使用思否猫素材实现一个轮播图
本文参与了1024程序员节,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入。
通过本文,你将学到:
- html
- css
- js
没错,就是html,css,js,现在是框架盛行的时代,所以很少会有人在意原生三件套,通过本文实现一个丝滑的轮播图,带你重温html,css和js基础知识。
为什么选用轮播图做示例?有如下几点:
- 业务当中最常用
- 轮播图说简单也不简单,说复杂也不复杂,可以说是一切项目的基石
- 轮播图更适合考察你对html,css,js的基础掌握
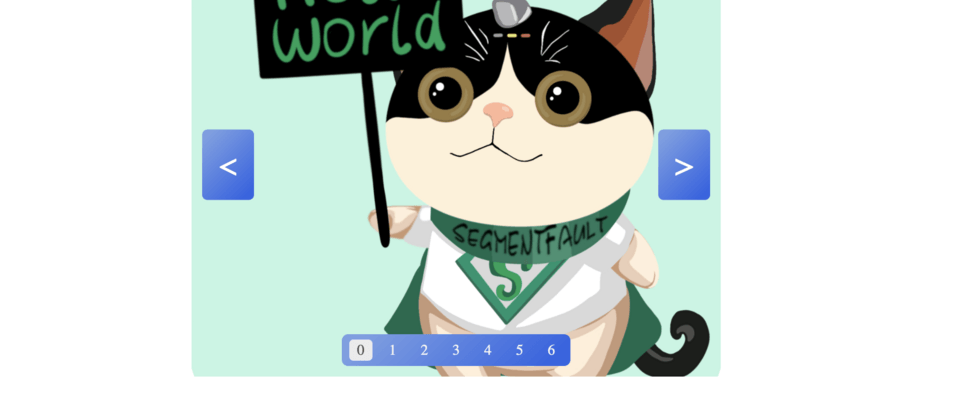
废话不多说,让我们先来看一下效果图,如下:
通过上图,我们可以知道,一个轮播图包含了三大部分,第一部分是轮播图的部分,第二部分则是轮播翻页部分,第三部分则是上一页和下一页。
所以一个轮播图的结构我们基本上就清晰了,让我们来详细看一下吧。
html文档结构
首先我们要有一个容器元素,如下:
<!--容器元素-->
<div class="carousel-box"></div>然后,我们第一部分轮播图也需要一个容器元素,随后就是轮播图的元素列表,结构如下:
<div class="carousel-content">
<div class="carousel-item active">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/1.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/2.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/3.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/4.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/5.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/6.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
<div class="carousel-item">
<img src="https://www.eveningwater.com/img/segmentfault/7.png" alt="" class="carousel-item-img">
</div>
</div>分析下来就三个,容器元素,每一个轮播图元素里面再套一个图片元素。
接下来是第二部分,同样的也是一个容器元素,套每一个轮播点元素,如下:
<div class="carousel-sign">
<div class="carousel-sign-item active">0</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">1</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">2</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">3</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">4</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">5</div>
<div class="carousel-sign-item">6</div>
</div>无论是轮播图部分还是轮播分页部分,都加了一个active类名,作为默认显示和选中的轮播图和轮播分页按钮。
第三部分,则是上一页和下一页按钮,这里如果我们将最外层的轮播容器元素设置了定位,这里也就不需要一个容器元素了,我们直接用定位,下一节写样式会详细说明。我们还是来看结构,如下:
<div class="carousel-ctrl carousel-left-ctrl"><</div>
<div class="carousel-ctrl carousel-right-ctrl">></div>这里采用了html字符实体用作上一页和下一页文本,关于什么是html字符实体,可以参考相关文章,这里不做详解。
通过以上的分析,我们一个轮播图的文档结构就完成了,接下来,让我们编写样式。
编写样式
首先我们根据效果图可以知道,容器元素,轮播图部分容器元素以及每一个轮播图元素都是百分之百宽高的,样式如下:
.carousel-box,.carousel-content,.carousel-item ,.carousel-item-img {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}其次,容器元素和轮播图元素,我们需要设置成相对定位,为什么轮播图也要设置成相对定位?因为我们这里是使用的绝对定位加left和right偏移从而实现的滑动轮播效果。
.carousel-box,.carousel-item {
position: relative;
}然后,由于轮播图只显示当前的轮播图,而超出的部分也就是溢出部分我们需要截断隐藏,因此为容器元素设置截断隐藏。
.carousel-box {
overflow: hidden;
}接着,每一个轮播图元素默认都是隐藏的,只有加了active类名,才显示。
.carousel-item {
display: none;
}
.carousel-item.active {
display: block;
left: 0;
