In recent years, more and more Chinese companies have begun to go abroad and enter the international market. In the era of digitization, the communication and marketing of enterprises to customers and users are inseparable from message communication, especially for overseas markets where business and digitization are more mature. The communication between Chinese Internet companies and users mainly includes APP push, SMS, WeChat, official account, Weibo, telephone and email. Among them, e-mail, as a mature traditional communication method, has become increasingly stable in China, especially after the era of mobile Internet.
1. In overseas markets, what role does email play in user communication preferences?
Radicati Group is a California-based market research firm covering e-mail, security regulations, wireless technologies, web services, instant messaging, social networking, unified communications, voice over IP, and more. The company was founded in 1993. Radicati Group released the report "Email Market, 2021-2025" in April 2021. According to the report, there will be approximately 4.1 billion email users worldwide in 2021, and this number is expected to grow to more than 4.5 billion by the end of 2025. In 2021, the total daily global email traffic (including business B2C and consumer C2C) is estimated to be approximately 319 billion.
It can be seen that the email user base in overseas markets is very large and continues to grow. However, with the continuous development of APP technology, especially the emergence of richer communication channels such as social media, online chat and short video, consumers' communication preferences are also constantly changing. Communication preferences of users around the world are revealed in SendGrid's 2022 Global Message Subscription Report, which collected quantitative and qualitative data and collected data from 4,800 respondents in Brazil, France, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. analyze. The report concluded that:
Email is still king. Globally, email remains the preferred way for consumers to communicate with brands. (SMS came in second.) 18% of respondents ranked email as one of the top three channels of communication. (22% in 2020) 77% of global recipients refresh their inboxes at least once a day. 31% of recipients check emails 2-5 times a day to make sure they don’t miss any important information or brand discounts.
Users in overseas markets continue to use e-mail, and e-mail is still vibrant. Email has the highest ROI of any marketing communications channel (statistically: $36 for every $1 spent).
2. Triggering and Marketing Types of Emails
When enterprises send emails, they must first distinguish whether the emails they send are trigger emails or marketing emails. Triggered emails are also called transactional emails, which are mainly sent when the user interacts with the website APP. The triggering email must contain some information about the user-triggered event. We can look at the common trigger email types: transaction confirmation or receipt: after the user has completed the business, the user receives the confirmation or receipt information from the enterprise. Request for feedback or comment: After the user completes an order or transaction, the company sends a request for comment email to the user. Such emails may have some marketing in them, but we generally classify them as trigger emails. Authentication: Businesses can use email as a way to authenticate users with 2FA. This will bring 2 additional benefits: 1. Verify that the email address entered by the user is correct; 2. The user confirms and allows joining the mailing list.
Password reset: The user chooses to forget their password, which triggers an email that directs the user to a link to reset the password. We can take a look at the common trigger email types: Account notifications: some important notification information sent by the enterprise to users, such as: security alerts for new device logins, account policy changes, account trial status ends, etc.
Marketing emails belong to the category of marketing activities, which aim to guide and promote users to participate in the business activities that enterprises want. Enterprises will pay attention to the effect of marketing activities, and calculate the ROI of marketing activities through delivery rate, open rate and click rate. When designing a marketing campaign, companies will involve the following matters: use an email editor, beautiful email templates to create and design email content, and use Tag and Segment recipient management tools to maintain and manage recipient lists to accurately target customers. Groups set specific CTA tracking metrics in emails to measure effectiveness (opens, clicks) Scheduling when and how often marketing campaigns are sent Common types of marketing emails: Promotions and sales: The most common marketing emails, with an emphasis on eye-catching and genuine content. Newsletters: Newsletters play a subtle role in marketing campaigns to maintain contact with users and maintain brand exposure. But emails must provide users with valuable content to avoid being rejected by users.
