis strings vs Redis hashes to represent JSON: efficiency?内容如下:
I want to store a JSON payload into redis. There's really 2 ways I can do this:
- One using a simple string keys and values.
key:user, value:payload (the entire JSON blob which can be 100-200 KB)
SET user:1 payload
- Using hashes
HSET user:1 username "someone"
HSET user:1 location "NY"
HSET user:1 bio "STRING WITH OVER 100 lines"Keep in mind that if I use a hash, the value length isn't predictable. They're not all short such as the bio example above.
Which is more memory efficient? Using string keys and values, or using a hash?
string 和 hash 直观测试
首先我们先测试用数据测试一下,测试数据结构如下:
values = {
"name": "gs",
"age": 1
}使用for 生成10w个key,key的生成规则为:
for i in range(100000):
key = "object:%d" % i把数据分别以hash 和 string(values 使用 json encode 为string )的形式存入redis。
结果如下:
hash 占用 10.16Mstring 占用 10.15M
这看起来和我们印象中hash 占空间比较大的观念不太一致,这是为什么呢?
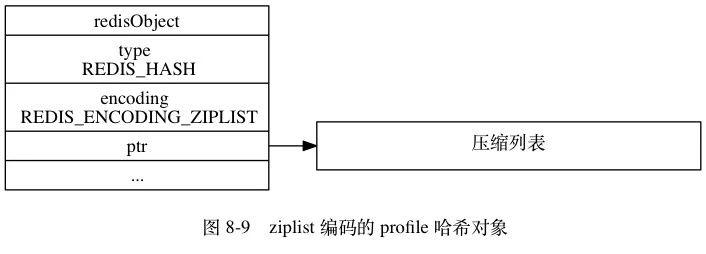
这里是因为Redis 的hash 对象有两种编码方式:
- ziplist(2.6之前是zipmap)
- hashtable
当哈希对象可以同时满足以下两个条件时, 哈希对象使用 ziplist 编码:
- 哈希对象保存的所有键值对的键和值的字符串长度都小于 64 字节;
- 哈希对象保存的键值对数量小于 512 个;
不能满足这两个条件的哈希对象需要使用 hashtable 编码。上述测试数据满足这两个条件,所以这里使用的是ziplist来存储的数据,而不是hashtable。
注意
这两个条件的上限值是可以修改的, 具体请看配置文件中关于 hash-max-ziplist-value 选项和 hash-max-ziplist-entries 选项的说明。hash-max-ziplist-entries for Redis >= 2.6
hash-max-ziplist-value for Redis >= 2.6
ziplist
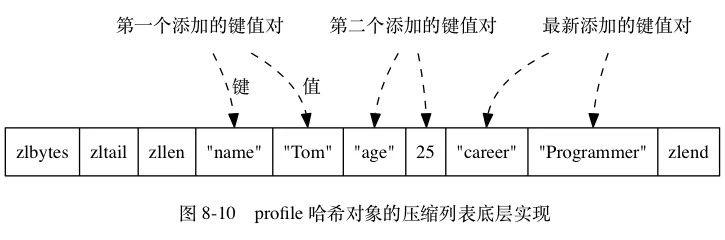
ziplist 编码的数据底层是使用压缩列表作为底层数据结构,结构如下:
hash 对象使用ziplist 保存时,程序会将保存了键的ziplist节点推入到列表的表尾,然后再将保存了值的ziplist节点推入列表的表尾。
使用这种方式保存时,并不需要申请多余的内存空间,而且每个Key都要存储一些关联的系统信息(如过期时间、LRU等),因此和String类型的Key/Value相比,Hash类型极大的减少了Key的数量(大部分的Key都以Hash字段的形式表示并存储了),从而进一步优化了存储空间的使用效率。
在这篇redis memory optimization官方文章中,作者强烈推荐使用hash存储数据
Use hashes when possible
Small hashes are encoded in a very small space, so you should try representing your data using hashes every time it is possible. For instance if you have objects representing users in a web application, instead of using different keys for name, surname, email, password, use a single hash with all the required fields.
But many times hashes contain just a few fields. When hashes are small we can instead just encode them in an O(N) data structure, like a linear array with length-prefixed key value pairs. Since we do this only when N is small, the amortized time for HGET and HSET commands is still O(1): the hash will be converted into a real hash table as soon as the number of elements it contains will grow too much (you can configure the limit in redis.conf).
This does not work well just from the point of view of time complexity, but also from the point of view of constant times, since a linear array of key value pairs happens to play very well with the CPU cache (it has a better cache locality than a hash table).
hashtable
hashtable 编码的哈希对象使用字典作为底层实现, 哈希对象中的每个键值对都使用一个字典键值对来保存:
- 字典的每个键都是一个字符串对象, 对象中保存了键值对的键;
- 字典的每个值都是一个字符串对象, 对象中保存了键值对的值。
hashtable 编码的对象如下所示:
第二次测试
values = {
"name": "gs",
"age": 1,
"intro": "long..long..long..string"
}第二次测试方式和第一次一样,只是把测试数据中加了一个大的字符串,以保证hash 使用hashtable 的方式存储数据
结果如下:
hashtable: 1.13Gstring: 1.13G
基本一样,这里应该主要是Hash类型极大的减少了Key的数量(大部分的Key都以Hash字段的形式表示并存储了),从而进一步优化了存储空间的使用效率。
NOTE: 读取和写入的速度基本一致,差别不大
回到这个问题,对于string 和 hash 该如何选择呢?
我比较赞同下面这个答案:
具体使用哪种数据结构,其实是需要看你要存储的数据以及使用场景。
如果存储的都是比较结构化的数据,比如用户数据缓存,或者经常需要操作数据的一个或者几个,特别是如果一个数据中如果filed比较多,但是每次只需要使用其中的一个或者少数的几个,使用hash是一个好的选择,因为它提供了hget 和 hmget,而无需取出所有数据再在代码中处理。
反之,如果数据差异较大,操作时常常需要把所有数据都读取出来再处理,使用string 是一个好的选择。
当然,也可以听Redis 的,放心的使用hash 吧。
还有一种场景:如果一个hash中有大量的field(成千上万个),需要考虑是不是使用string来分开存储是不是更好的选择。
参考链接
[1] Redis strings vs Redis hashes to represent JSON: efficiency?: https://stackoverflow.com/que...
[2] redis memory optimization: https://redis.io/topics/memor...
[3] Redis 设计与实现: http://redisbook.com/preview/...
最后,感谢女朋友支持和包容,比❤️
也可以在公号输入以下关键字获取历史文章:公号&小程序 | 设计模式 | 并发&协程


**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。