}再然后分别是向左还是向右,这里我们是通过添加类名的方式来实现滑动,所以我们在这里额外为轮播元素增加了left和right类名,如下:
.carousel-item.active.left {
left: -100%;
}
.carousel-item.active.right {
left: 100%;
}有意思的点还在这里,就是每一个轮播图元素还额外的增加了next和prev类名,为什么要增加这两个类名?试想我们当前轮播图显示的时候,前面的是不是应该被隐藏,而后面的下一个应该是紧紧排在当前轮播图之后,然后做准备,而这两个类名的目的就是在这里,让效果看起来更加丝滑一些。
.carousel-item.next,
.carousel-item.prev {
display: block;
position: absolute;
top: 0;
}
.carousel-item.next {
left: 100%;
}
.carousel-item.prev {
left: -100%;
}
.carousel-item.next.left,
.carousel-item.prev.right {
left: 0%;
}最后补充一个轮播图片元素的样式,如下:
.carousel-item-img {
object-fit: cover;
}到了这里,其实轮播图的核心思路已经出现了,就是利用的绝对定位加left偏移来实现,而在javascript逻辑中,我们只需要操作类名就可以了。
这样做的好处很显然,我们将动画的逻辑包装在css中,因此轮播的动画逻辑也比较好修改,修改css代码总比修改js代码简单吧?
到了这里,轮播部分的样式我们就已经完成了,接下来看分页按钮组的样式。
根据图片示例,分页按钮组元素是在底部的,其实分页按钮组也可以说是很常规的按钮布局,所以样式都是一些很基础的,也没有必要做太多的详解。
.carousel-sign {
position: absolute;
bottom: 10px;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%);
padding: 5px 3px;
border-radius: 6px;
user-select: none;
background: linear-gradient(135deg,#73a0e4 10%,#1467e4 90%);
}
.carousel-sign-item {
width: 22px;
height: 20px;
font-size: 14px;
font-weight: 500;
line-height: 20px;
text-align: center;
float: left;
color:#f2f3f4;
margin: auto 4px;
cursor: pointer;
border-radius: 4px;
}
.carousel-sign-item:hover {
color:#fff;
}
.carousel-sign-item.active {
color:#535455;
background-color: #ebebeb;
}最后就是上一页下一页的样式,有意思的是上一页下一页默认是不应该显示的,鼠标悬浮到轮播图容器元素上,才会显示,所以这里也用到了定位。
.carousel-ctrl {
position: absolute;
top: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
font-size: 30px;
font-weight: 300;
user-select: none;
background: linear-gradient(135deg,#73a0e4 10%,#1467e4 90%);
color: #fff;
border-radius: 5px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: all .1s cubic-bezier(0.075, 0.82, 0.165, 1);
text-align: center;
padding: 1rem;
}
.carousel-ctrl.carousel-left-ctrl {
left: -50px;
}
.carousel-ctrl.carousel-right-ctrl {
right: -50px;
}
.carousel-box:hover .carousel-ctrl.carousel-left-ctrl {
left: 10px;
}
.carousel-box:hover .carousel-ctrl.carousel-right-ctrl {
right: 10px;
}
.carousel-ctrl:hover {
background-color: rgba(0,0,0,.8);
}到了这里,样式的布局就完成了,接下来是javascript核心逻辑,让我们一起来看一下吧。
轮播图的核心逻辑
我们将轮播图封装在一个类当中,然后通过构造函数调用的方式来使用它,我们先来看使用方式,如下:
const options = {
el: '.carousel-box',
speed: 1000, // 轮播速度(ms)
delay: 0, // 轮播延迟(ms)
direction: 'left', // 图片滑动方向
monitorKeyEvent: true, // 是否监听键盘事件
monitorTouchEvent: true // 是否监听屏幕滑动事件
}
const carouselInstance = new Carousel(options);
carouselInstance.start();通过使用方式,我们得到了什么?