Triggering and marketing emails, because the two types of emails belong to different business scenarios, the user engagement (open, click) is very different, and the engagement of marketing emails is much lower. (Whether it is a trigger or a marketing email, SendCloud provides customers with beautiful and practical email templates). After figuring out the types of emails that need to be sent right now, here's what businesses need to pay attention to: Quarantine between the two email types sent. When sending e-mails, separate management of trigger and marketing e-mails is required, and different senders, IPs and sending domain names are used to achieve their respective sending services. Marketing emails will have more negative phenomena such as low user engagement and being marked as spam, which will further affect the sender's credibility. If marketing and trigger emails are not quarantined at this time, it may cause "more important" trigger emails to go to the trash, or be rejected. If you do quarantined sending, you will not encounter the problem of mutual influence between marketing and triggering email credibility.
Gmail advises senders to avoid mixing different types of content (marketing and triggering) in the same message; Gmail encourages the use of different senders based on the category or type of message;
For companies with multiple brands, it is more sensible to isolate each brand by sender, sending domain name, and IP, and then further isolate the marketing and triggered mail flow under each brand to obtain more fine-grained reports and Reputation management. SendCloud's expert consulting services provide customers with an overall solution for email sending services, including domain name planning, reputation enhancement, IP warm-up, and IP maintenance.
Trigger-verification emails (registration confirmation, password reset, transaction confirmation, etc.) use service@mail.example.com to send to 1 IP; trigger-notification emails (order notification, remote login, etc.) use notification@mails.example .com is sent to 1 IP; marketing-promotional emails (discount promotions, newsletters, etc.) are sent to 1 IP using deals@newsletter.example.com ;
The sender's reputation
Whether or not an email reaches the recipient's inbox as expected is largely determined by the sender's reputation with the inbox provider.
Common inbox service providers such as QQ, 163, Gmail, Yahoo, Hotmail, Mail.ru, etc. These inbox providers filter spam, phishing, and other unwanted emails by validating outgoing rules, scanning email content, and collecting user engagement (active, passive), etc. The inbox service provider will accumulate the sender's reputation through historical sending data, and the carrier is generally the sending domain name and sending IP.
Sender reputation depends on a number of factors: Domain reputation (historical accumulation) IP reputation (historical accumulation) Email content Recipient list management Spam complaints Invalid addresses Recipient engagement When considering sender reputation, The first thing to focus on is domain reputation and IP reputation. How can we know whether the reputation is high or low? No service provider will feedback this result, but we can obtain domain name and IP reputation through third-party tools. Different third-party tools are based on different data sources and give credibility scores according to the sender's actual sending results. This score usually doesn't tell the whole story, but it can be used as a reference. Commonly used third-party tools are as follows: SenderScore.org Like credit score, sender score is a measure of credibility, and the score ranges from 0 to 100. The higher the score, the higher the credibility and the higher the email delivery rate. high
Barracuda Reputation System provides domain name and IP reputation lookup. You can enter the domain name and IP to see if it has entered the "poor" list.
Google offers senders their Postmaster tool, which allows businesses to track data on messages sent to Gmail. Useful data provided by Postmaster includes IP reputation checks, domain reputation checks, Gmail delivery errors, and more.
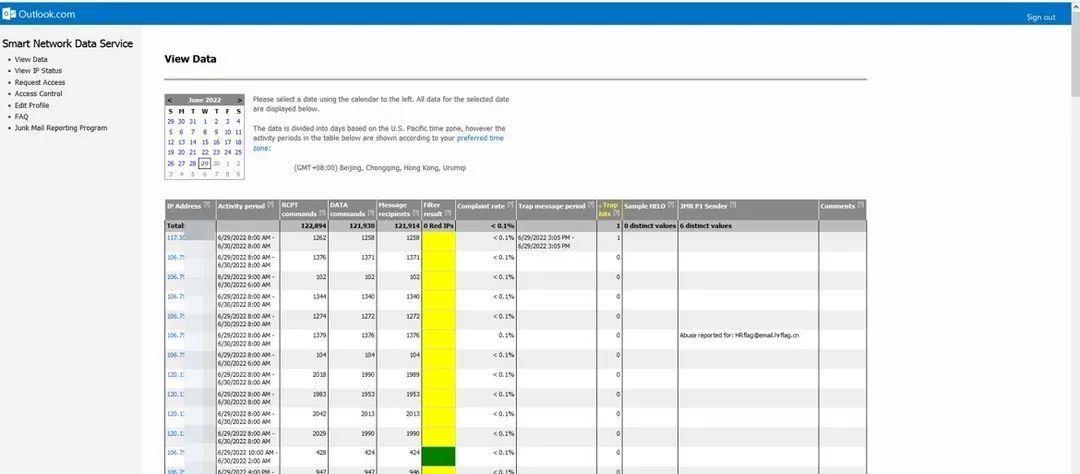
Microsoft provides a service called Smart Network Data Services (SDNS). SNDS provides businesses with feedback on email data sent to Microsoft-based mailboxes, such as the reputation of sending IPs, the volume sent to trapped mailboxes, and the company's spam complaint rate.
Tips: The credit ratings given by third parties vary greatly and can only be used for reference. It is often found that SenderScore gives an IP a score of 99, but the outgoing mail is still in the trash. Another thing to look at when it comes to sender reputation is recipient engagement. The so-called recipient engagement can be understood as how recipients interact with the company's emails. For example (regularly) opening, reading, and clicking on emails, or recipients replying, forwarding, marking emails, sorting emails, and putting them in folders, all of these actions will signal to the inbox service provider that the company's emails are very popular. Welcome and valuable to the recipient. Conversely, if the recipient directly ignores, deletes, or marks spam, the inbox service provider may filter future emails sent by the enterprise as spam. The interaction metrics that can be tracked by the existing technology are "opens, clicks, unsubscribes, spam reports". We generally use open rate to measure the level of recipient engagement.
4. Sending domain name
In the SMTP conversation with the inbox service provider, the domain name of the sender (also called mail from) is the domain name of the sender. In overseas markets, email spam and fraudulent use are very common, so email authentication is a must. The recipient will verify the sender's identity, and emails that fail to be verified will be directly rejected and judged as spam. Therefore, before sending formal emails, enterprises need to configure the verification protocol for the sending domain name. The 3 most important email authentication protocols: SPF, DKIM, DMARC. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) is an IP address authentication technology for email senders. An SPF record is a DNS TXT record for a domain name. This TXT record configures the range of sending IPs permitted by the domain name. If a message is sent from an IP address other than the one listed above, it is likely that the message is forged. During SPF authentication, the recipient will first query the SPF record of the sending domain name, and then check whether the sender's IP address is included in the SPF record. If the IP address is in the SPF record, the SPF check passes; otherwise, it fails.
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a verification technology to prevent email fraud. It detects whether the sender, subject, content, attachments and other parts have been tampered with by means of message encryption and authentication. The DKIM record is a DNS TXT record of the domain name, and this TXT record is configured with the public key information of the domain name. Generally, the sender will insert DKIM-Signature and electronic signature information in the header field of the email. During DKIM verification, the recipient will first query the DKIM record of the sender domain name to obtain the public key, and use the public key to verify the validity of the DKIM signature of the email. In this way, it is confirmed whether the email has been maliciously tampered with in the process of email sending, and the integrity of the email content is guaranteed. DMARC (Domain Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance) is a