轮播图的配置对象
- el: 容器元素
- speed: 轮播速度
- delay: 轮播执行延迟时间
- direction: 滑动方向,主要有left和right两个值
- monitorKeyEvent: 是否监听键盘事件,也就是说是否可以通过点击键盘上的左右来切换轮播图
- monitorTouchEvent: 是否监听屏幕滑动事件,也就是说是否可以通过滑动屏幕来切换图片
- Carousel是一个构造函数
- carousel构造函数内部提供了一个start方法用来开始轮播,很显然这里是开始自动轮播
根据以上的分析,让我们来一步步实现Carousel这个东西吧。
首先它是一个构造函数,支持传入配置对象,所以,我们定义一个类,并且这个类还有一个start方法也初始化,如下:
class Carousel {
constructor(options){
//核心代码
}
start(){
//核心代码
}
}在初始化的时候我们需要做什么?
首先我们要获取到轮播元素,还有上一页下一页按钮以及我们的分页按钮元素。如下:
class Carousel {
constructor(options){
// 容器元素
this.container = $(options.el);
// 轮播图元素
this.carouselItems = this.container.querySelectorAll('.carousel-item');
// 分页按钮元素组
this.carouselSigns = $$(('.carousel-sign .carousel-sign-item'),this.container);
// 上一页与下一页
this.carouselCtrlL = $$(('.carousel-ctrl'),this.container)[0];
this.carouselCtrlR = $$(('.carousel-ctrl'),this.container)[1];
}
start(){
//核心代码
}
}这里用到了$和$$方法,看起来和jQuery的获取DOM很像,用到了jQuery?那当然不是了,我们来看这2个方法的实现。
const $ = (v,el = document) => el.querySelector(v);
const $$ = (v,el = document) => el.querySelectorAll(v);也就是获取dom元素的简易封装啦。
- document.querySelector API
- document.querySelectorAll API
就是基于以上两个dom查询节点的方法封装的,让我们来看下一步,首先我们需要有一个确定当前轮播图的索引值,然后获取所有轮播图元素的长度,然后就是初始化配置对象。代码如下:
class Carousel {
constructor(options){
//省略了代码
// 当前图片索引
this.curIndex = 0;
// 轮播盒内图片数量
this.numItems = this.carouselItems.length;
// 是否可以滑动
this.status = true;
// 轮播速度
this.speed = options.speed || 600;
// 等待延时
this.delay = options.delay || 3000;
// 轮播方向
this.direction = options.direction || 'left';
// 是否监听键盘事件
this.monitorKeyEvent = options.monitorKeyEvent || false;
// 是否监听屏幕滑动事件
this.monitorTouchEvent = options.monitorTouchEvent || false;
}
//省略了代码
}初始化完成之后,接下来我们有两个逻辑还需要在初始化里面完成,第一个逻辑是添加动画过渡效果,也就是让动画看起来更丝滑一些,第二个就是添加事件逻辑。继续在构造函数中调用2个方法,代码如下:
class Carousel {
constructor(options){
//省略了代码
// 添加了事件
this.handleEvents();
// 设置过渡效果
this.setTransition();
}
//省略了代码
}我们先来看最简单的setTransition方法,其实这个方法很简单,就是通过在head标签内添加一个style标签,通过insertRule方法添加样式。代码如下:
setTransition() {
const styleElement = document.createElement('style');
document.head.appendChild(styleElement);
const styleRule = `.carousel-item {transition: left ${this.speed}ms ease-in-out}`
styleElement.sheet.insertRule(styleRule, 0);
}很显然这里是为每个轮播图元素添加过渡效果,接下来我们来看绑定事件方法内部,我们可以尝试思考一下,都有哪些事件呢?总结如下:
- 上一页与下一页
- 分页按钮组
- 滑动事件
- 键盘事件
- 轮播盒子元素的鼠标悬浮与鼠标移出事件
根据以上分析,我们的handleEvents方法就很好实现了,如下:
handleEvents() {
// 鼠标从轮播盒上移开时继续轮播