set of email authentication mechanism based on SPF and DKIM. It establishes an email feedback mechanism between the sender and receiver of emails, which is convenient for the sender and receiver of the email to jointly improve and improve the management of domain names. Supervision. DMARC requires domain names to set up SPF records and DKIM records in DNS records, and to explicitly state a policy for handling verification failure emails. The recipient will first query the DMARC record of the sender's domain name, then perform SPF verification and DKIM verification on the email, process the email that fails the verification based on the DMARC record, and feed back the processing result to the sender. DMARC is an upgrade to SPF and DKIM. The improvement is that the sender can receive feedback from the recipient about its verification results. By setting the parameters of rua and ruf, the sender can receive the authentication statistics and failure details of the domain name. ARC (Authenticated Received Chain) 2020 M3AAWG released the best practices for email authentication "M3AAWG Email Authentication Recommended Best Practices", which mentioned ARC. ARC was published in RFC8617 in July 2019 and is still in the experimental stage. ARC mainly solves the problem that the DMARC verification of the subsequent recipient fails due to the modification of some fields (such as From) during the relaying and forwarding of the mail. The method is to add the ARC-Authentication-Results header when forwarding between trusted relays during the mail forwarding process. If the subsequent recipient DMARC verification fails, the verification information of the ARC chain can be used to consider the mail DMARC. Verification is passed. During this period, there will also be header information such as ARC-Message-Signature and ARC-Seal to ensure the trust relationship between relay and forwarding nodes. Therefore, ARC is generally implemented by ISP and ESP. Currently, both Microsoft and Google support ARC. With enough ISPs supporting ARC, there will be fewer failed emails caused by relaying and forwarding, and recipients will not receive many inexplicable DMARC failure reports. With SendCloud, the enterprise fills in the sending domain name, and the system will give the DNS configuration record values of SPF, DKIM and DMARC. Enterprises only need to copy and paste to the DNS domain name management service provider to complete the configuration of the authentication protocol for the domain name sent. It's convenient~
5. Sending IP
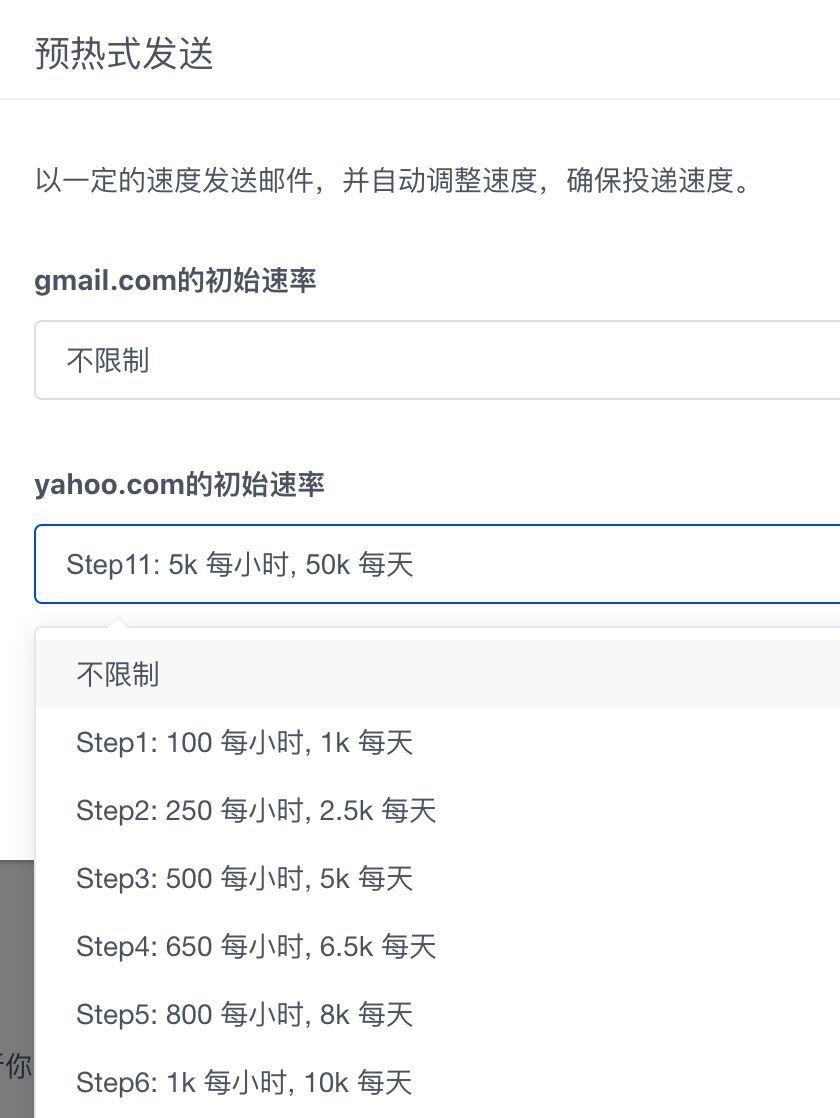
In the SMTP conversation with the inbox service provider, the IP address of the network connection used by the sender is the outgoing IP. According to M3AAWG's best practices, forward and reverse resolutions must be configured by IP before sending letters. Forward DNS is the forward resolution domain name configured for IP. The forward resolution domain name must share the root domain with the sender domain name. Reverse DNS is a reverse DNS domain name configured for IP. The reverse DNS domain name and forward DNS domain name need to be adapted to corresponding rules. The sending IP can be divided into shared IP and independent IP according to the usage of the enterprise. The difference between the two is as follows: the type advantage is insufficient. The shared IP has no additional cost, and the cheap IP reputation is affected by other senders. Independent IP IP reputation is independently controlled For additional costs, it is necessary to accumulate initial