this.container.addEventListener('mouseleave', this.start.bind(this));
// 鼠标移动到轮播盒上暂停轮播
this.container.addEventListener('mouseover', this.pause.bind(this));
// 点击左侧控件向右滑动图片
this.carouselCtrlL.addEventListener('click', this.clickCtrl.bind(this));
// 点击右侧控件向左滑动图片
this.carouselCtrlR.addEventListener('click', this.clickCtrl.bind(this));
// 点击分页按钮组后滑动到对应的图片
for (let i = 0; i < this.carouselSigns.length; i++) {
this.carouselSigns[i].setAttribute('slide-to', i);
this.carouselSigns[i].addEventListener('click', this.clickSign.bind(this));
}
// 监听键盘事件
if (this.monitorKeyEvent) {
document.addEventListener('keydown', this.keyDown.bind(this));
}
// 监听屏幕滑动事件
if (this.monitorTouchEvent) {
this.container.addEventListener('touchstart', this.touchScreen.bind(this));
this.container.addEventListener('touchend', this.touchScreen.bind(this));
}
}这里有意思的点在于bind方法更改this对象,使得this对象指向当前轮播实例元素,还有一点就是我们为每个分页按钮设置了一个slide-to的索引值,后续我们就可以根据这个索引值来切换轮播图。
接下来,让我们看看每一个事件对应的回调方法,首先是start方法,其实很容易就想到,start方法就是开始轮播,开始轮播也就是自动轮播,自动轮播我们需要用到定时器,因此我们的start函数就很好实现了,代码如下:
start() {
const event = {
srcElement: this.direction == 'left' ? this.carouselCtrlR : this.carouselCtrlL
};
const clickCtrl = this.clickCtrl.bind(this);
// 每隔一段时间模拟点击控件
this.interval = setInterval(clickCtrl, this.delay, event);
}这里有意思的点在于我们的自动轮播,是直接去模拟点击上一页下一页进行切换的,除此之外,这里根据方向将srcElement元素作为事件对象传递,也就是说后面我们会根据这个元素来做方向上的判断。
接下来我们来看暂停函数,很简单,就是清除定时器即可,如下:
// 暂停轮播
pause() {
clearInterval(this.interval);
}接下来,让我们来看clickCtrl方法,思考一下,我们是如何修改当前轮播图的索引值的,正常情况下,比如说,我们是向左滑动,索引值实际上就是将当前索引值相加,然后再判断是否超出了轮播图元素组的长度,重置索引值。
但是这里有一个更为巧妙的实现方式,那就是取模,将当前索引值加1然后与轮播图元素组的长度取模,这样也就保证了我们的索引值始终不会超过轮播图元素组的长度。
如果是向右滑动,那么我们应该是加上轮播图元素组的长度 - 1再取模,也就是与向左方向相反,根据以上分析,我们的代码就好实现了,如下:
// 处理点击控件事件
clickCtrl(event) {
if (!this.status) return;
this.status = false;
let fromIndex = this.curIndex, toIndex, direction;
if (event.srcElement == this.carouselCtrlR) {
toIndex = (this.curIndex + 1) % this.numItems;
direction = 'left';
} else {
toIndex = (this.curIndex + this.numItems - 1) % this.numItems;
direction = 'right';
}
this.slide(fromIndex, toIndex, direction);
this.curIndex = toIndex;
}在这个方法里面还有一个slide方法,顾名思义就是轮播图的滑动方法,其实通篇下来,最核心的就是这个slide方法,这个方法主要做的逻辑就是根据索引值来切换class。代码如下:
slide(fromIndex, toIndex, direction) {
let fromClass, toClass;
if (direction == 'left') {
this.carouselItems[toIndex].className = "carousel-item next";
fromClass = 'carousel-item active left';