IP reputation. Most enterprises will start with shared IP, and then gradually migrate to independent IP as the sending volume grows. The stable combination of independent IP and sending domain name is more conducive to the accumulation of sender credibility for inbox service providers. If the user scale of the enterprise is large, we recommend that you directly use a dedicated IP for sending. IP warm-up inbox providers use IP addresses to identify senders, track sending behavior, and provide reputation scores for IPs. With the increase in the amount of mail sent, enterprises need to increase the IP to improve the efficiency of mail sending (an IP can be imagined as a water pipe). However, the new IP has never sent emails and has no reputation accumulation. Such IPs are generally called cold IPs (Cold IPs). How to use cold IP to send mail? The answer is WarmUp. Warm-up sending is to start a small amount of emails on the cold IP, and gradually increase the sending volume according to a certain rhythm. During the process, the recipient will reduce the suspicious identification of the IP, gradually accumulate the reputation history of the IP, and avoid the problem caused by the cold IP. Spam or reject. Ultimately, increase your business's sending volume to the expected "normal" level.
If a cold IP is used to send mail, it may be rejected due to the low reputation of the IP.
SendCloud has a huge IP reserve pool, and will preheat each reserve IP, so that the independent IP applied by the customer directly has a certain initial sending threshold. SendCloud also provides personalized warm-up plans for enterprises. When starting a warm-up plan, enterprises can independently set the warm-up sending volume for different recipient domains. The system will automatically plan the sending plan for the next day based on the sending data and effects of the current day, whether to increase or decrease, or continue to stabilize at the current sending stage. If the sending data of the enterprise has been stable, the warm-up level will gradually increase until the sending demand of the enterprise is met.
About SendCloud:
SendCloud is a SaaS platform developed and operated by Wuhan Shanda Technology Co., Ltd. to provide customers with email and SMS sending services. Since the platform was launched in 2013, it has provided tens of thousands of enterprise customers with stable, efficient and secure email and SMS sending services and accurate and timely sending data reports. On March 9, 2022, Jiguang officially completed the acquisition of a majority stake in Wuhan SendCloud Technology Co., Ltd. (SendCloud). Since then, SendCloud has officially become a sub-brand of Jiguang.
About Aurora
Aurora Mobile (NASDAQ: JG), founded in 2011, is a leading customer interaction and marketing technology service provider in China. At the beginning of its establishment, Jiguang focused on providing stable and efficient message push services for enterprises. With its first-mover advantage, it has grown into a mobile message push service provider with a far leading market share. With the continuous strengthening of enterprises' demand for customer contact and marketing growth, Jiguang has proactively launched solutions such as message cloud and marketing cloud to help enterprises achieve multi-channel customer contact and interaction needs, as well as artificial intelligence and big data. The application of marketing technology to help the digital transformation of enterprises.









**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。