toClass = 'carousel-item next left';
} else {
this.carouselItems[toIndex].className = "carousel-item prev";
fromClass = 'carousel-item active right';
toClass = 'carousel-item prev right';
}
this.carouselSigns[fromIndex].className = "carousel-sign-item";
this.carouselSigns[toIndex].className = "carousel-sign-item active";
setTimeout((() => {
this.carouselItems[fromIndex].className = fromClass;
this.carouselItems[toIndex].className = toClass;
}).bind(this), 50);
setTimeout((() => {
this.carouselItems[fromIndex].className = 'carousel-item';
this.carouselItems[toIndex].className = 'carousel-item active';
this.status = true; // 设置为可以滑动
}).bind(this), this.speed + 50);
}这里分成了两块替换类名的逻辑,第一块是轮播图元素的替换类名,需要判断方向,第二块则是分页按钮组的类名替换逻辑,当然分页按钮组的逻辑是不需要替换类名的。
其实分析到这里,这个轮播图的核心基本已经完成了,接下来就是完善了,让我们继续看分页按钮组的事件回调逻辑。
其实这里的逻辑也就是拿到索引值,前面为每个分页按钮组设置了一个slide-to属性,这里很显然就通过获取这个属性,然后生成slide方法所需要的参数,最后调用slide方法就行了。代码如下:
clickSign(event) {
if (!this.status) return;
this.status = false;
const fromIndex = this.curIndex;
const toIndex = parseInt(event.srcElement.getAttribute('slide-to'));
const direction = fromIndex < toIndex ? 'left' : 'right';
this.slide(fromIndex, toIndex, direction);
this.curIndex = toIndex;
}最后还剩两个逻辑,一个是键盘事件,另一个是滑动事件逻辑,我们先来看键盘事件逻辑,键盘事件逻辑无非就是利用keyCode判断用户是否点击的是上一页和下一页,然后像自动开始轮播那样模拟调用上一页下一页按钮事件逻辑即可。代码如下:
keyDown(event) {
if (event && event.keyCode == 37) {
this.carouselCtrlL.click();
} else if (event && event.keyCode == 39) {
this.carouselCtrlR.click();
}
}最后就是滑动事件了,滑动事件最难的点在于如何判断用户滑动的方向,其实我们可以通过计算滑动角度来判断,这里的计算逻辑是来自网上的一个公式,感兴趣的可以查阅相关资料了解。我们来看代码如下:
touchScreen(event) {
if (event.type == 'touchstart') {
this.startX = event.touches[0].pageX;
this.startY = event.touches[0].pageY;
} else { // touchend
this.endX = event.changedTouches[0].pageX;
this.endY = event.changedTouches[0].pageY;
// 计算滑动方向的角度
const dx = this.endX - this.startX
const dy = this.startY - this.endY;
const angle = Math.abs(Math.atan2(dy, dx) * 180 / Math.PI);
// 滑动距离太短
if (Math.abs(dx) < 10 || Math.abs(dy) < 10) return;
if (angle >= 0 && angle <= 45) {
// 向右侧滑动屏幕,模拟点击左控件
this.carouselCtrlL.click();
} else if (angle >= 135 && angle <= 180) {
// 向左侧滑动屏幕,模拟点击右控件
this.carouselCtrlR.click();
}
}
}到此为止,我们的一个轮播图就完成了,总结一下我们学到了什么?
- CSS过渡效果
- CSS基本布局
javascript事件
- 鼠标悬浮与移出事件
- 滑动事件
- 键盘事件
- 元素点击事件
- javascript定时器
PS: 以后再也不用自己写轮播了,业务当中遇到,可以直接拿去用了,😄。

**粗体** _斜体_ [链接](http://example.com) `代码` - 列表 > 引用。你还可以使用@来通知其他用户。